Question: 2 Ag(s) + Cu+ (aq) + 2 Ag+ (aq) + Cu(s) Half-Reaction Standard Reduction Potential, E (V) +0.80 Ag+ (aq) +e Ag(8) Cu+ (aq) +
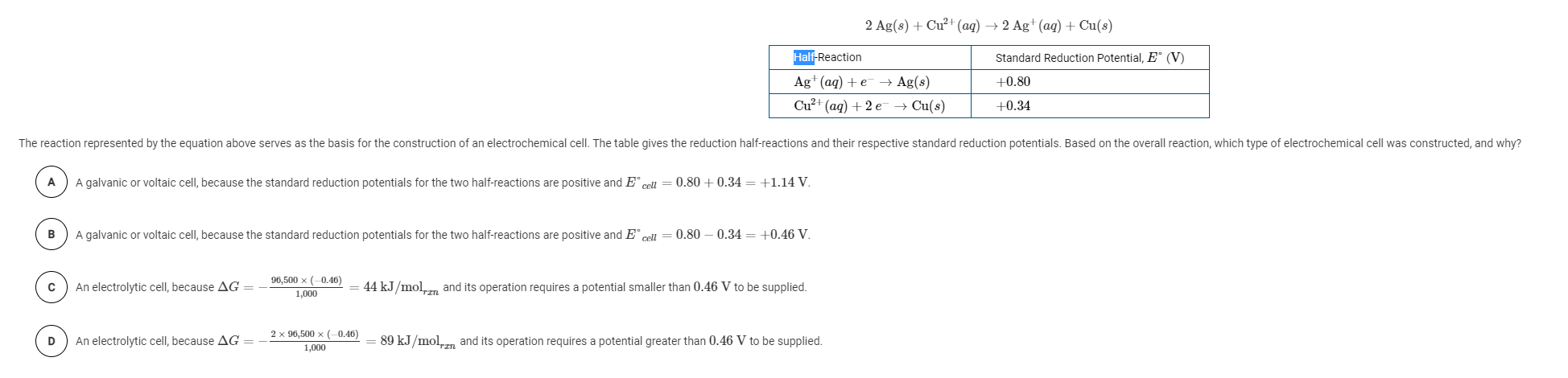
2 Ag(s) + Cu+ (aq) + 2 Ag+ (aq) + Cu(s) Half-Reaction Standard Reduction Potential, E (V) +0.80 Ag+ (aq) +e Ag(8) Cu+ (aq) + 2 e + Cu(s) +0.34 The reaction represented by the equation above serves as the basis for the construction of an electrochemical cell. The table gives the reduction half-reactions and their respective standard reduction potentials. Based on the overall reaction, which type of electrochemical cell was constructed, and why? A galvanic or voltaic cell, because the standard reduction potentials for the two half-reactions are positive and Ecell = 0.80 +0.34 = +1.14 V. B A galvanic or voltaic cell, because the standard reduction potentials for the two half-reactions are positive and Ecell = 0.80 0.34 = +0.46 V. An electrolytic cell, because AG = 96,500 x (0.46) 1,000 44 kJ/mol en and its operation requires a potential smaller than 0.46 V to be supplied. D An electrolytic cell, because AG = 2 x 96,500 (-0.46) 1,000 89 kJ/molin and its operation requires a potential greater than 0.46 V to be supplied
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


