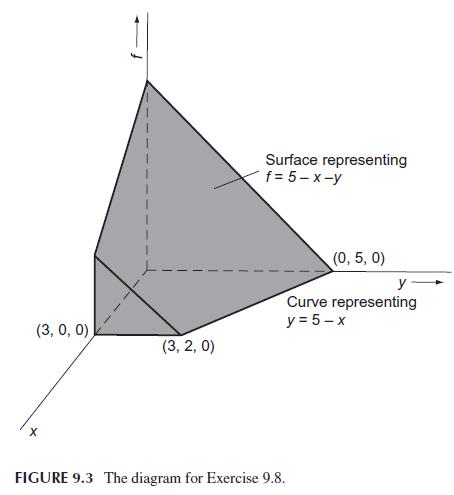
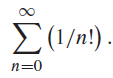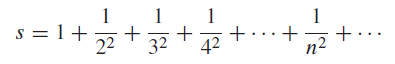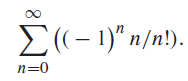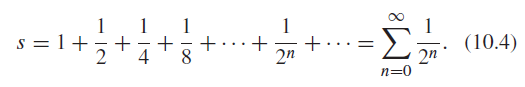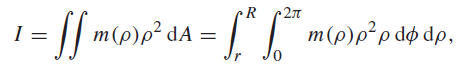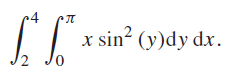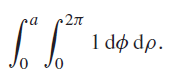![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


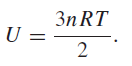
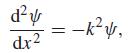
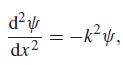
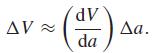
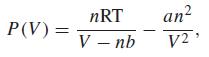
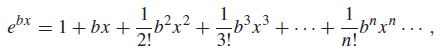
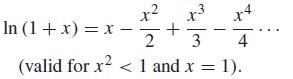
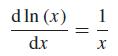
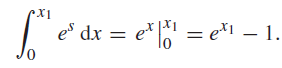
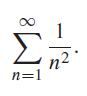
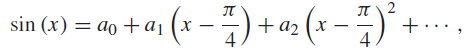
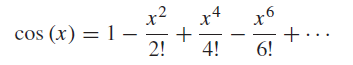
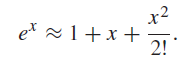
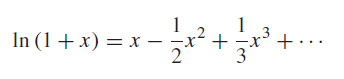
![d [In (1 +x)] dx](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1545/9/9/3/9875c25ff03b865f1545976565611.jpg)
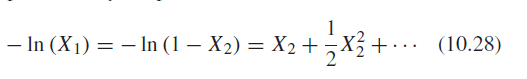
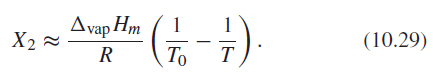
![EIIN (2)]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1545/9/9/3/7265c25fdfe75aeb1545976304293.jpg)