Question: Loops and Files Lab objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures inlo Java oode Be able to write a while loop a



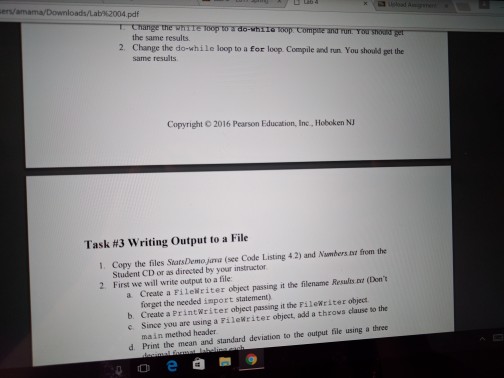

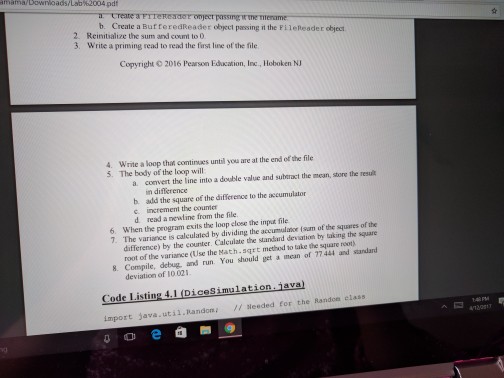
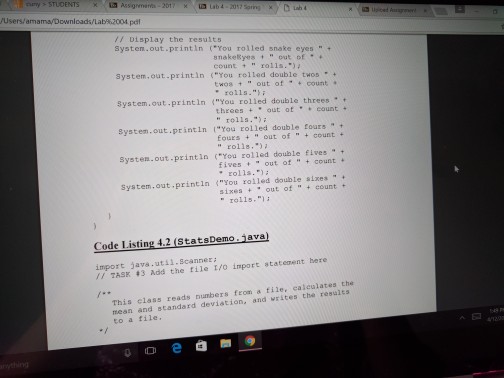
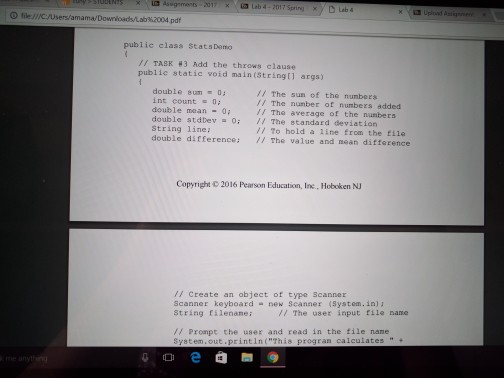
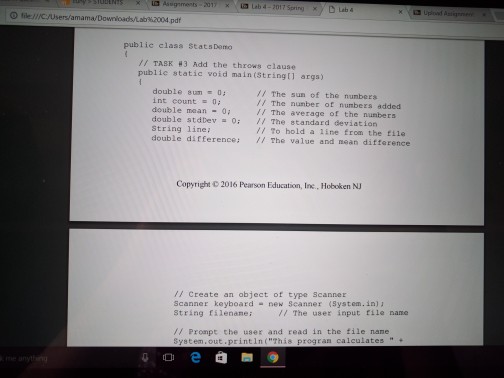
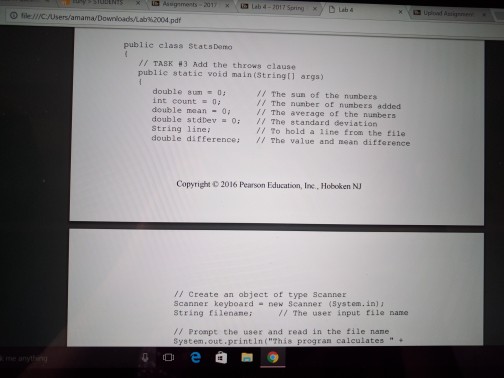
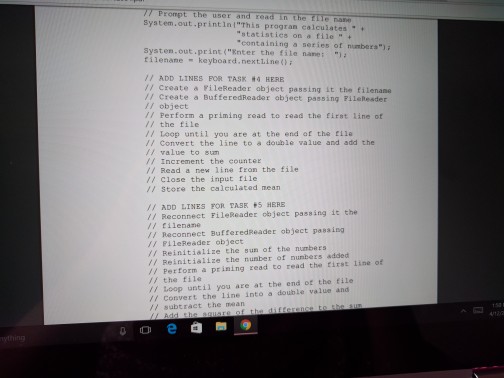
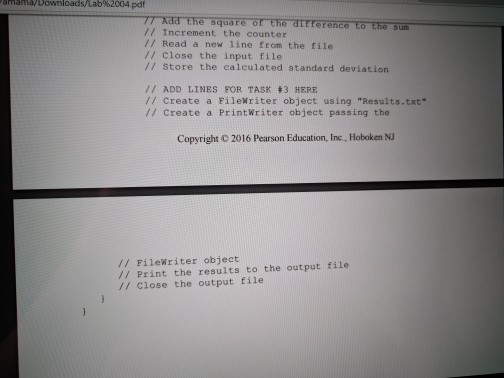
Loops and Files Lab objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures inlo Java oode Be able to write a while loop a do-while loop Be able to write Be able to write a for loop Be able use the Randon class to genenale random numbers Be able to use file streams for Vo Be able write a loop that reads until the end ofa file Be able to implement anaccumulator and a counter Introduction This is a simulation of rolling dice. Acual results approach theory only when the sample size is large So we will need to repeat rolling the dice a large number of times (we will use 10.000) The theoretical probability ofrolling doubles of a specific number is l out of 36 or approximately 278 out of 10.000 times that you roll the pair of dice. Since this is a mumbers will varya each you run Check out how to use the random number generator (introduced in Section 4.1i of the text to get a number between 1 and to create the simulation 6 We will continue to use control structures that we have already learned, while esploring control structures used for repetition. shall also our work wwh we by translating a given algorithm java order to complete our program a will start with a while kop, then use the same program, changing the while kop do while loop, and then a for loop. a file, line by line, We will be introduced to file input and output. We will read Loops and Files Lab objectives Be able to convert an algorithm using control structures inlo Java oode Be able to write a while loop a do-while loop Be able to write Be able to write a for loop Be able use the Randon class to genenale random numbers Be able to use file streams for Vo Be able write a loop that reads until the end ofa file Be able to implement anaccumulator and a counter Introduction This is a simulation of rolling dice. Acual results approach theory only when the sample size is large So we will need to repeat rolling the dice a large number of times (we will use 10.000) The theoretical probability ofrolling doubles of a specific number is l out of 36 or approximately 278 out of 10.000 times that you roll the pair of dice. Since this is a mumbers will varya each you run Check out how to use the random number generator (introduced in Section 4.1i of the text to get a number between 1 and to create the simulation 6 We will continue to use control structures that we have already learned, while esploring control structures used for repetition. shall also our work wwh we by translating a given algorithm java order to complete our program a will start with a while kop, then use the same program, changing the while kop do while loop, and then a for loop. a file, line by line, We will be introduced to file input and output. We will read
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


