Question: Using the first branch instruction in the given code as an example, describe the hazard detection logic needed to support branch execution in the ID
Using the first branch instruction in the given code as an example, describe the hazard detection logic needed to support branch execution in the ID stage as in Figure 4.62. Which type of hazard is this new logic supposed to detect?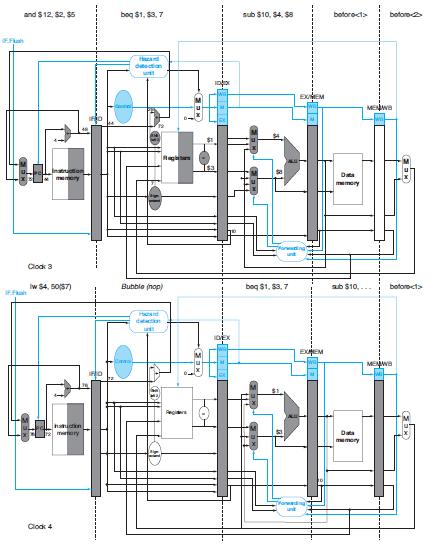
This exercise is intended to help you understand the relationship between delay slots, control hazards, and branch execution in a pipelined processor. In this exercise, we assume that the following MIPS code is executed on a pipelined processor with a 5-stage pipeline, full forwarding, and a predict-taken branch predictor:
of Flash and $12, $2, $5 Clock 3 mumory Iw $4,50(57) Clock 4 nauction mary ------ boq $1,$3,7 Hard detection Rag Bubble (nop) Hand dat und sub $10, $4, $8 boq $1, $3,7 EXMEM EXEM botoroct> Da ab $10.... Data mory MENWB botor-2 MENW botorect> KEE
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
In Figure 462 the hazard detection logic is designed to identify hazards that could potentially stall the pipeline to ensure correct instruction execu... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


