3. What impact will the Personal Pair system have on the supply chain shown in Exhibit 3? Be careful to consider how each element of the supply chain will be affected, if at all.
4. Provide and/or calculate the following supply chain metrics Inventory Turnover, (Replenishment) Lead Time, and Cash-to-cash Cycle Time for Levis and interpret them. If Levis choses to implement Personal Pair jeans system, how do you think these three measures would change? Provide a short explanation of your reasoning.




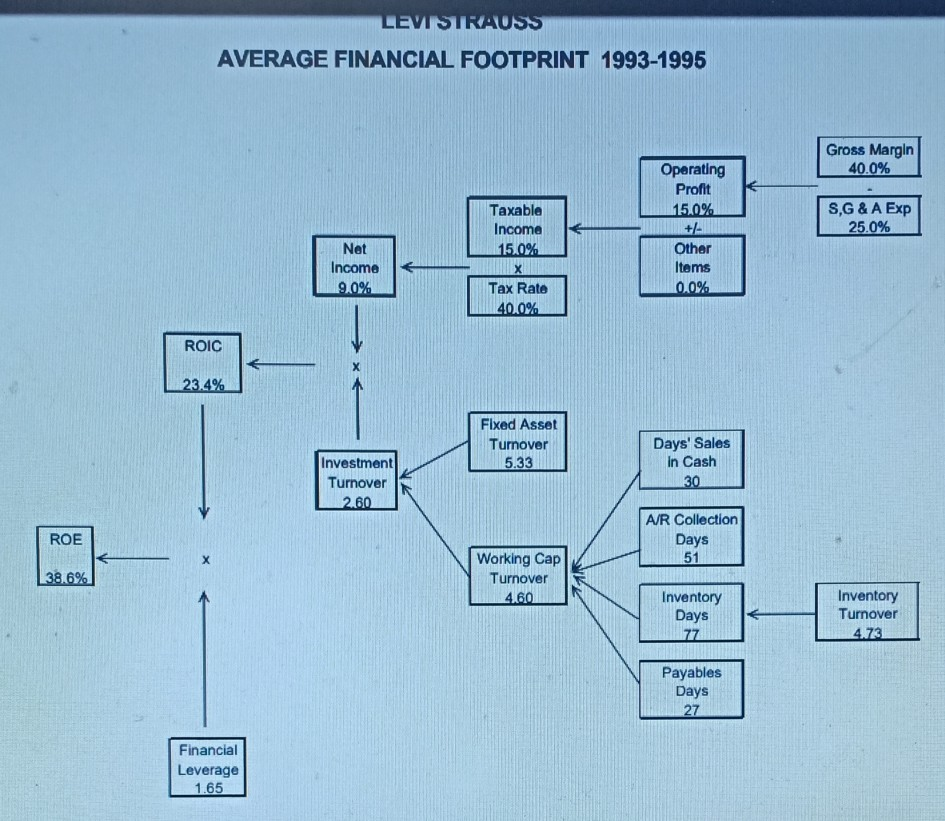
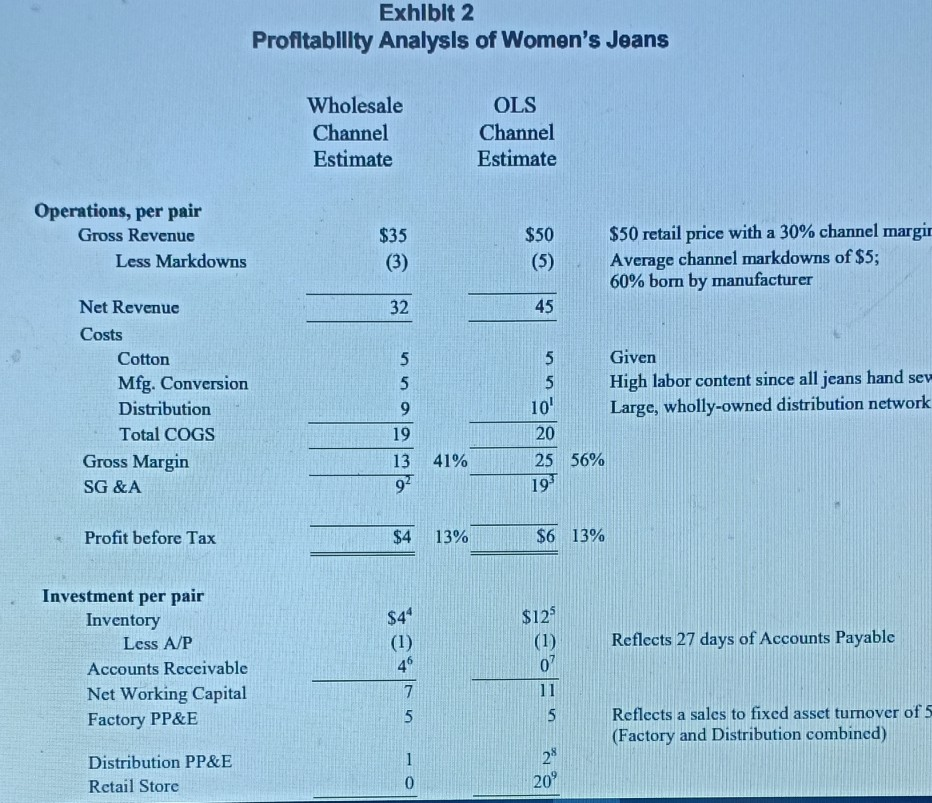

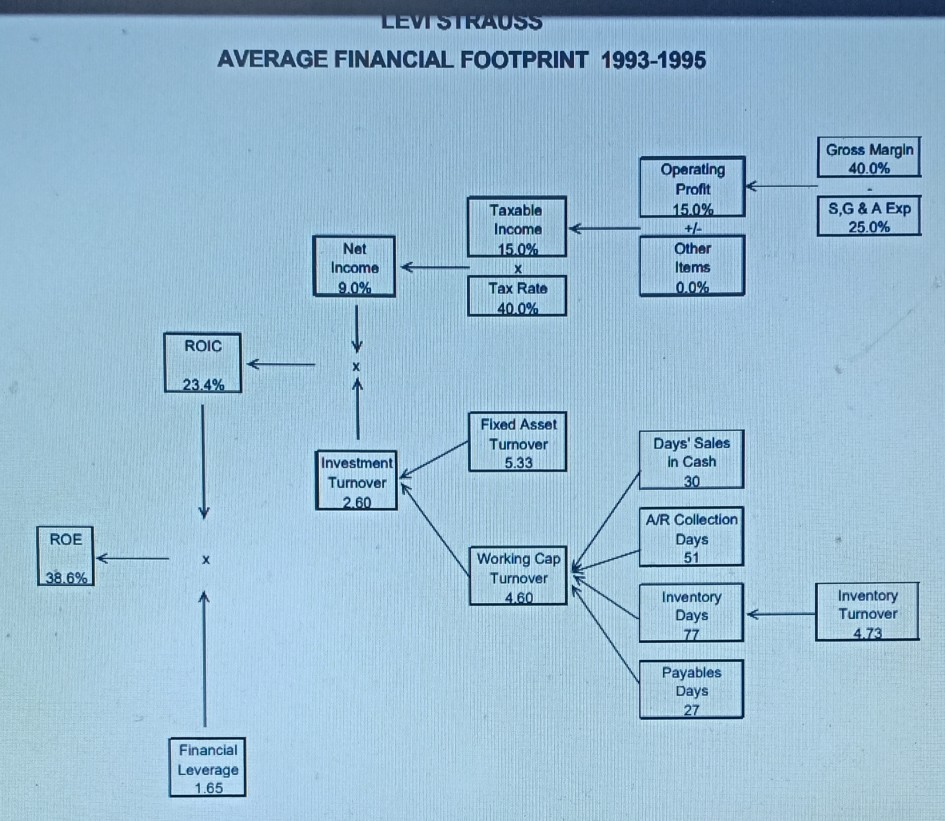
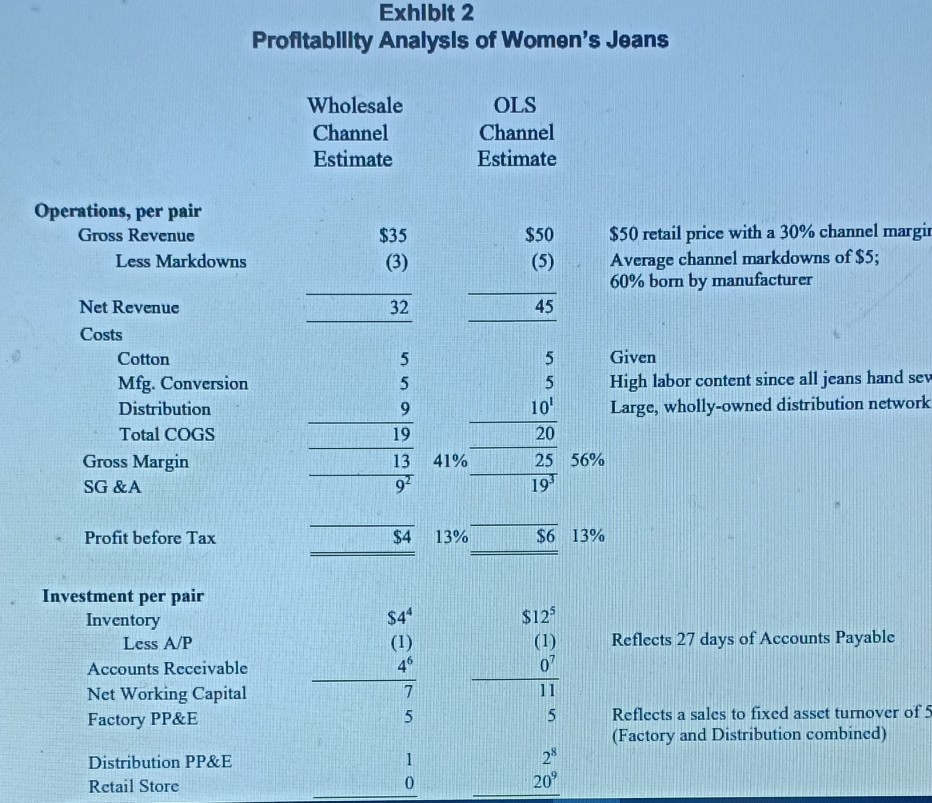
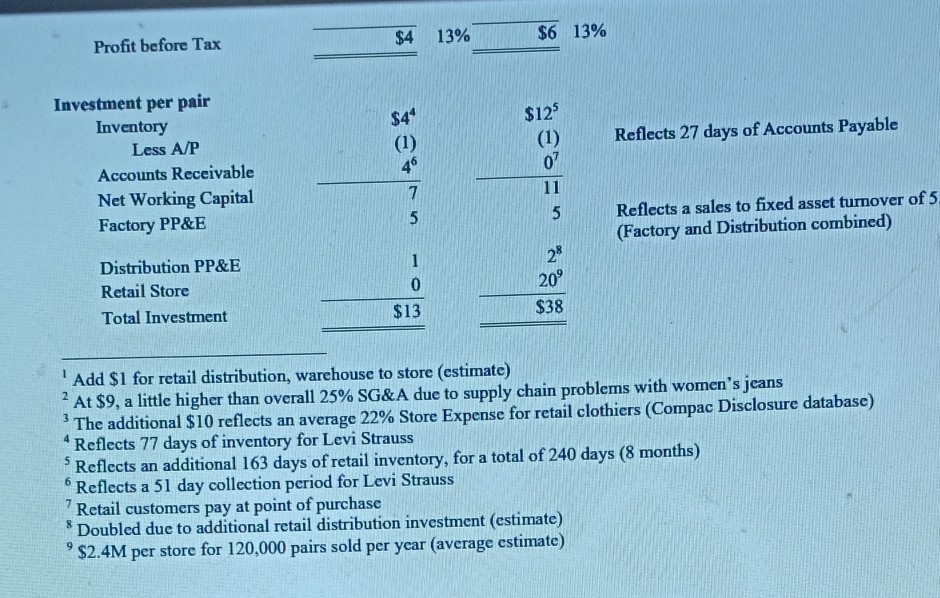
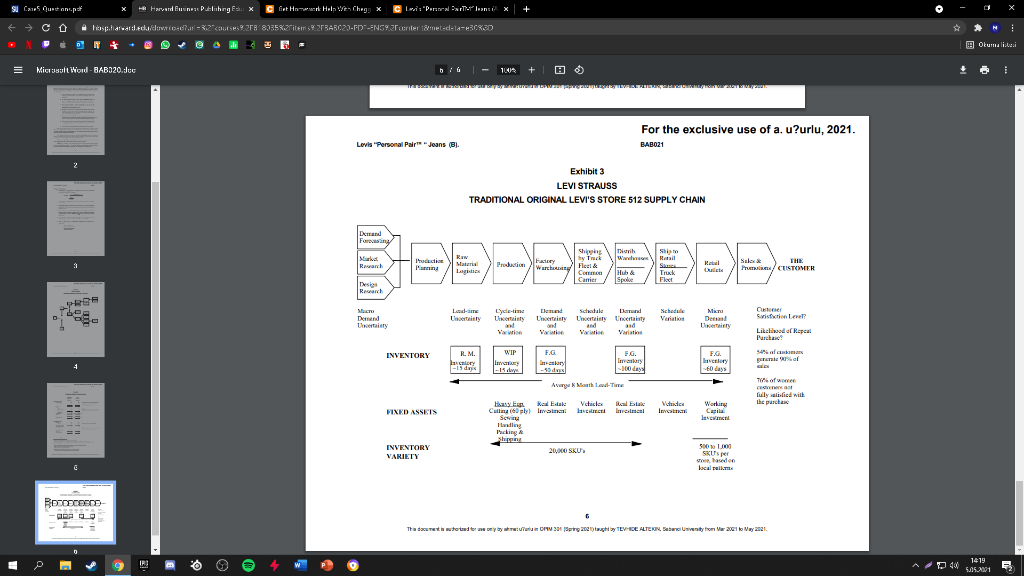
Levi's "Personal PairTM Jeans (A) In 1995, women's jeans was a $2 billion fashion category in the US and growing fast. Levi-Strauss was the market leader, but its traditional dominant position was under heavy attack. Standard Levi's women's jeans, sold in 51 size combinations (waist and inseam), had been the industry leading product for decades, but "fashion was now taking over the category. Market research showed that only 24 percent of women were "fully satisfied" with their purchase of standard jeans at about $50 per pair. "Fashion in jeans meant more styles, more colors, and better fit. All of these combined to create a level of product line complexity that was a nightmare for manufacturing-oriented, push-based companies like Strauss. By 1995, Strauss operated 19 Original Levi's retail stores across the country (2,000 to 3,000 square foot mall stores) to put them in closer touch with the ultimate