A pendulum of length L oscillates in a vertical plane. Assuming that the mass of the pendulum
Question:
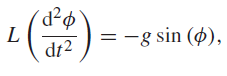
where g is the acceleration due to gravity and Ï• is the angle between the pendulum and the vertical. This equation cannot be solved exactly. For small oscillations such that
sin (Ï•) ‰ˆ Ï•,
find the solution to the equation. What is the period of the motion? What is the frequency? Find the value of L such that the period equals 2.000 s.
´d²p> = -g sin (ø), df2
Step by Step Answer:
The real solution to this e...View the full answer



Related Video
In Physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity, i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. In this video, the concept of force and torque is demonstrated with the practical application of changing the flat tire of the car.
Students also viewed these Mathematics questions
-
Consider a pendulum of length L meters swinging only under the influence of gravity. Suppose the pendulum starts swinging with an initial displacement of 0 radians (see figure). The period (time to...
-
On page 431 of Physics: Calculus, 2d ed., by Eugene Hecht (Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole, 2000), in the course of deriving the formula T = 2L/g for the period of a pendulum of length L, the author...
-
A pendulum consists of a mass, called a bob, that is affixed to the end of a string of length L (see Figure 6.24). When the bob is moved from its rest position and released, it swings back and forth....
-
Find the probability | (p)| 2d3 p of the particular momentum p for the ground-state hydrogen atom. (This is a nice exercise in three-dimensional Fourier transforms. To perform the angular...
-
What is an invoice? What purpose does it serve?
-
Discuss the role of cultural diversity in biodiversity conservation, exploring how traditional ecological knowledge, indigenous stewardship practices, and community-based conservation initiatives...
-
Design teams are confronted with "multiobjective" decision making. Is it possible for objectives to lead to conflicting designs? Give an example(s).
-
Johnson, Larson, and Kragen own an advertising agency that they operate as a partnership. The partnership agreement includes the following: a. Johnson receives a salary of $50,000. b. Larson receives...
-
7)A certain city covers an area of 62.294 mil 2 . How many square kilometers is this ?Use the conversion factor 1 mile = 1.61 km 8) A projectile is fired at 422.8 mi/hr. How fast is that in meters...
-
Jefferson Animal Rescue is a private not-for-profit clinic and shelter for abandoned domesticated animals, chiefly dogs and cats. At the end of 2011, the organization had the following account...
-
Use Mathematica to obtain a numerical solution to the pendulum equation in the previous problem without approximation for the case that L = 1.000 m with the initial conditions (0) = 0.350 rad (about...
-
Radioactive nuclei decay according to the same differential equation which governs first-order chemical reactions, Eq. (12.71). In living matter, the isotope 14 C is continually replaced as it...
-
What is the cause of uncertainty in the cash budget, and what two techniques can be used to cope with this uncertainty?
-
Outline the environment where each of the compared operating system would be appropriate. For example, gamers might be interested in one operating system, mobile users may prefer another operating...
-
Calculate inventory amounts when costs are declining During the year, Hooker Incorporated has the following inventory transactions. Date January 1 Transaction Beginning inventory March 4 Purchase...
-
3. Market demand is given by: 100-Q, P(Q) = if Q <100 otherwise Suppose there are two firms both with constant marginal cost 50 and no fixed cost and capacity constraint. Assume that firms produce...
-
Based upon the labs and research from this topic, research the automation capabilities of the Linux server platform. Is it possible to automate account creation? How? Are there such things as User or...
-
A company constructs a building for its own use. Construction began on January 1 and ended on December 30. The expenditures for construction were as follows: January 1, $500,000; March 31, $600,000;...
-
Show that the line integral of the vector potential A about any closed path is equal to the magnetic flux enclosed by the path, or A dL = B dS.
-
Determine the optimal use of Applichem's plant capacity using the Solver in Excel.
-
Perform the test in Problem 9.63, and report a p-value (two-tailed)? Endocrinology A study to assess the effect of a low-fat diet on estrogen metabolism recruited 6 healthy women ages 2132 [5]. The...
-
Suppose the investigators are reluctant to assume that the change in LVM over four years is normally distributed. What test can be used to assess if there is a change in mean LVM over four years?...
-
What are the hypotheses being tested with this test? Cardiovascular Disease Left ventricular mass (LVM) is an important risk factor for subsequent cardiovascular disease. A study is proposed to...
-
Assume that you are the leadership team of a convenience store chain that has more than 300 outlets. The company is facing an inventory shrinkage problem, and store managers report that the main...
-
1 . An employee at Amy's candles has noticed that some order quantities in the two reports presented are different although the order numbers are the same. We normally refer to such data as dirty....
-
On Monday, April 5, 2010, just before 3:00 in the afternoon, miners at Massey Energy Corporation's Upper Big Branch coal mine in southern West Virginia were in the process of a routine shift change....

Study smarter with the SolutionInn App


