Question: This is a calculus optimization question. Both the QUESTION and the SOLUTION are shown below: 1. My first query relates to the values shown as:


This is a calculus optimization question.
Both the QUESTION and the SOLUTION are shown below:
1. My first query relates to the values shown as:
h=w=2d
which is underlined in RED.
Please explain how this is determined?
2. I would also like to know how
(h,w,d)=(32V,32V,3V/4)
, underlined in BLUE, is obtained in much more detail ?
If you are using hand-written notes, then please ensure they are tidy and legible as untidy written notes are difficult to interpret. Alternatively use LaTeX.
QUESTION
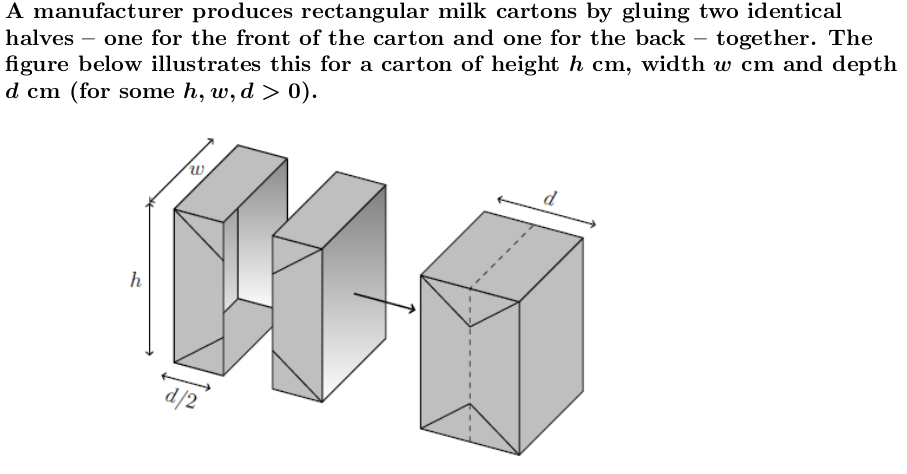
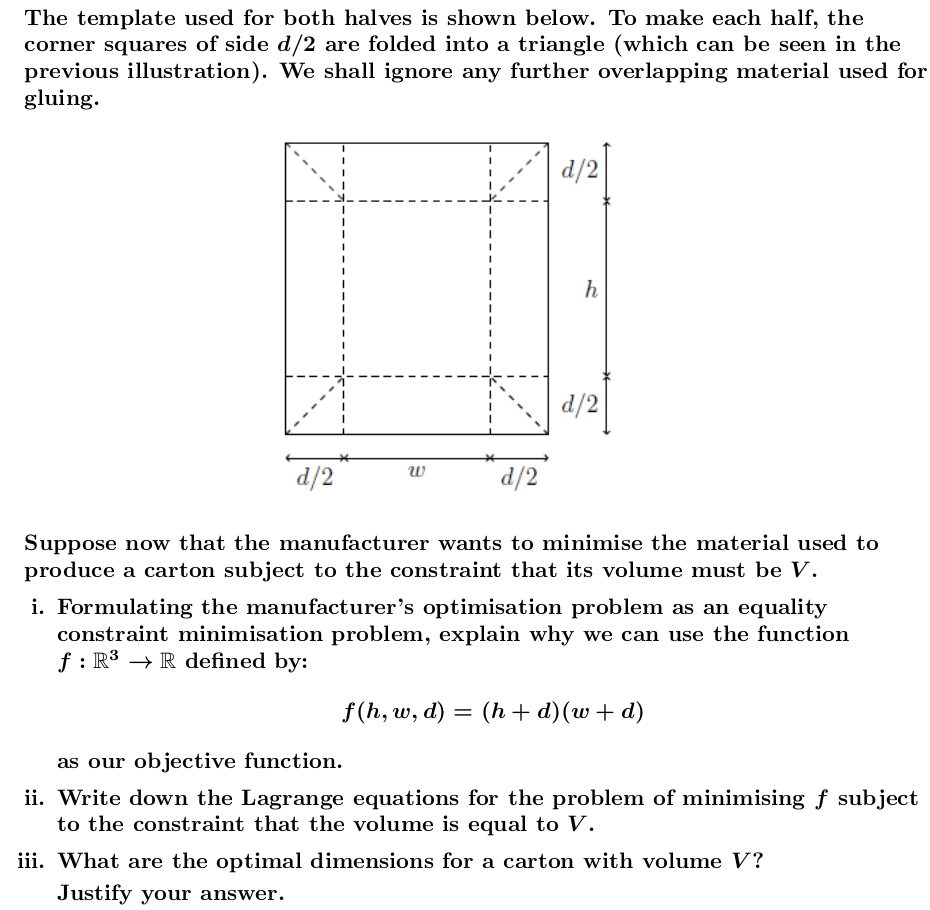


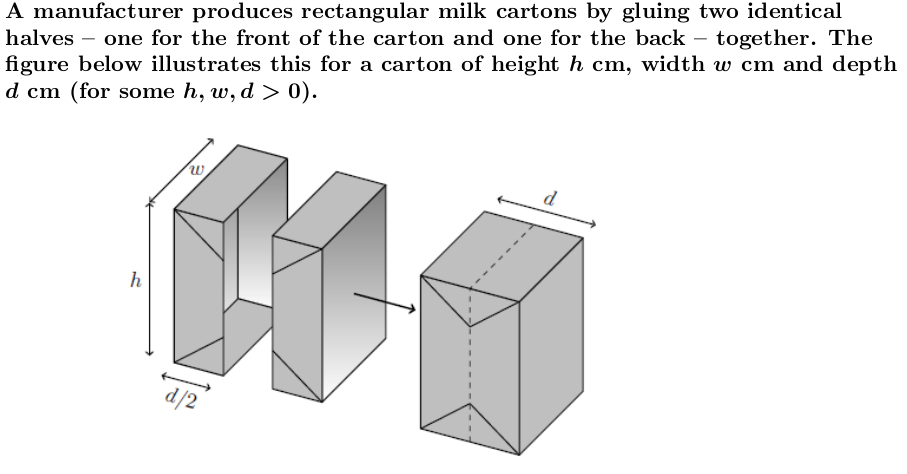
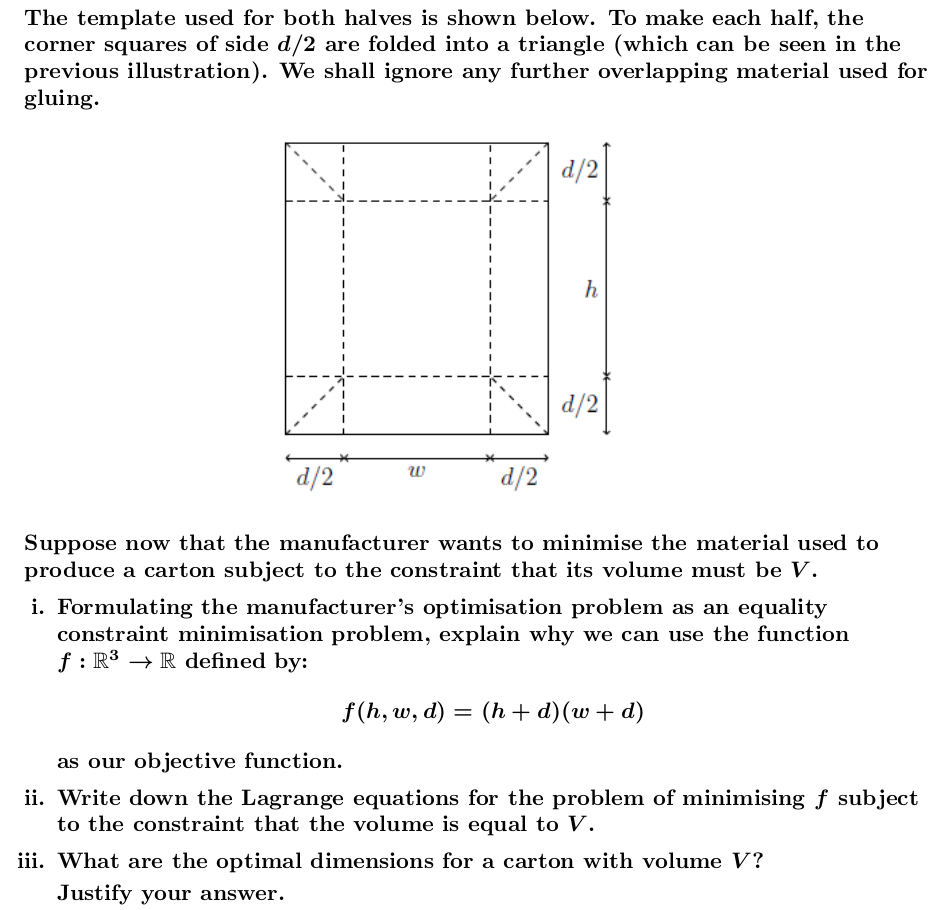
A manufacturer produces rectangular milk cartons by gluing two identical halves one for the front of the carton and one for the back together. The gure below illustrates this for a carton of height 1']; cm, width to cm and depth d cm (for some h, w,d > 0). The template used for both halves is shown below. To make each half, the corner squares of side d/2 are folded into a triangle (which can be seen in the previous illustration). We shall ignore any further overlapping material used for gluing. d /2 h d/2 d/2 W d/2 Suppose now that the manufacturer wants to minimise the material used to produce a carton subject to the constraint that its volume must be V. i. Formulating the manufacturer's optimisation problem as an equality constraint minimisation problem, explain why we can use the function f : R3 - R defined by: f (h, w, d) = (h + d)(w + d) as our objective function. ii. Write down the Lagrange equations for the problem of minimising f subject to the constraint that the volume is equal to V. iii. What are the optimal dimensions for a carton with volume V? Justify your answer.i. ii. The total area for one half of a carton is: (h+2> 0, the constraint qualification holds everywhere. Therefore, any solution to the optimisation problem must arise as a solution to the equations in part (c). The first-order conditions yield h = w = 2d which, upon substitution into the constraint equality, gives optimal values: (h*, w*, d*) = V2V, V2V. 3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


