Question: Repeat Problem 4.4-3 for the case that the filter solves the difference equation [m(k+1)=0.5 e(k+1)-(0.5)(0.8) e(k)+0.485 m(k)] the sampling rate is (10 mathrm{~Hz}), and the
Repeat Problem 4.4-3 for the case that the filter solves the difference equation
\[m(k+1)=0.5 e(k+1)-(0.5)(0.8) e(k)+0.485 m(k)\]
the sampling rate is \(10 \mathrm{~Hz}\), and the plant transfer function is given by
\[G_{p}(s)=\frac{5}{(s+1)(s+2)}\]
Problem 4.4-3
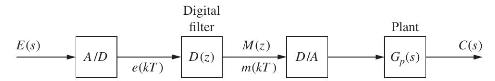
For the system of Fig. P4.4-3, the filter solves the difference equation \[
m(k)=0.8 m(k-1)+0.1 e(k)
\]
The sampling rate is \(1 \mathrm{~Hz}\) and the plant transfer function is given by \[
G_{p}(s)=\frac{1}{s+0.2}
\]
(a) Find the system transfer function \(C(z) / E(z)\).
(b) Find the system dc gain from the results of part (a).
(c) Verify the results of part (b) by finding the dc gain of the filter using \(D(z)\) and that of the plant using \(G_{p}(s)\).
(d) Use the results of part (b) to find the steady-state value of the unit-step response.
(e) Verify the results of part (d) by calculating \(c(k T)\) for a unit-step input.
(f) Note that in part (e), the coefficients in the partial-fraction expansion add to zero. Why does this occur?
Fig. P4.4-3
Digital filter Plant E(s) M(z) C(s) A/D D(z) DIA e(KT) m(kt) Gp(s)
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


