A 20-cm-long, zero-resistance slide wire moves outward, on zero-resistance rails, at a steady speed of 10 m/s
Question:
The mass of the resistor is 50 mg.
Figure 30.26
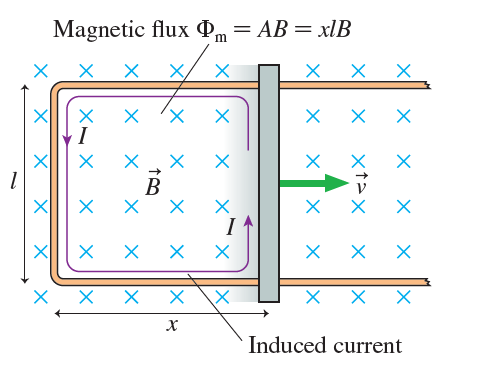 a. What is the induced current in the circuit?
a. What is the induced current in the circuit?
b. How much force is needed to pull the wire at this speed?
c. If the wire is pulled for 10 s, what is the temperature increase of the carbon? The specific heat of carbon is 710 J/kg K.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Physics for Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics
ISBN: 978-0133942651
4th edition
Authors: Randall D. Knight
Question Posted:





