Question: 5. In this question you will double encrypt/decrypt your first and last name (separated by a using public and symmetric key approaches (if you are
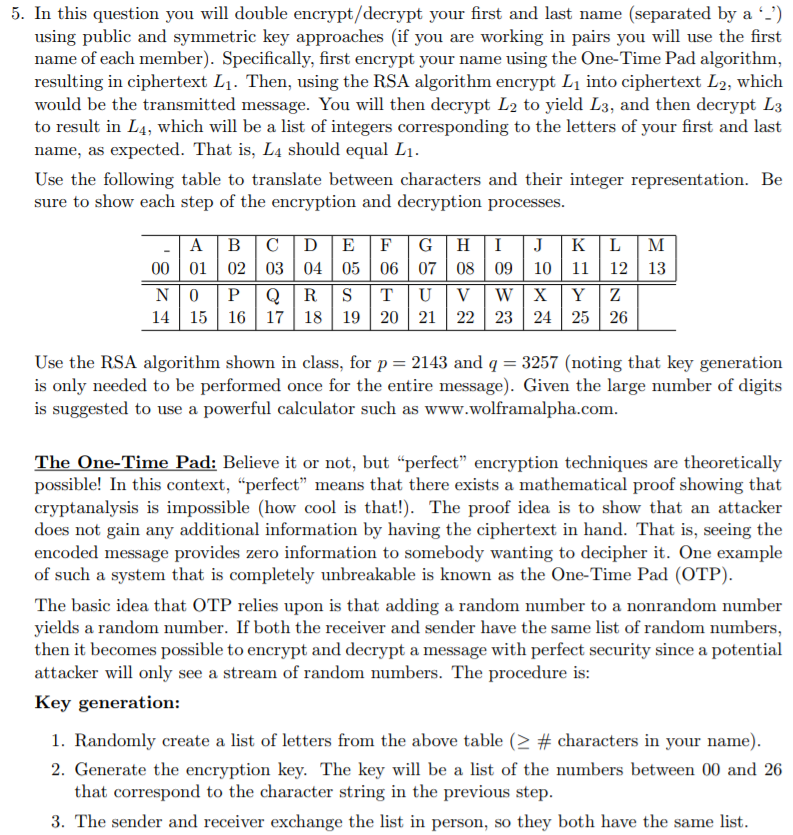


5. In this question you will double encrypt/decrypt your first and last name (separated by a using public and symmetric key approaches (if you are working in pairs you will use the first name of each member). Specifically, first encrypt your name using the One-Time Pad algorithm resulting in ciphertext L1. Then, using the RSA algorithm encrypt L1 into ciphertext L2, which would be the transmitted message. You will then decrypt L2 to yield L3, and then decrypt L3 to result in L4, which will be a list of integers corresponding to the letters of your first and last name, as expected. That is, L4 should equal L1. Use the following table to translate between characters and their integer representation. Be sure to show each step of the encryption and decryption processes. A | B |C |D | E |F |G | H | 1 |J |K | L |M 00 0102 0304 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 21 2223 24 25 26 Use the RSA algorithm shown in class, for p 2143 and q 3257 (noting that key generation is only needed to be performed once for the entire message). Given the large number of digits is suggested to use a powerful calculator such as www.wolframalpha.com. The One-Time Pad: Believe it or not, but "perfect" encryption techniques are theoretically possible! In this context, "perfect" means that there exists a mathematical proof showing that cryptanalysis is impossible (how cool is that!). The proof idea is to show that an attacker does not gain any additional information by having the ciphertext in hand. That is, seeing the encoded message provides zero information to somebody wanting to decipher it. One example of such a system that is completely unbreakable is known as the One-Time Pad (OTP) The basic idea that OTP relies upon is that adding a random number to a nonrandom number yields a random number. If both the receiver and sender have the same list of random numbers, then it becomes attacker will only see a stream of random numbers. The procedure is possible to encrypt and decrypt a message with perfect security since a potential ey generation: 1. Randomly create a list of letters from the above table (-# characters in your name) 2. Generate the encryption key. The key will be a list of the numbers between 00 and 26 that correspond to the character string in the previous step 3. The sender and receiver exchange the list in person, so they both have the same list 5. In this question you will double encrypt/decrypt your first and last name (separated by a using public and symmetric key approaches (if you are working in pairs you will use the first name of each member). Specifically, first encrypt your name using the One-Time Pad algorithm resulting in ciphertext L1. Then, using the RSA algorithm encrypt L1 into ciphertext L2, which would be the transmitted message. You will then decrypt L2 to yield L3, and then decrypt L3 to result in L4, which will be a list of integers corresponding to the letters of your first and last name, as expected. That is, L4 should equal L1. Use the following table to translate between characters and their integer representation. Be sure to show each step of the encryption and decryption processes. A | B |C |D | E |F |G | H | 1 |J |K | L |M 00 0102 0304 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 21 2223 24 25 26 Use the RSA algorithm shown in class, for p 2143 and q 3257 (noting that key generation is only needed to be performed once for the entire message). Given the large number of digits is suggested to use a powerful calculator such as www.wolframalpha.com. The One-Time Pad: Believe it or not, but "perfect" encryption techniques are theoretically possible! In this context, "perfect" means that there exists a mathematical proof showing that cryptanalysis is impossible (how cool is that!). The proof idea is to show that an attacker does not gain any additional information by having the ciphertext in hand. That is, seeing the encoded message provides zero information to somebody wanting to decipher it. One example of such a system that is completely unbreakable is known as the One-Time Pad (OTP) The basic idea that OTP relies upon is that adding a random number to a nonrandom number yields a random number. If both the receiver and sender have the same list of random numbers, then it becomes attacker will only see a stream of random numbers. The procedure is possible to encrypt and decrypt a message with perfect security since a potential ey generation: 1. Randomly create a list of letters from the above table (-# characters in your name) 2. Generate the encryption key. The key will be a list of the numbers between 00 and 26 that correspond to the character string in the previous step 3. The sender and receiver exchange the list in person, so they both have the same list
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


