Wood pellets, Stream 1 in Figure P13.32, are first dried by indirect heating with the flue gas
Question:
Wood pellets, Stream 1 in Figure P13.32, are first dried by indirect heating with the flue gas and then combusted. Model this system using a heat exchanger, E-2001, followed by a flash separator, V-2001. The dried wood pellets are combusted in an adiabatic combustor, R-2001, where combustion air is supplied in 15% excess of the stoichiometric requirement. The hot flue gas is used for raising steam in a boiler. The boiler can be simply modeled as a heat exchanger where the flue gas is cooled to 300°C. The flue gas then exchanges heat in E-2001 before being vented through the stack. For simplicity consider the pressure drop through each piece of equipment to be 0.1 bar. The composition of wood pellets is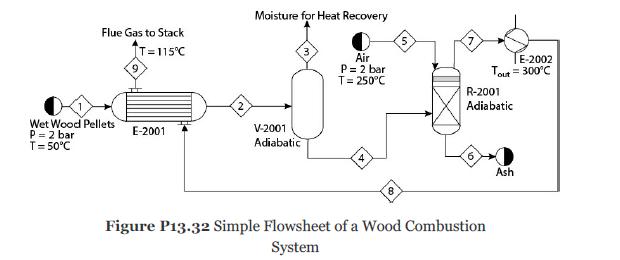
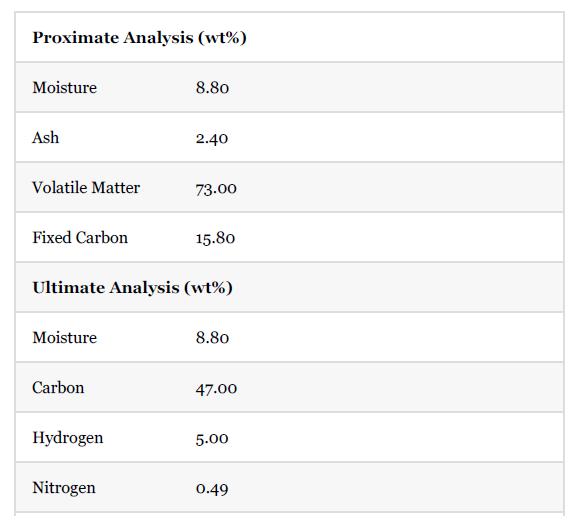
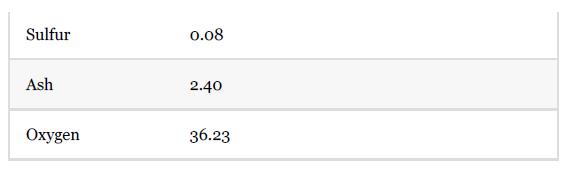
The HHV of the wood pellets is 18,969 kJ/kg. Feel free to include additional blocks in the process simulator that you need to use to model the combustor operations appropriately. Assume the conversion of carbon to be 100%. As many commercial process simulators do not have the capability to model the SVE for such processes, assume that 90% of the moisture in the feed is separated in the dryer (i.e., leaves in Stream 3).
1. What are the temperatures of Streams 2, 4, and 7?
2. What is the composition of Stream 7?
3. Perform an overall energy analysis of this system and compare with the reported HHV. Modify the parameters of the enthalpy model to match the HHV.
Step by Step Answer:

Analysis Synthesis And Design Of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 9780134177403
5th Edition
Authors: Richard Turton, Joseph Shaeiwitz, Debangsu Bhattacharyya, Wallace Whiting





