Question: Consider the wage equation in Example 10.5. a. Two possible instruments for EDUC are NEARC4 and NEARC2, where these are dummy variables indicating whether the
Consider the wage equation in Example 10.5.
a. Two possible instruments for EDUC are NEARC4 and NEARC2, where these are dummy variables indicating whether the individual lived near a 4-year college or a 2-year college at age 10 . Speculate as to why these might be potentially valid IV.
b. Explain the steps (not the computer command) required to carry out the regression-based Hausman test, assuming we use both IV.
c. Using a large data set, the \(p\)-value for the regression-based Hausman test for the model in Example 10.5, using only NEARC4 as an IV 0.28 ; using only NEARC 2 the \(p\)-value is 0.0736 , and using both IV the \(p\)-value is 0.0873 [with robust standard errors it is 0.0854 ]. What should we conclude about the endogeneity of \(E D U C\) in this model?
d. We compute the IV/2SLS residuals, using both NEARC4 and NEARC2 as IV. In the regression of these 2SLS residuals on all exogenous variables and the IV, with \(N=3010\) observations, all regression \(p\)-values are greater than 0.30 and the \(R^{2}=0.000415\). What can you conclude based on these results?
e. The main reason we seldom use OLS to estimate the coefficients of equations with endogenous variables is that other estimation methods are available that yield better fitting equations. Is this statement true or false, or are you uncertain? Explain the reasoning of your answer.
f. The \(F\)-test of the joint significance of NEARC4 and NEARC2 in the first-stage regression is 7.89 . The \(95 \%\) interval estimates for the coefficient of education using OLS is 0.0678 to 0.082 , and using 2SLS it is 0.054 to 0.260 . Explain why the width of the interval estimates is so different.
Data From Example 10.5:-
In addition to education a worker's experience is also important in determining their wage. Because additional years of experience have a declining marginal effect on wage use the quadratic model
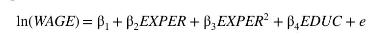
where EXPER is years of experience. This is the same specification. We assume that EXPER is an exogenous variable that is uncorrelated with the worker's ability and therefore uncorrelated with the random error \(e\). Two instrumental variables for years of education, \(E D U C\), are mother's and father's years of education, MOTHEREDUC and FATHEREDUC, introduced in the previous examples. The first-stage equation is
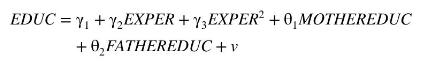
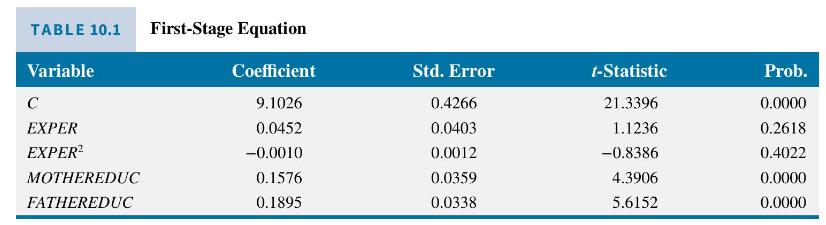
Using the 428 observations in the data file mroz the estimated first-stage equation is reported in Table 10.1. The IV/2SLS estimates, with correctly computed standard errors, are

The estimated return to education is approximately \(6.1 \%\), and the estimated coefficient is statistically significant with a \(t=1.96\).
In(WAGE) = B+ BEXPER+ BEXPER + BEDUC + e
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (172 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


