Question: One glass-membrane sodium ion-selective electrode has a selectivity coefficient . When this electrode was immersed in 1.00 mM NaCl at pH 8.00, a potential of
One glass-membrane sodium ion-selective electrode has a selectivity coefficient . When this electrode was immersed in 1.00 mM NaCl at pH 8.00, a potential of -38 mV (versus S.C.E.) was recorded.
(a) Neglecting activity coefficients, calculate the potential with Equation 14-10 if the electrode were immersed in 5.00 mM NaCl at pH 8.00.
(b) What would the potential be for 1.00 mM NaCl at pH 3.87? You can see that pH is a critical variable for the sodium electrode.
Figure 14-10
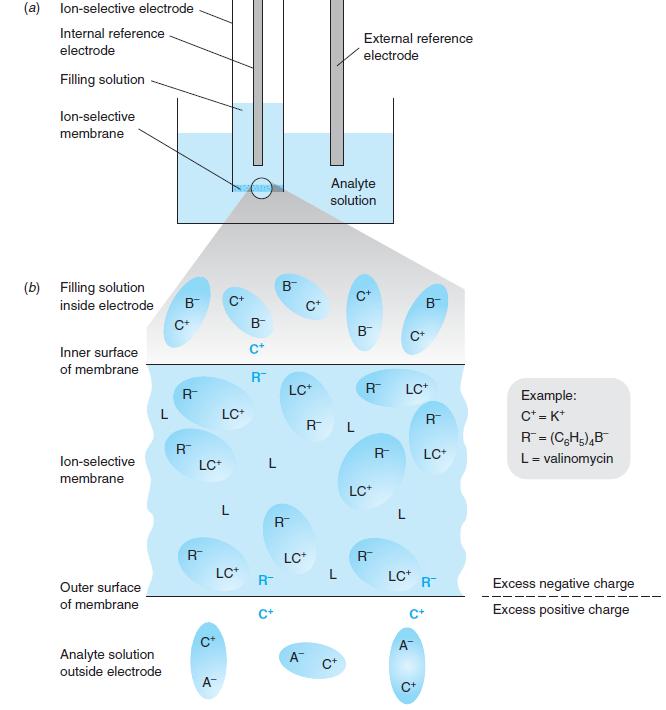
(a) lon-selective electrode Internal reference External reference electrode electrode Filling solution lon-selective membrane Analyte solution (b) Filling solution inside electrode B B c+ B C+ B B C* Inner surface C+ of membrane R LC+ R LC* Example: C* = K* R= (CH;),B L= valinomycin LC+ R R L %3! R LC+ lon-selective LC+ L membrane LC* L L R R LC* R LC* L LC* R Outer surface R Excess negative charge of membrane C+ Excess positive charge C* A Analyte solution outside electrode A A- C+
Step by Step Solution
3.41 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Using Equation 1410 E E RT zF ln aNa For 100 mM NaCl at pH 800 aNa 103 and pH 800 so we can find ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


