Question: 7) Data Design: In a Context Diagram, an external entity is an external person or anything that interacts with an information system. In data design,
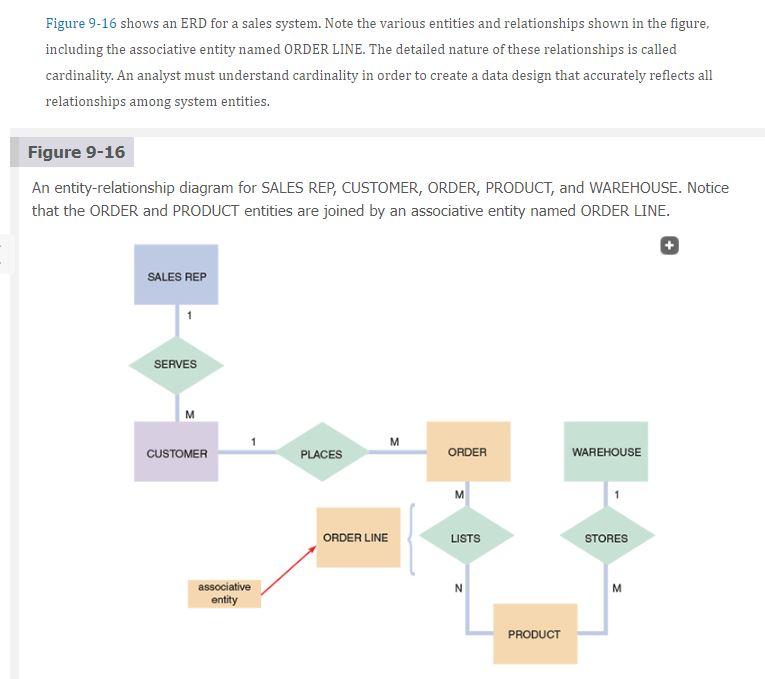
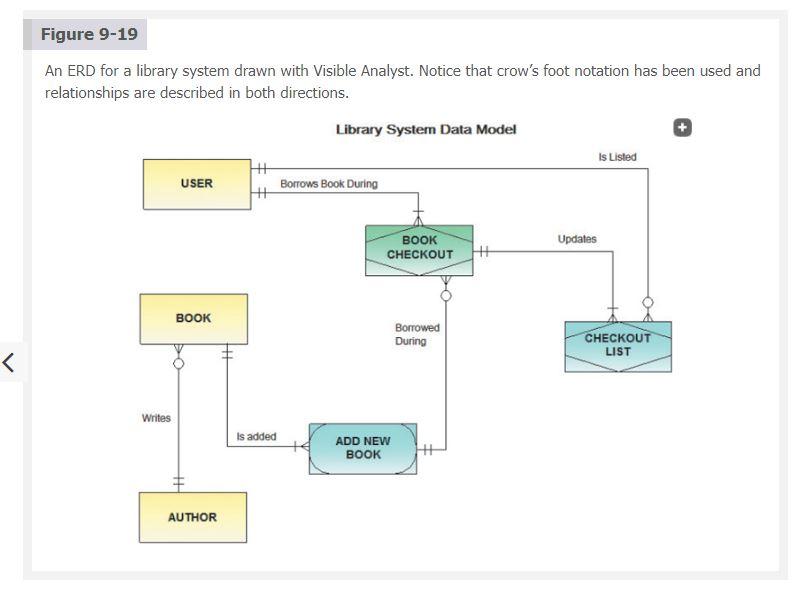
7) Data Design: In a Context Diagram, an external entity is an external person or anything that interacts with an information system. In data design, however, the definition is slightly different. In data design, an "entity' (data entity) is defined as "a person, a place, a thing, or an event for which data is collected and maintained. (Tilley, 2020, p.280). Please design and create the following data design diagrams (see examples on the following page): a) Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) of the data entities (at least 8) in your proposed system. Please use Cardinality notation in your diagram. For an example, see Figure 9-16 & Figure 9-19 in Sections 9.5.2 & 9.5.3 of the textbook. b) Class Diagram (Relational Database Diagram) of the objects (minimum of 8) in your proposed system. See the list of system objects (with attributes and methods) listed on the previous page. In your Class Diagram, for each object, please include the possible attributes and methods, as shown in the example provided in Figure 11-17 in Section 11.4.1 of the textbook. Figure 9-16 shows an ERD for a sales system. Note the various entities and relationships shown in the figure, including the associative entity named ORDER LINE. The detailed nature of these relationships is called cardinality. An analyst must understand cardinality in order to create a data design that accurately reflects all relationships among system entities. Figure 9-16 An entity-relationship diagram for SALES REP, CUSTOMER, ORDER, PRODUCT, and WAREHOUSE. Notice that the ORDER and PRODUCT entities are joined by an associative entity named ORDER LINE. SALES REP SERVES M M CUSTOMER PLACES ORDER WAREHOUSE M ORDER LINE LISTS STORES N associative entity M PRODUCT Figure 9-19 An ERD for a library system drawn with Visible Analyst. Notice that crow's foot notation has been used and relationships are described in both directions. Library System Data Model Is Listed Borrows Book During USER + Updates BOOK CHECKOUT BOOK Borrowed During CHECKOUT LIST T Writes Is added ADD NEW BOOK + AUTHOR 7) Data Design: In a Context Diagram, an external entity is an external person or anything that interacts with an information system. In data design, however, the definition is slightly different. In data design, an "entity' (data entity) is defined as "a person, a place, a thing, or an event for which data is collected and maintained. (Tilley, 2020, p.280). Please design and create the following data design diagrams (see examples on the following page): a) Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD) of the data entities (at least 8) in your proposed system. Please use Cardinality notation in your diagram. For an example, see Figure 9-16 & Figure 9-19 in Sections 9.5.2 & 9.5.3 of the textbook. b) Class Diagram (Relational Database Diagram) of the objects (minimum of 8) in your proposed system. See the list of system objects (with attributes and methods) listed on the previous page. In your Class Diagram, for each object, please include the possible attributes and methods, as shown in the example provided in Figure 11-17 in Section 11.4.1 of the textbook. Figure 9-16 shows an ERD for a sales system. Note the various entities and relationships shown in the figure, including the associative entity named ORDER LINE. The detailed nature of these relationships is called cardinality. An analyst must understand cardinality in order to create a data design that accurately reflects all relationships among system entities. Figure 9-16 An entity-relationship diagram for SALES REP, CUSTOMER, ORDER, PRODUCT, and WAREHOUSE. Notice that the ORDER and PRODUCT entities are joined by an associative entity named ORDER LINE. SALES REP SERVES M M CUSTOMER PLACES ORDER WAREHOUSE M ORDER LINE LISTS STORES N associative entity M PRODUCT Figure 9-19 An ERD for a library system drawn with Visible Analyst. Notice that crow's foot notation has been used and relationships are described in both directions. Library System Data Model Is Listed Borrows Book During USER + Updates BOOK CHECKOUT BOOK Borrowed During CHECKOUT LIST T Writes Is added ADD NEW BOOK + AUTHOR