customers. But this channel was a very small part of their overall $6 Billion sales which were still primarily to distributors and/or independent retailers. Exhibit 1 shows Levi's financial footprint. Strauss was as aggressive as most apparel manufacturers and retailers in investing in process improvements and information technology to improve manufacturing and delivery cycle times and pull-based responsiveness to actual buying patterns. But the overall supply chain from product design to retail sales was still complex, expensive and slow. In spite of substantial improvements in recent years (including extensive use of EDI) there was still an eight month lag, on average, between ordering cotton fabric and selling the final pair of jeans. The industry average lag was still well over twelve months in 1995. The financial footprint for one pair of women's jeans sold through the normal wholesale channel compared to one pair sold through an Original Levi's Store is summarized in Exhibit 2. Although the retail channel was less profitable for Strauss, it was seen as an investment in understanding end-use customers better. made possible by a partnership with Custom Clothing Technology Corp. (CCTC), a small Newton, MA-based software firm specializing in client/server applications linking point of sale custom fitting programs directly with single ply cutting programs in apparel factories. The new process operated as follows: 1. The "Personal PairTM kiosk was a separate booth in the retail store, staffed by specially-trained sales clerks and equipped with touch screen PCs. 2. A sales clerk used a tape to take three measurements from the customer (waist, hips and rise) and recorded them on the touch There were 4224 possible combinations of these three measurements. screen. 