Question: Part 1 : Dynamic Modeling The tank shown in Figure 1 is used for continuous extraction of a solute from a liquid solution to a
Part : Dynamic Modeling
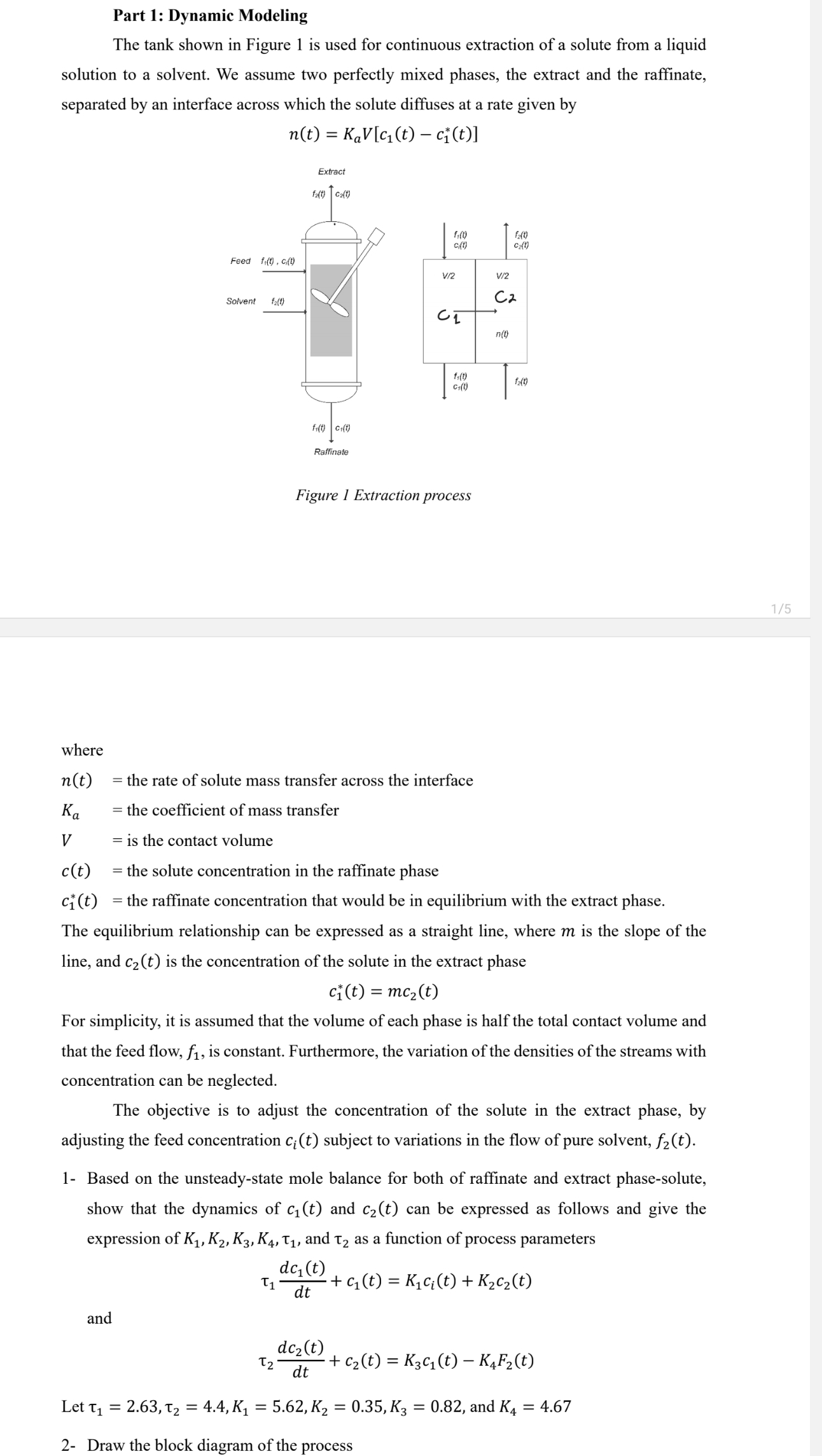
The tank shown in Figure is used for continuous extraction of a solute from a liquid
solution to a solvent. We assume two perfectly mixed phases, the extract and the raffinate,
separated by an interface across which the solute diffuses at a rate given by
where
the rate of solute mass transfer across the interface
the coefficient of mass transfer
is the contact volume
the solute concentration in the raffinate phase
the raffinate concentration that would be in equilibrium with the extract phase.
The equilibrium relationship can be expressed as a straight line, where is the slope of the
line, and is the concentration of the solute in the extract phase
For simplicity, it is assumed that the volume of each phase is half the total contact volume and
that the feed flow, is constant. Furthermore, the variation of the densities of the streams with
concentration can be neglected.
The objective is to adjust the concentration of the solute in the extract phase, by
adjusting the feed concentration subject to variations in the flow of pure solvent,
Based on the unsteadystate mole balance for both of raffinate and extract phasesolute,
show that the dynamics of and can be expressed as follows and give the
expression of and as a function of process parameters
and
Let and
Draw the block diagram of the process
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


