The reversible gas-phase elementary reaction The chemical equation shows the formation of Ethyl benzene by the gas-phase
Question:
The reversible gas-phase elementary reaction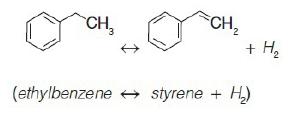
The chemical equation shows the formation of Ethyl benzene by the gas-phase reversible reaction of styrene and two molecules of hydrogen. Styrene (CH2 double bonded with six carbon rings including three double bonds) reacts with two molecules of hydrogen which tends to form ethyl benzene (CH3 single-bonded with six carbon rings including three double bonds). is carried out in an isothermal CSTR with no pressure drop. The feed enters at a volumetric flow rate of υ0=5000dm3hr. The feed consists of half ethyl benzene (i.e., A) and half inerts on a molar basis and is well mixed before it enters the reactor (I). The pressure in the reactor is 6 atm (so PA0 = 3 atm and PI0 = 3 atm, making the
entering concentration of ethyl benzene, A, CA0=0.04 × moldm3). The molar flow rate of A is FA0=200molhr. At the reaction temperature of 640°C, the rate constant, kA, is 5.92moldm3⋅hr⋅atm. The equilibrium constant, KP, is 9 atm and the corresponding equilibrium conversion is Xe = 0.84.
a. Write out each step of the algorithm.
b. Write the rate of reaction, –rA, solely as a function of PA0 X, KP, and k.
c. Calculate the reactor volume necessary to achieve 90% of the equilibrium conversion, Xe.
d. How would the conversion from part (a) be affected if the reactor diameter increased and height decreased but total volume remained the same? Explain.
Step by Step Answer:






