Question: a Q2. Consider a bimolecular reaction in a thin liquid film as shown in Fig 2. We will solve for the concentration profiles in this

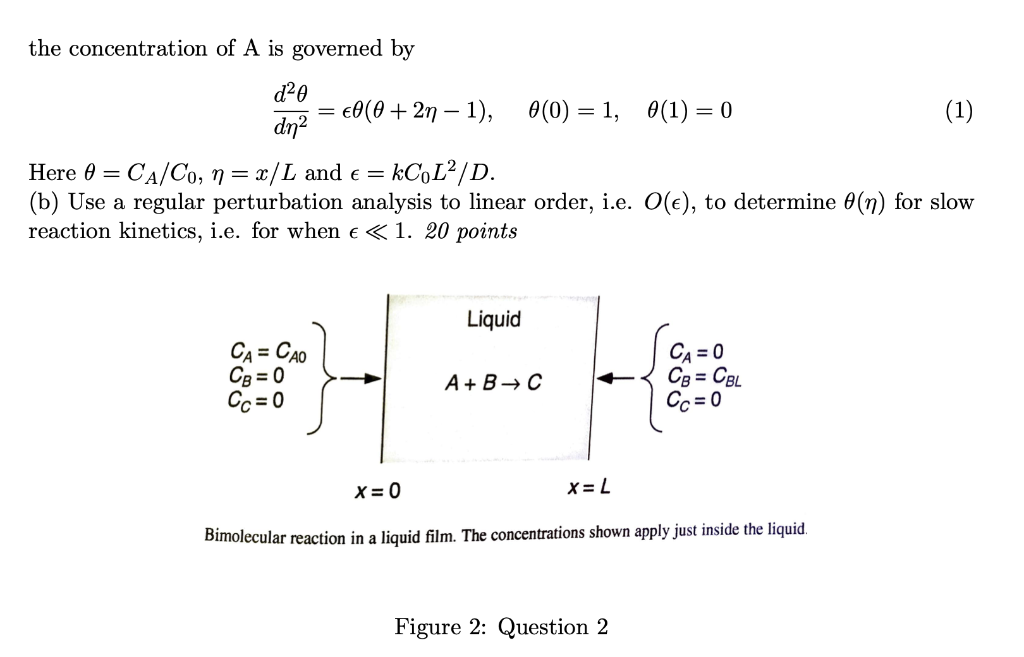
a Q2. Consider a bimolecular reaction in a thin liquid film as shown in Fig 2. We will solve for the concentration profiles in this system, but assuming that the reaction is relatively slow, and steady state. The reaction is A + B + C in the liquid film. Species A is introduced at O and B at x = L. The bimolecular rate constant is k. Assume that the diffusivities and the boundary concentrations are equal, i.e. Da= DB D and CAO = CBL = Co. (a) Combine the conservation equations for A and B and solve for CB. Using this, show that X = = = - the concentration of A is governed by d2e dn2 - 0(0 + 2n 1), 0(0) = 1, 0(1) = 0 (1) Here 0 = CA/Co, n= x/L and = = kCoL2/D. (b) Use a regular perturbation analysis to linear order, i.e. O(e), to determine 6(n) for slow reaction kinetics, i.e. for when
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


