Hydrogen peroxide, H 2 O 2 , is a nontoxic bleaching agent being used as a replacement
Question:
Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, is a nontoxic bleaching agent being used as a replacement for chlorine in industry and home laundries. The bleaching process is an oxidation, and when hydrogen peroxide acts as a bleaching agent, the only waste it generates is H2O.
(a) Draw the Lewis structure of hydrogen peroxide and determine the formal charge on each atom. What is the oxidation number of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide? Which is more useful in predicting the ability of H2O2 to act as an oxidizing agent, formal charge or oxidation number? Explain your reasoning.
(b) Predict the bond angles at each O atom in H2O2. Are all the atoms in the same plane? Is the molecule polar or nonpolar? Explain your reasoning.
(c) Write the valence electron configuration of (i) O2; (ii) O2–; (iii) O2+ ; (iv) O22–. For each species, give the expected bond order and indicate which, if any, are paramagnetic.
(d) The following bond lengths have been reported: (i) O2, 121 pm; (ii) O2–, 134 pm; (iii) O2+, 112 pm; (iv) O22–, 149 pm. Suggest a reason for the differences based on the configurations in part (c).
(e) One reaction in which H2O2 acts as an oxidizing agent is Fe2+(aq) + H2O2 (aq) + H+ (aq) → Fe3+ (aq) + H2O(l). Balance the equation and determine what mass of iron(II) can be oxidized to iron(III) by 43.2 mL of 0.200 m H2O2(aq).
(f) Hydrogen peroxide can also act as a reducing agent, as in Fe3+ (aq) + H2O2 (aq) + OH– (aq) → Fe2+ (aq) + H2O(l) + O2 (g). Balance the equation and determine what mass of iron(III) can be reduced to iron(II) by 41.8 mL of 0.200 m H2O2 (aq).
(g) Hydrogen peroxide must be kept in brown bottles because, in the presence of light, it can disproportionate, which means that it oxidizes and reduces itself in the reaction 2 H2 O2 (aq) → 2 H2 O(l) + O2(g). How many electrons are transferred in the reaction represented by this equation?
(h) Although peroxides do not generate hazardous waste, they can cause problems in the atmosphere. For example, if a hydrogen peroxide molecule makes its way to the stratosphere, it can break into two · OH radicals, which threaten the ozone layer that protects Earth from harmful radiation. Use data in Table 2D.2 to calculate the minimum frequency and corresponding wavelength of light needed to break the HO—OH bond.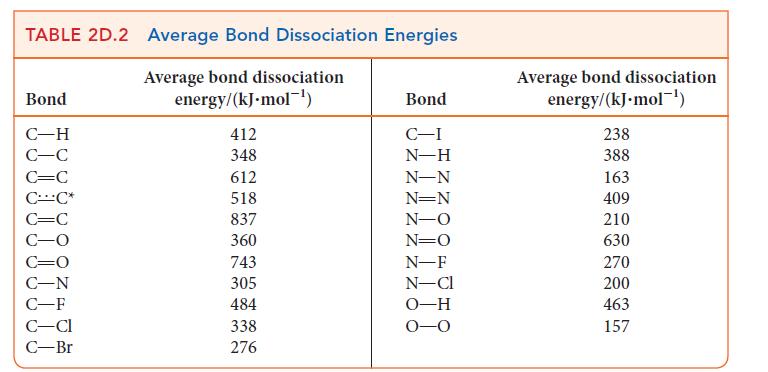
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight
ISBN: 9781464183959
7th Edition
Authors: Peter Atkins, Loretta Jones, Leroy Laverman