3. The computer flashed a code corresponding to one of the 400 prototype pairs stocked at the kiosk. The sales clerk retrieved the prototype pair for the customer to try on. 4. Within one or two tries, the customer was wearing the best available prototype. Then the sales clerk used the tape again to determine the exact measurements for the customer (4224 possible combinations) and to note the length required (inseam). 5. The sales clerk entered the 4 final measurements in the touch screen and recorded the order. Initially, the system was available only for the Levi's 512 style, but 5 color choices were offered in both tapered and boot cut legs. 6. The customer paid for the jeans and chose either Fed Ex delivery (a $5 extra charge, per pair) or store pick up. Delivery was promised in "not more than three weeks. fit will be much better? 4. In general, how will Personal PairTM change the various elements of the financial footprint? Is the overall result a higher or lower ROIC? 5. What is your advice to management regarding the Personal Pairt experiment? Further expansion? Extend to other products? Changes to the system? Overall evaluation? in "not more than three weeks. 7. There was a money back guarantee of full satisfaction on every order. Each Personal PairTM customer order was transmitted by modem from the kiosk to CCTC where it was logged and immediately retransmitted directly to a Levi's factory in Mountain City, TN where each pair of jeans was individually cut. In the regular supply chain, patterns were cut from rolls of denim in stacks 60 layers thick. After cutting, each pair was hand-sewn, inspected and individually packed for shipment. Jeans were normally sewn one pair at a time, but there was high WIP at each process stage and several pairs were made in sequence to minimize change-over time. Each Personal PairTM garment included a sewn-in bar code unique to the customer for easy re-ordering at the store where the bar code was on file in the kiosk. Exhibit 3 is a summary of the normal supply chain for jeans sold through the Original Levi's Store distribution channel. The exhibit includes some additional information about LEVI STRAUSS AVERAGE FINANCIAL FOOTPRINT 1993-1995 Gross Margin 40.0% Operating Profit 15.0% +/- Other Items 0.0% SG & A Exp 25.0% Taxable Income 15.0% Tax Rate 40.0% Net Income 9.0% ROIC 23.4% Fixed Asset Turnover 5.33 Investment Turnover 2.60 Days' Sales In Cash 30 ROE A/R Collection Days 51 38.6% Working Cap Turnover 4.60 Inventory Days 77 Inventory Turnover 473 Payables Days 27 Financial Leverage 1.65 Exhlblt 2 Profitability Analysis of Women's Jeans Wholesale Channel Estimate OLS Channel Estimate Operations, per pair Gross Revenue Less Markdowns $35 (3) $50 (5) $50 retail price with a 30% channel margir Average channel markdowns of $5; 60% bom by manufacturer 32 45 5 Net Revenue Costs Cotton Mfg. Conversion Distribution Total COGS Gross Margin SG &A 5 5 9 19 13 92 5 Given 5 High labor content since all jeans hand sev 10' Large, wholly-owned distribution network 20 25 56% 41% 19 Profit before Tax $4 13% $6 13% $4" Reflects 27 days of Accounts Payable Investment per pair Inventory Less A/P Accounts Receivable Net Working Capital Factory PP&E (1) 49 7 5 $123 (1) 0? 