Measurements of the rate of absorption of CO 2 in water and in aqueous NaOH solutions are
Question:
Measurements of the rate of absorption of CO2 in water and in aqueous NaOH solutions are to be used to determine the mass transfer coefficient, , and the gas-liquid interfacial area,
a, in a counter-current laboratory-scale column packed with a new proprietary packing. The column has a diameter of 0.15 m, contains 0.75 m of packing, and is operated at 30°C and 1 atm absolute pressure. Air containing 5.0 mol% CO2 is supplied at the rate of 0.31 mol/s. The liquid is supplied at the rate of 4.2 mol/s. Two experiments are conducted. In the first, the liquid fed is pure water while in the second it is an aqueous solution containing 3 mol/L NaOH. At steady-state, the following data are obtained:
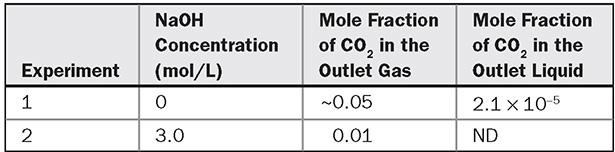
(a) Determine the product of the gas-liquid interfacial area and the liquid side mass transfer coefficient ![]() in units of s-1 from experiment 1. (b)Determine the gas-liquid interfacial area a in units of m2 per m3 of column from experiment 2 assuming that absorption occurs in the fast pseudo-first-order reaction regime. Verify that this assumption is appropriate. (c) Combine the results in (a) and (b) to obtain the liquid-side mass transfer coefficient in units of m/s. The following additional data can be used for this problem: physical solubility of CO2 in water and NaOH solutions = 5.0 × 10-4 mol CO2/mol atm; diffusivity of dissolved CO2 = 1.3 × 10-9 m2/s; rate constant for reaction of CO2 with OH- = 2 × 104 L/mol s. The gas-side resistance and the change in OH- concentration due to absorption of CO2 in experiment 2 can be neglected.
in units of s-1 from experiment 1. (b)Determine the gas-liquid interfacial area a in units of m2 per m3 of column from experiment 2 assuming that absorption occurs in the fast pseudo-first-order reaction regime. Verify that this assumption is appropriate. (c) Combine the results in (a) and (b) to obtain the liquid-side mass transfer coefficient in units of m/s. The following additional data can be used for this problem: physical solubility of CO2 in water and NaOH solutions = 5.0 × 10-4 mol CO2/mol atm; diffusivity of dissolved CO2 = 1.3 × 10-9 m2/s; rate constant for reaction of CO2 with OH- = 2 × 104 L/mol s. The gas-side resistance and the change in OH- concentration due to absorption of CO2 in experiment 2 can be neglected.
Step by Step Answer:

Heat And Mass Transfer For Chemical Engineers Principles And Applications
ISBN: 9781264266678
1st Edition
Authors: Giorgio Carta





