Question: Compare the cost/performance ratio with and without this improvement. When processor designers consider a possible improvement to the processor datapath, the decision usually depends on
Compare the cost/performance ratio with and without this improvement.
When processor designers consider a possible improvement to the processor datapath, the decision usually depends on the cost/performance trade-off. In the following three problems, assume that we are starting with a datapath from Figure 4.2, where I-Mem, Add, Mux, ALU, Regs, D-Mem, and Control blocks have latencies of 400ps, 100ps, 30ps, 120ps, 200ps, 350ps, and 100ps, respectively, and costs of 1000, 30, 10, 100, 200, 2000, and 500, respectively. The remaining three problems in this exercise refer to the following processor improvement: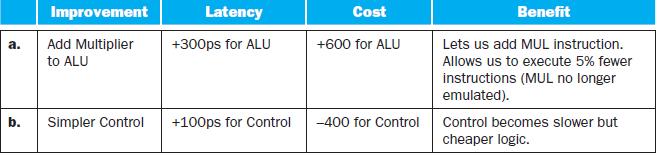
Figure 4.2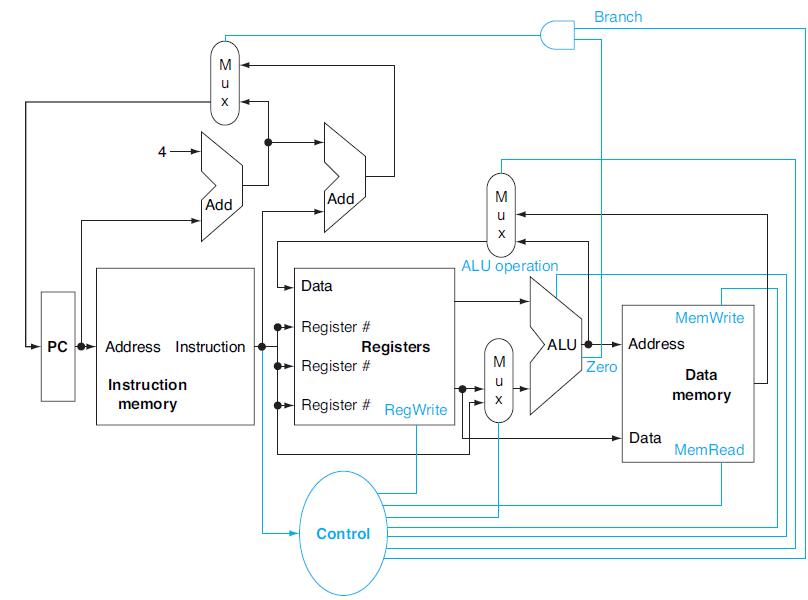
a. b. Improvement Add Multiplier to ALU Simpler Control Latency +300ps for ALU +100ps for Control Cost +600 for ALU -400 for Control Benefit Lets us add MUL instruction. Allows us to execute 5% fewer instructions (MUL no longer emulated). Control becomes slower but cheaper logic.
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lets first compute the cost and performance of the processor datapath before and after the upgrade a... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


