Question: Please help me answer the following, Only the odd numbered problems 1,3,5,7,9. I really need help right now, Shortcut answers is okay as long as
Please help me answer the following, Only the odd numbered problems 1,3,5,7,9. I really need help right now, Shortcut answers is okay as long as the process are still clear, and accurate answers please...thank you!



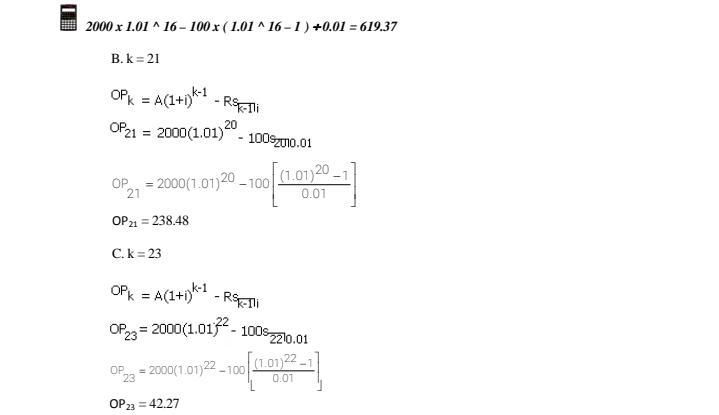
EXERCISES 4.2 01. An obligation will be amortized by semiannual payments of 230 for 8 years. If interest is at 8% compounded semiannually, find A. the present value of the loan B. the outstanding loan balance after 6 years C. the outstanding loan balance just after the 10" payment D. the remaining liability just before the 10" payment 02. A loan is to be paid by payments of 410 at the end of each 6 months for 5 years. If the rate is 7.2% compounded semiannually, find A. the present value of the loan B. the outstanding loan balance after 3 years C. the outstanding loan balance just after the 9" payment D. the remaining liability just before the 9" payment 03. Mr. Fernandez borrows 120,000 with interest rate of 6% compounded quarterly. The loan will be amortized by payments of 10,000 at the end of each three months for as long as necessary. Find A. the outstanding principal at the end of three years B. the remaining liability after the seventh payment 04. A businesswoman borrows 1 million with interest rate of 4.6% compounded semiannually. The loan will be amortized by payments of 125,000 at the end of each six months for as long as necessary. Find A. the outstanding principal at the end of three years B. the remaining liability after the fifth payment 108 AMORTIZATION OF DEBT AND SINKING FUND 4.3 Interest and Principal Included in any Amortization Payment 05. Mrs. Ramirez bought a property worth 10,000 by paying 2,400 down and the balance in monthly installments of 400 for as long as necessary. If the interest rate is 5% converted monthly, find the remaining liability at the end of the sixth payment. 06. Mr. Shou bought a house worth 80,000 by paying 25,400 down and the balance in quarterly installments of 10,000 for as long as necessary. If the interest rate is 6% converted quarterly, find the remaining liability at the end of the third payment. 07. Without using the amortization schedule in example 1, find the outstanding principal just after the third payment. 08. Without using the amortization schedule in example 1, find the outstanding principal just after the fourth payment. 09. A loan is being repaid with five semiannual payments of 2,000 followed by five semiannual payments of 1,000. If the nominal rate of interest converted semiannually is 10%, find the outstanding loan balance immediately after three payments have been made. Construct the table. 10. A loan is being repaid with five semiannual payments of 1,000 followed by five semiannual payments of 2,000. If the nominal rate of interest converted semiannually is 8%, find the outstanding loan balance immediately after four payments have been made. Construct the table.4.2 OUTSTANDING PRINCIPAL There are times that a borrower would want to know his outstanding principal after payment of R for a certain period. Either he may want to pay off the rest of the debt in a lump sum or just to have a record of his balance. When the number of payments is too large, constructing an amortization schedule becomes laborious. Hence, short cut methods are adopted to determine the outstanding loan balance. To find the outstanding principal just after any particular payment, two possible solutions are presented. The first solution, called the prospective solution, considers the future payments of the debt. The outstanding loan balance is equivalent to the present value of all unpaid payments. PROSPECTIVE SOLUTION OR = Ran-kill i Outstanding principal = present value of the remaining payments The second solution, called the retrospective solution, considers the history of the debt. The outstanding loan balance is equivalent to the excess of the accumulated value of the loan over the accumulated value of the past payments. RETROSPECTIVE SOLUTION OR= A(1 +1) . Re Eni Outstanding principal = accumulated value of investment A at time k - Accumulated value of past payments The decision on what solution to use depends on the nature of the problem. If the size and number of payments are known the prospective solution is more accurate. On the other hand, if the number of payments or the size of final irregular payment is not known then the retrospective solution is usually more accurate. Example 3. A loan is to be amortized by equal payments of 5,000 at the end of each month for 5 years. If the interest is based on 12% compounded monthly, find A) the present value of the loan; B) outstanding principal just after the 28" payment; and C) the remaining liability after 4 years.Solutions: Given: R = 5,000, j = 12%, m = 12, t= 5 years, n = 60 A. A = Rami A = 500036010.01 A = 5000 1-(1.01)-60 0.01 A = 224,775.19 B. Since the outstanding principal after the 28" payment is required then k = 29. The size and the number of payments are known thus prospective solution is more accurate. K = Ran-kelli OP 29 = 500033210.01 OP2 = 5000 1- (1.01)-32 0.07 OP 29 = 136,347.95 This means that the principal has decreased by 224,775.19 - 136,347.95 = 88,427.24, although the total payment is 5,000 x 29 = 145,000 because large part of it goes to the interest. C. The remaining liability after 4 years is the outstanding principal at the beginning of the 49" period hence k = 49. OPK = Ra n.k+ili OP49 = 500031210.01 OP = 5000 1 - (1.01)-12 0.01 OP49 = 56,275.39 Example 4. A loan of 2,000, with interest at 4% converted quarterly is to be amortized by payments of 100 at the end of each quarter for as long as necessary, find A) the outstanding principal at the end of 4 years; B) the remaining liability just after the 20th payment; and C) the remaining liability after 5.5 years. Solution: Given: A = 2,000, R = 100, j = 4%, m = 4 In this example, the number of payments is unknown thus, retrospective solution is more accurate. A. The outstanding principal at the end of 4 years is also the outstanding principal at beginning of the 17" period hence k = 17. OPK = A(1+1) - RSK-ni OR17 = 2000(1.06) - 100$1610.01 OP,7 = 2000(1.01)16 -100 (1.01)16-1 0.01 OP 17 = 619.372000 x 1.01 ^ 16 - 100 x ( 1.01 * 16- 1 ) +0.01 = 619.37 B. k = 21 OFK = A(1+1)K - RS-Tli OP21 = 2000(1.01) - 1009210.01 OP = 2000(1.01)20 -100 (1.01)20 -1 21 0.01 OP 21 = 238.48 C. k = 23 OPK = A(1+1)- RS Ti OF23 = 2000(1.015 - 100s 2210.01 OP = 2000(1.01)22 -100 (1.01)22 -1 0.01 OP 23 = 42.27
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


