Question: Make the given changes in the indicated examples of this section and then solve the resulting quadratic equations by completing the square. In Example 2,
Make the given changes in the indicated examples of this section and then solve the resulting quadratic equations by completing the square.
In Example 2, change the − sign before 6x to +.
Data from Example 2
To find the roots of the quadratic equation
x2 − 6x − 8 = 0
first note that the left side is not factorable. [However, x2 − 6x is part of the special product (x − 3)2 = x2 − 6x + 9 and this special product is a perfect square.] By adding 9 to x2 − 6x, we have (x − 3)2 . Therefore, we rewrite the original equation as
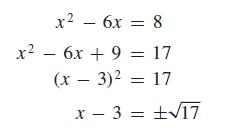
The ± sign means that x − 3 = √17 or x − 3 = − √17.
By adding 3 to each side, we obtain x = 3 ± √17
which means x = 3 + √17 and x = 3 − √17 are the two roots of the equation. Therefore, by adding 9 to x2 − 6x on the left, we have x2 − 6x + 9, which is the perfect square of x − 3. This means, by adding 9 to each side, we have completed the square of x − 3 on the left side. Then, by equating x − 3 to the positive and negative square root of the number on the right side, we were able to find the two roots of the quadratic equation by solving two linear equations.
x - 6x = 8 x - 6x + 9 = 17 (x 3)2 = 17 - x - 3 = 17
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
If we change the minus sign before 6x to plus in the quadratic equation x... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


