The Beattie-Bridgman equation, a famous equation of state for real gases, may be written Eq. 1.61 where
Question:
The Beattie-Bridgman equation, a famous equation of state for real gases, may be written
Eq. 1.61
![11 RT[1-c/(vT)] [u + Bo (1-)]- (1-7) (1.61)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1697/5/2/6/850652e344260f6f1697526850066.jpg)
where a, A0, b, B0 and c are experimental constants and ν is the molar volume, 1/g mol.
(a) Show that this equation can be put into the form of Eq. (1.54), and derive equations for the virial coefficients B, C, and D in terms of the constants in Eq. (1.61).
Eq. 1.54
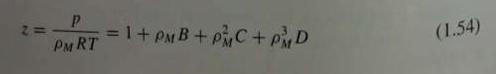
(b) For air the constants are a = 0.01931, A0 = 1.3012, b = -0.01101, B0 = 0.04611, and c x 10-4 = 66.00, all in cgs units (atmospheres, liters, gram moles, kelvins, with R = 0.08206). Calculate values of the virial coefficients for air in SI units.
(c) Calculate z for air at a temperature of 300 K and a molar volume of 300 K and a molar volume of 0.200 m3/kg mol.
Step by Step Answer:

Unit Operations Of Chemical Engineering
ISBN: 9780072848236
7th Edition
Authors: Warren McCabe, Julian Smith, Peter Harriott





