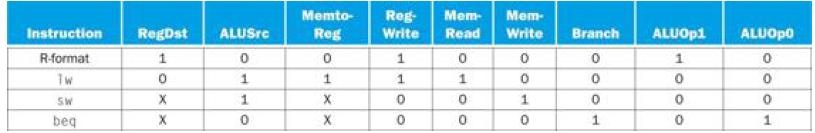
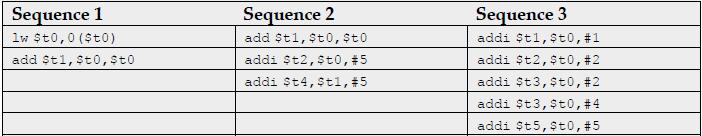
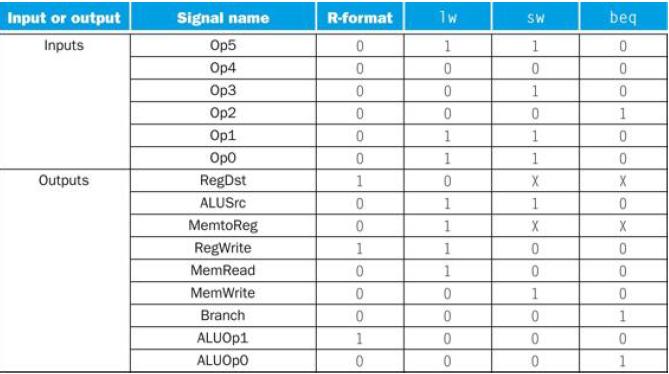
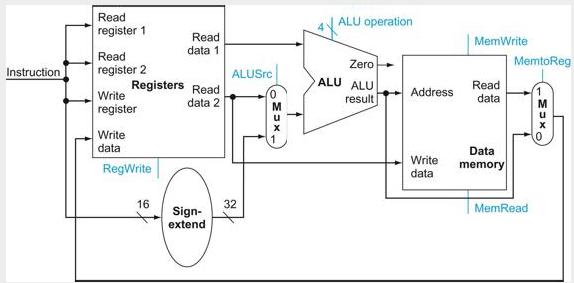
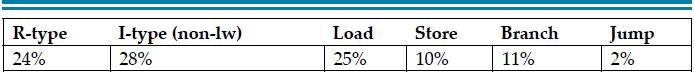
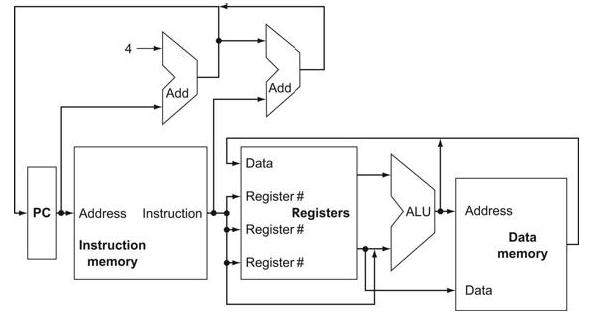
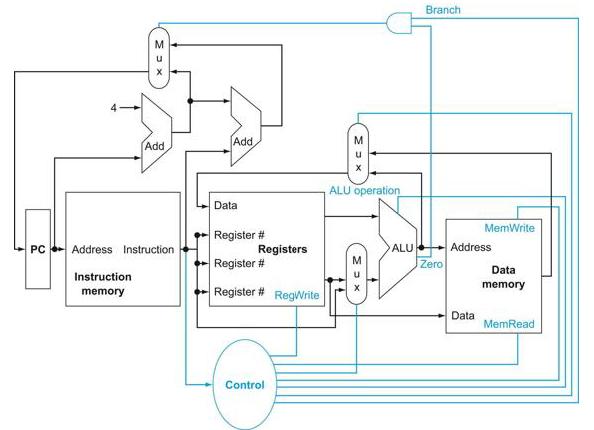
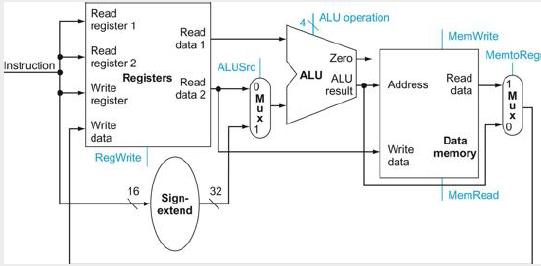
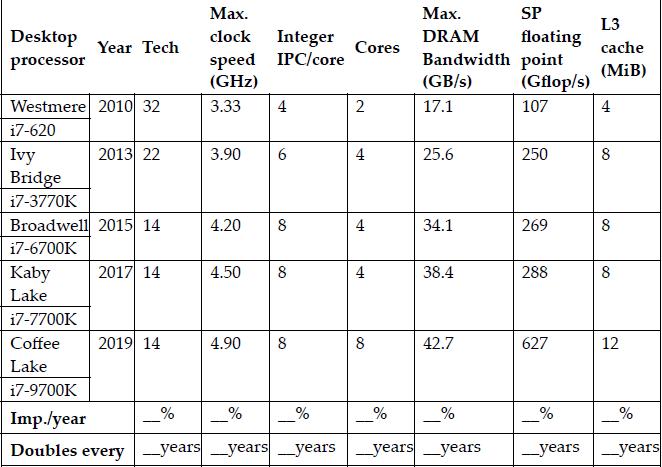
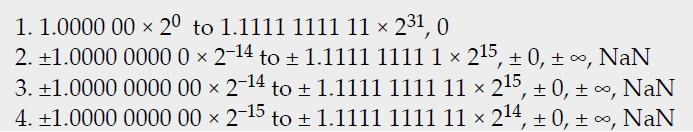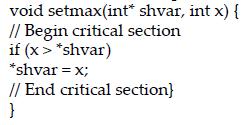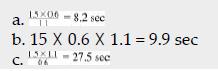![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


![PC Add Read address Instruction (31-01 Instruction [31-26] Instruction [25-21] Instruction [20-16]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1703/7/6/8/476658d719c50eb01703768474996.jpg)
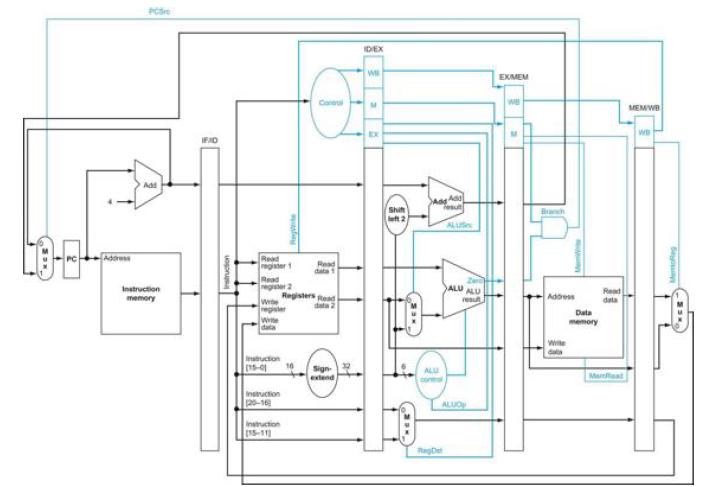
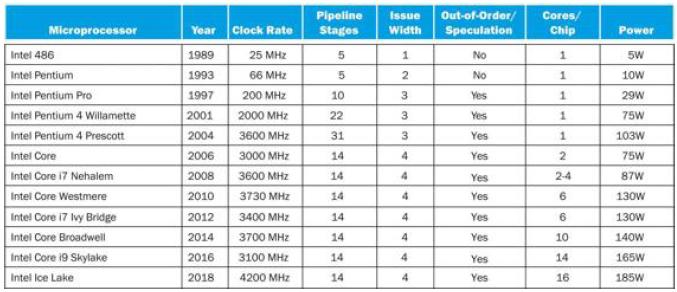
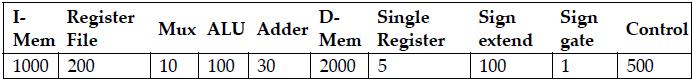
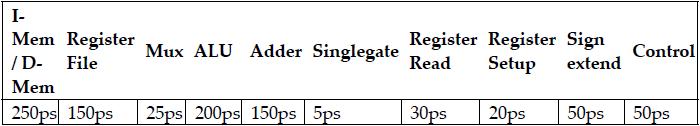
![PC Add Read address Instruction [31-0] Instruction [31-26] Instruction [25-21] Instruction [20-16]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1703/7/6/7/655658d6e67c2ecb1703767654663.jpg)