Ethyl alcohol in the solvent CCl 4 forms a hydrogen-bonded complex with an equilibrium constant K eq
Question:
Ethyl alcohol in the solvent CCl4 forms a hydrogen-bonded complex with an equilibrium constant Keq = 11.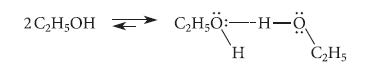
(a) What happens to the concentration of the complex as the concentration of ethanol is increased? Explain.
(b) What is the standard free-energy change for this reaction at 25°C?
(c) If one mole of ethanol is dissolved in one liter of CCl4, what are the concentrations of free ethanol and of complex?
(d) The equilibrium constant for the analogous reaction of ethanethiol is 0.004. Which forms stronger hydrogen bonds, thiols or alcohols?
(e) Which would be more soluble in water: CH3OCH2CH2SH or its isomer CH3SCH2CH2OH? Explain.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





