A 20-cm-long, zero-resistance wire is pulled outward, on zero-resistance rails, at a steady speed of (10 mathrm{~m}
Question:
A 20-cm-long, zero-resistance wire is pulled outward, on zero-resistance rails, at a steady speed of \(10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\) in a \(0.10 \mathrm{~T} \mathrm{mag}\) netic field. (See Figure P25.63.) On the opposite side, a \(1.0 \Omega\) carbon resistor completes the circuit by connecting the two rails. The mass of the resistor is \(50 \mathrm{mg}\).
a. What is the induced current in the circuit?
b. How much force is needed to pull the wire at this speed?
c. How much does the temperature of the carbon increase if the wire is pulled for \(10 \mathrm{~s}\) ? The specific heat of carbon is \(710 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{kg} \cdot \mathrm{K}\). Neglect thermal energy transfer out of the resistor.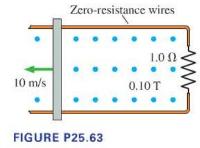
Step by Step Answer:

College Physics A Strategic Approach
ISBN: 9780321907240
3rd Edition
Authors: Randall D. Knight, Brian Jones, Stuart Field





