Question: Q2.Carrier Injection and Vr Shift (a) For the flash memory device shown in Fig. 1, the dielectric between the floating gate (FG) and the control
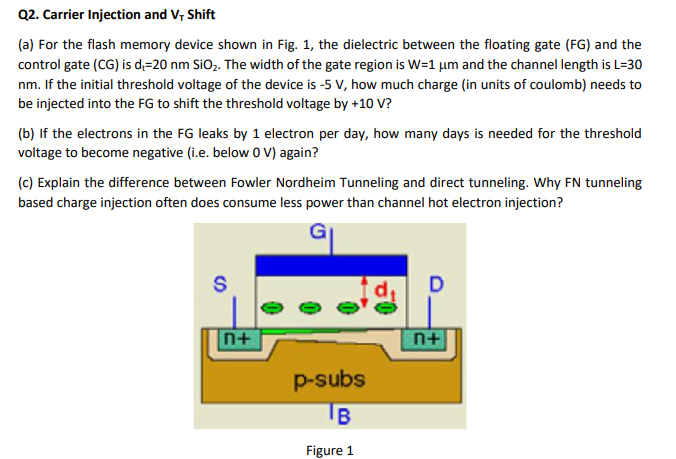

Q2.Carrier Injection and Vr Shift (a) For the flash memory device shown in Fig. 1, the dielectric between the floating gate (FG) and the control gate (CG) is d 20 nm SiO2. The width of the gate region is W-1 um and the channel length is L 30 nm. If the initial threshold voltage of the device is -5 V, how much charge (in units of coulomb) needs to be injected into the FG to shift the threshold voltage by +10 V? (b) If the electrons in the FG leaks by 1 electron per day, how many days is needed for the threshold voltage to become negative (i.e. below 0 V) again? (c) Explain the difference between Fowler Nordheim Tunneling and direct tunneling. Why FN tunneling based charge injection often does consume less power than channel hot electron injection? d, D n+ n+ p-subs Figure 1 Q5. Multi-level Cells (a) If the threshold voltage of a 2-bit MLC flash memory device is -5 V in the erased state and +5 V in the fully charged state, what would you choose as the reference voltages? If the dielectric between the floating gate (FG) and the control gate (CG) is 20 nm SiO2, the width of the gate region is W-1 um and the changing between neighboring threshold levels? (b) If we have a 4-bit MLC memory device, how many threshold levels do we need to have? How many reference voltages do we need to specify? Approximately how many time would the cell density be increased compared to a 2-bit MLC memory? How many times would the signal to noise ratio be degraded compared to a 3-bit MLC memory? Q2.Carrier Injection and Vr Shift (a) For the flash memory device shown in Fig. 1, the dielectric between the floating gate (FG) and the control gate (CG) is d 20 nm SiO2. The width of the gate region is W-1 um and the channel length is L 30 nm. If the initial threshold voltage of the device is -5 V, how much charge (in units of coulomb) needs to be injected into the FG to shift the threshold voltage by +10 V? (b) If the electrons in the FG leaks by 1 electron per day, how many days is needed for the threshold voltage to become negative (i.e. below 0 V) again? (c) Explain the difference between Fowler Nordheim Tunneling and direct tunneling. Why FN tunneling based charge injection often does consume less power than channel hot electron injection? d, D n+ n+ p-subs Figure 1 Q5. Multi-level Cells (a) If the threshold voltage of a 2-bit MLC flash memory device is -5 V in the erased state and +5 V in the fully charged state, what would you choose as the reference voltages? If the dielectric between the floating gate (FG) and the control gate (CG) is 20 nm SiO2, the width of the gate region is W-1 um and the changing between neighboring threshold levels? (b) If we have a 4-bit MLC memory device, how many threshold levels do we need to have? How many reference voltages do we need to specify? Approximately how many time would the cell density be increased compared to a 2-bit MLC memory? How many times would the signal to noise ratio be degraded compared to a 3-bit MLC memory
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


