Question: Question 2. Aggregate Production Plan (20 marks) Input your student ID into the cell B1 of sheetID in the spreadsheet file LGT2106_Assignment_Data.xlsx. Then, use the

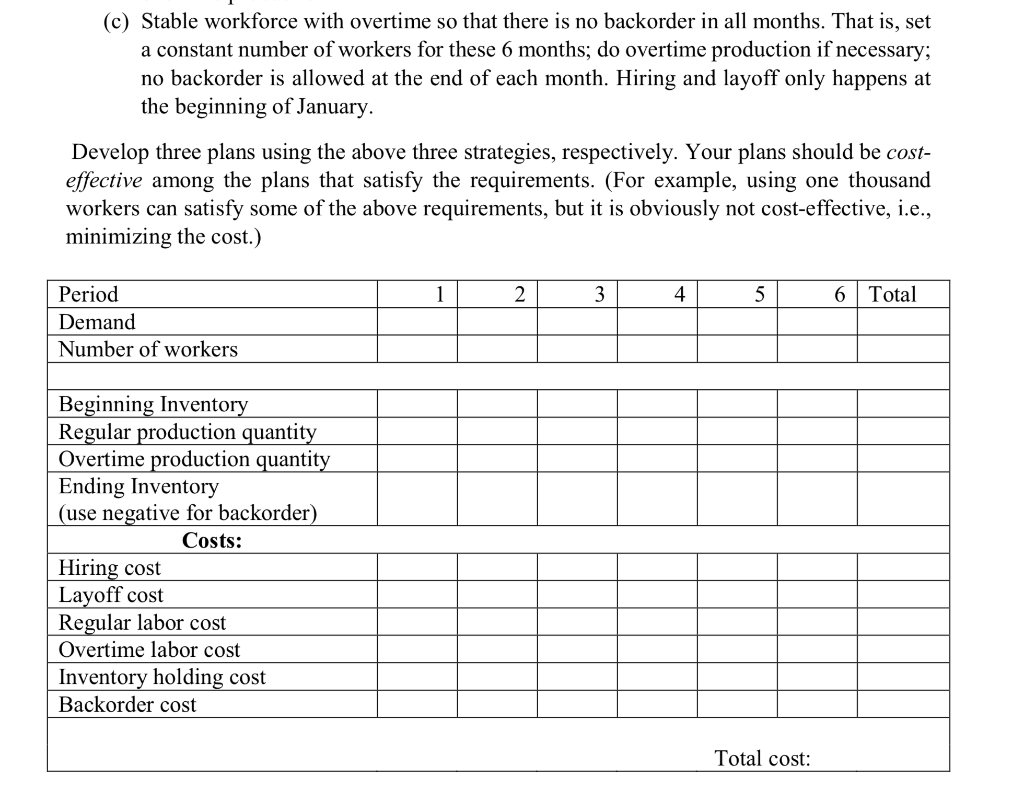
Question 2. Aggregate Production Plan (20 marks) Input your student ID into the cell "B1 of sheet"ID" in the spreadsheet file LGT2106_Assignment_Data.xlsx. Then, use the forecasted demand and other data shown in sheet Aggregate to help Helen Industries to plan its production for the next 6 months. In order to satisfy the production requirement, the company can vary its capacity by hiring or laying off workers and running overtime production. The following assumptions are made. Inventory and backorder costs are calculated using ending inventory/backorder of each month. Hiring or layoff costs are incurred when the number of workers changes. The number of workers in each month should be an integer. Once scheduled, all workers will produce at their full potential each month. The ending inventory requirement of June stated in CellB11" of the sheet Aggregate must be satisfied. Consider the following three different strategies. (a) A chase strategy by varying the number of workers. That is, use the minimum number of workers in each month to make the ending inventory of each month non-negative. No overtime production. (b) A level strategy to meet the overall production requirement. That is, use a constant number of workers for these 6 months; demand variations are absorbed by inventory and backorders. Hiring and layoff only happens at the beginning of January. No overtime production. (c) Stable workforce with overtime so that there is no backorder in all months. That is, set a constant number of workers for these 6 months; do overtime production if necessary; no backorder is allowed at the end of each month. Hiring and layoff only happens at the beginning of January. Develop three plans using the above three strategies, respectively. Your plans should be cost- effective among the plans that satisfy the requirements. (For example, using one thousand workers can satisfy some of the above requirements, but it is obviously not cost-effective, i.e., minimizing the cost.) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Period Demand Number of workers Beginning Inventory Regular production quantity Overtime production quantity Ending Inventory (use negative for backorder) Costs: Hiring cost Layoff cost Regular labor cost Overtime labor cost Inventory holding cost Backorder cost Total cost: Question 2. Aggregate Production Plan (20 marks) Input your student ID into the cell "B1 of sheet"ID" in the spreadsheet file LGT2106_Assignment_Data.xlsx. Then, use the forecasted demand and other data shown in sheet Aggregate to help Helen Industries to plan its production for the next 6 months. In order to satisfy the production requirement, the company can vary its capacity by hiring or laying off workers and running overtime production. The following assumptions are made. Inventory and backorder costs are calculated using ending inventory/backorder of each month. Hiring or layoff costs are incurred when the number of workers changes. The number of workers in each month should be an integer. Once scheduled, all workers will produce at their full potential each month. The ending inventory requirement of June stated in CellB11" of the sheet Aggregate must be satisfied. Consider the following three different strategies. (a) A chase strategy by varying the number of workers. That is, use the minimum number of workers in each month to make the ending inventory of each month non-negative. No overtime production. (b) A level strategy to meet the overall production requirement. That is, use a constant number of workers for these 6 months; demand variations are absorbed by inventory and backorders. Hiring and layoff only happens at the beginning of January. No overtime production. (c) Stable workforce with overtime so that there is no backorder in all months. That is, set a constant number of workers for these 6 months; do overtime production if necessary; no backorder is allowed at the end of each month. Hiring and layoff only happens at the beginning of January. Develop three plans using the above three strategies, respectively. Your plans should be cost- effective among the plans that satisfy the requirements. (For example, using one thousand workers can satisfy some of the above requirements, but it is obviously not cost-effective, i.e., minimizing the cost.) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Total Period Demand Number of workers Beginning Inventory Regular production quantity Overtime production quantity Ending Inventory (use negative for backorder) Costs: Hiring cost Layoff cost Regular labor cost Overtime labor cost Inventory holding cost Backorder cost Total cost






