Question: Please EXPLAIN and solve EACH / ALL part(s) in Question #6 ! DOUBLE CHECK YOUR WORK AND ANSWER(S) . PLEASE NEATLY SHOW ALL WORK, EXPLANATIONS
Please EXPLAIN and solve EACH/ALL part(s) in Question #6!
DOUBLE CHECK YOUR WORK AND ANSWER(S).
PLEASE NEATLY SHOW ALL WORK, EXPLANATIONS, & CALCULATIONS STEP-BY-STEP USING PEN AND PAPER! I AM NEW TO CHEMISTRY! I AM A COMPLETE NEWBIE!
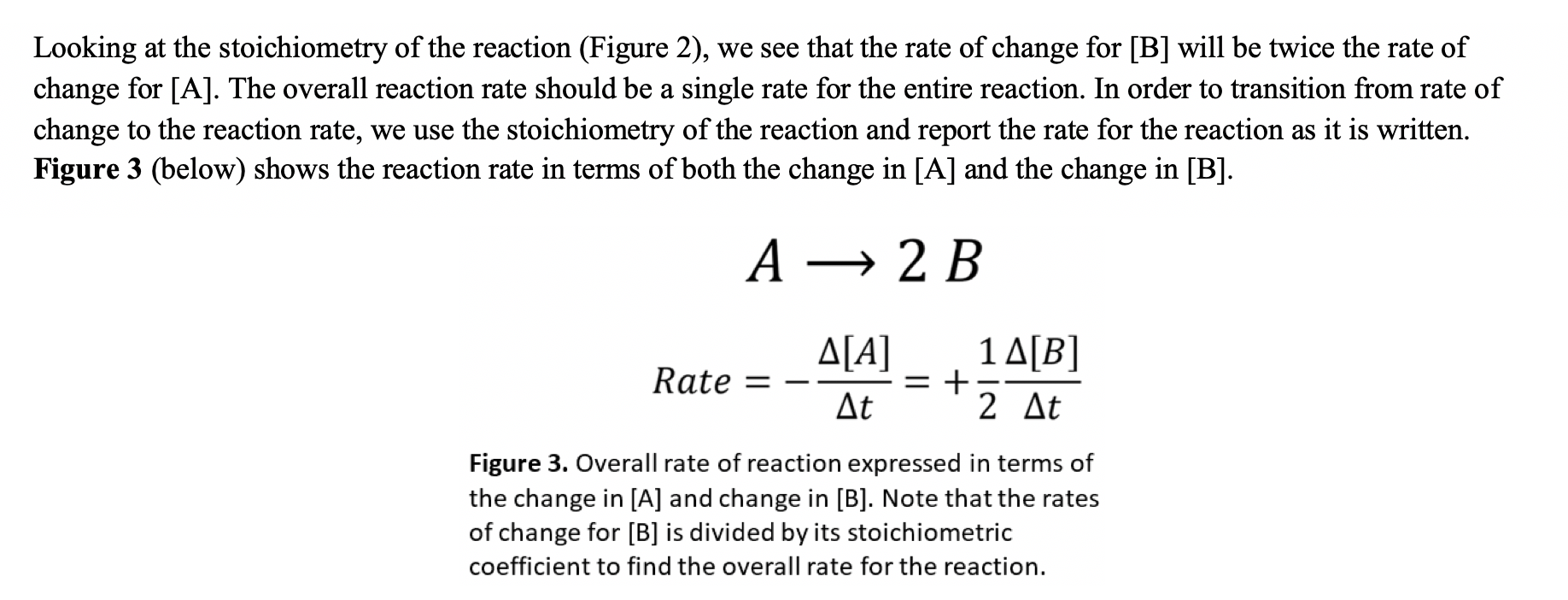
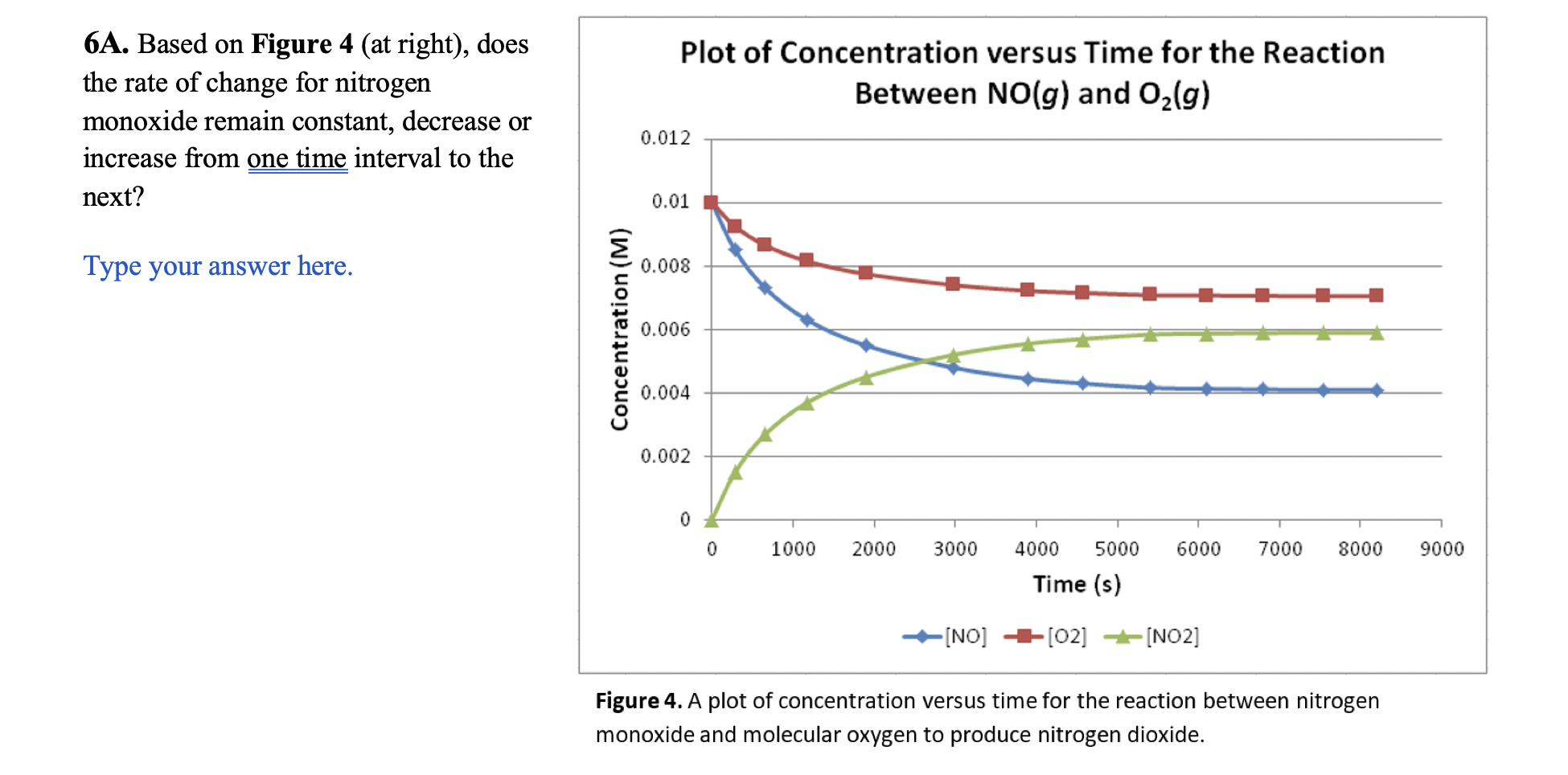

Looking at the stoichiometry of the reaction (Figure 2), we see that the rate of change for [B] will be twice the rate of change for [A]. The overall reaction rate should be a single rate for the entire reaction. In order to transition from rate of change to the reaction rate, we use the stoichiometry of the reaction and report the rate for the reaction as it is written. Figure 3 (below) shows the reaction rate in terms of both the change in [A] and the change in [B]. A2BRate=t[A]=+21t[B] Figure 3. Overall rate of reaction expressed in terms of the change in [A] and change in [B]. Note that the rates of change for [B] is divided by its stoichiometric coefficient to find the overall rate for the reaction. 6A. Based on Figure 4 (at right), does the rate of change for nitrogen monoxide remain constant, decrease or increase from one time interval to the next? Type your answer here. Figure 4. A plot of concentration versus time for the reaction between nitrogen monoxide and molecular oxygen to produce nitrogen dioxide. Part 3 Factors Affecting Reaction Rates 6B. What are the major factors that affect reaction rates? Type your answer here. In order for a chemical reaction to occur, reactant molecules must collide with each other. Keep this in mind as you answer the following questions. 6C. Looking at Figure 4 again, we see that the rate of reaction slows as the reaction proceeds. How is the change in concentration of reactant (NO or O2) related to the change in the rate of reaction? Type your answer here. 6D. Based on your answer to 6C, why might the rate of reaction decrease and the amount of reactant decreases? How are these two things related to each other? Type your answer here. 6E. According to our textbook, increasing the temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction. Thinking in terms of molecules colliding again, how might temperature play a role in increasing the reaction rate? Type your answer here
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


