Question: Make the given changes in the indicated examples of this section, and then solve the resulting problems. In Example 2, change A(3,2) to A(0,2) and
Make the given changes in the indicated examples of this section, and then solve the resulting problems.
In Example 2, change A(−3,−2) to A(0,−2) and then find the fourth vertex.
Data from Example 2
Three vertices of the rectangle in Fig. 3.10 are A(−3,−2), B(4,−2), and C(4, 1). What is the fourth vertex?
We use the fact that opposite sides of a rectangle are equal and parallel to find the solution. Because both vertices of the base AB of the rectangle have a y-coordinate of −2, the base is parallel to the x-axis. Therefore, the top of the rectangle must also be parallel to the x-axis. Thus, the vertices of the top must both have a y-coordinate of 1, because one of them has a y-coordinate of 1. In the same way, the x-coordinates of the left side must both be −3. Therefore, the fourth vertex is D(−3, 1).
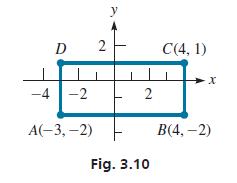
D 2 -4 -2 A(-3,-2) y 2 Fig. 3.10 C(4,1) -X B(4,-2)
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
In Example 2 we are given three vertices of a rectangle and we are asked to find the fourth vertex W... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


