Question: In a 2-issue static superscalar whose predictor can only handle one branch per cycle, what speedup is achieved by adding the ability to predict two
In a 2-issue static superscalar whose predictor can only handle one branch per cycle, what speedup is achieved by adding the ability to predict two branches per cycle? Assume a stall-on-branch policy for branches that the predictor cannot handle.
In this exercise, we make several assumptions. First, we assume that an N-issue superscalar processor can execute any N instructions in the same cycle, regardless of their types. Second, we assume that every instruction is independently chosen, without regard for the instruction that precedes or follows it. Third, we assume that there are no stalls due to data dependences, that no delay slots are used, and that branches execute in the EX stage of the pipeline. Finally, we assume that instructions executed in the program are distributed as follows: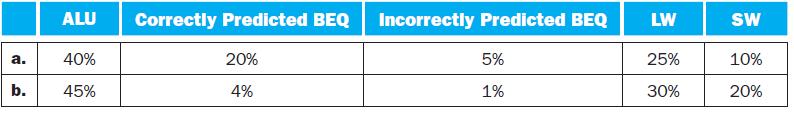
a. b. ALU 40% 45% Correctly Predicted BEQ Incorrectly Predicted BEQ 20% 4% 5% 1% LW 25% 30% SW 10% 20%
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We must account for how the accuracy of the branch prediction affects the programs execution time in ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