11 5 Reflects a sales to fixed asset turnover of 5 (Factory and Distribution combined) 1 Distribution PP&E Retail Store 28 20 0 Assignment Questions 1. Profitability, for any business can be thought of in terms of the basic Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) equation: Revenue - Cost Profitability Working Capital + Property & Equip. Profit Investment Calculate the pretax ROIC for Levi Strauss for both channels shown in Exhibit 2. So what? 2. What impact will the Personal PairTM system have on the value chain shown in Exhibit 3? Be careful to consider how each element of the chain will be affected, if at all. 3. How would you price the Personal PairTM jeans (versus $50 for standard, off-the-shelf jeans)? Would you lower the price, since the customer must wait up to three weeks for delivery? Would you raise the price, since the fit will be much better? 4. In general, how will Personal PairTM change the various elements of the financial footprint? Is the overall result a higher or lower ROIC? 5. What is your advice to management regarding the Personal PairTM experiment? Further expansion? Extend to other products? $4 13% $6 13% Profit before Tax $125 Investment per pair Inventory Less A/P Accounts Receivable Net Working Capital Factory PP&E $4" (1) 46 Reflects 27 days of Accounts Payable (1) 07 11 5 7 5 Reflects a sales to fixed asset turnover of 5 (Factory and Distribution combined) 28 20 Distribution PP&E Retail Store Total Investment 1 0 $13 $38 2 3 Add $1 for retail distribution, warehouse to store (estimate) At $9, a little higher than overall 25% SG&A due to supply chain problems with women's jeans The additional $10 reflects an average 22% Store Expense for retail clothiers (Compac Disclosure database) *Reflects 77 days of inventory for Levi Strauss Reflects an additional 163 days of retail inventory, for a total of 240 days (8 months) Reflects a 51 day collection period for Levi Strauss Retail customers pay at point of purchase Doubled due to additional retail distribution investment (estimate) $2.4M per store for 120,000 pairs sold per year (average estimate) 6 8 9 Si Cres Oustan x * Harvard Fusine Putlishing Echo x fist Howark Help We-Chugg * Permal Prix hosphard.edcovodu-2 courses 28 833582 item BABC2-FD ENSZF ante metadata-30630 Okuma l Microsoft Word - BABI20.Juc 0/0 1001 + o + For the exclusive use of a. u?urlu, 2021. BABO21 Lovis "Personal Par Jeans (0) 2 Exhibit 3 LEVI STRAUSS TRADITIONAL ORIGINAL LEVI'S STORE 512 SUPPLY CHAIN Ir Demand Forny Rewart ww | Malarin Lariatins | Predactiefactory Shipping by the Warch/Fleel Courtmen Carrier Distri Ware H Spole Retail Sim Truck Fleet Real Lucts THE Pre/CUSTOMER Tesis Research dos YRST Schedule Demand Uncertainty Swisttel Lydi | Schable Darund ) Ucrainty Unity Unity Uncertainty and and View VW Mica Demand Ulertainty Likeld of Repen Purchase WIP INVENTORY F.G R.M. Lavender 1-19 days FG. Levery 100 days F.G. heche 60 days 4 1-5 dy Tower Avage Medie fully satisfied will the purchase Vehicle havice Bale Video Invan FIXED ASSETS Hay Red Edale Cumply love Sovi Hustling Packing Working lanean INVENTORY VARIETY 20,000 SKU, 5000 1.100 SKU's per based local plom. BBDOBCEERD Thureth water my by malin ON 201 Spring 2021) taught by TEV-DEALTEKIN. Dabei wnity on 2001 to Vw2021. 9 W * 1419 505.2001















