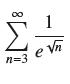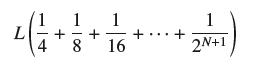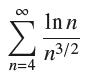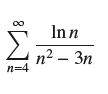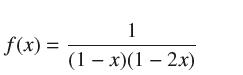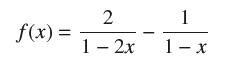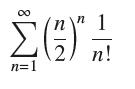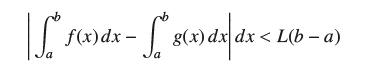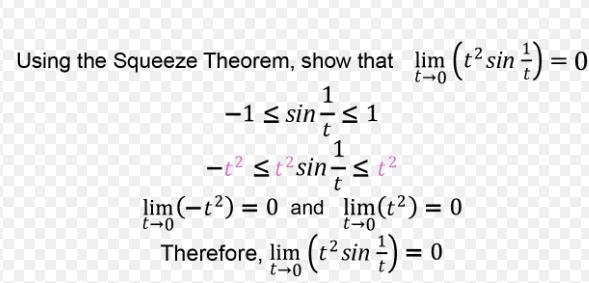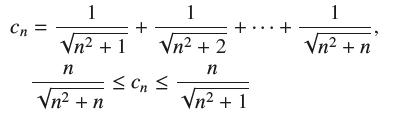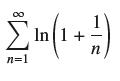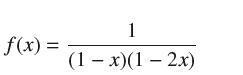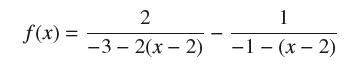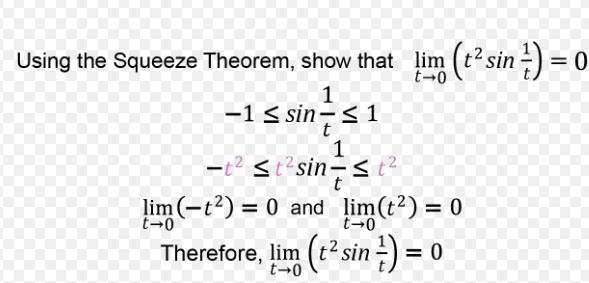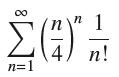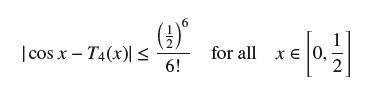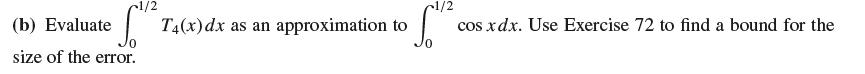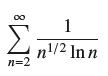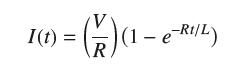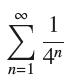![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


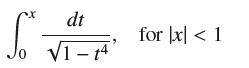
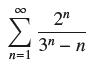
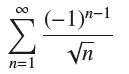
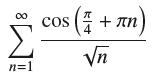
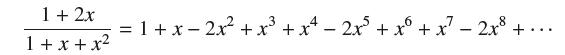
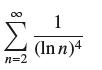
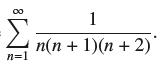
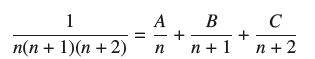
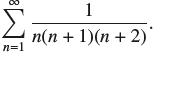
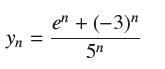
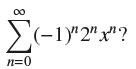
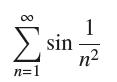
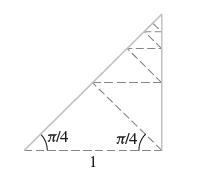
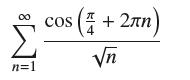
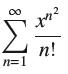
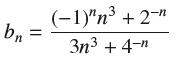
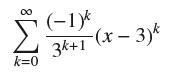
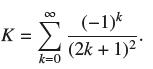
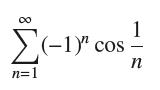
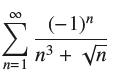

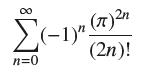
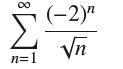
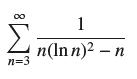
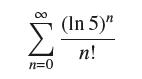
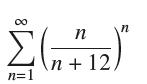
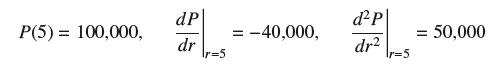
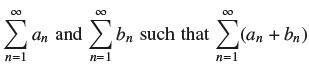
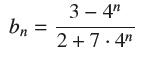
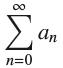
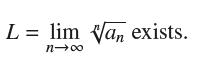

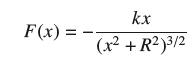
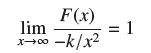
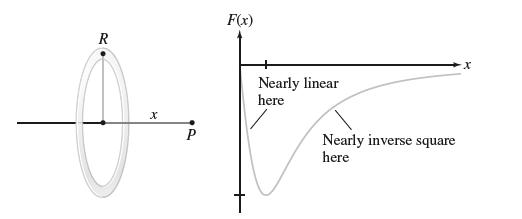
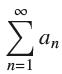

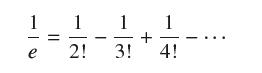
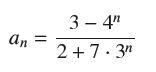
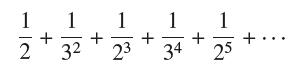
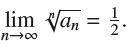
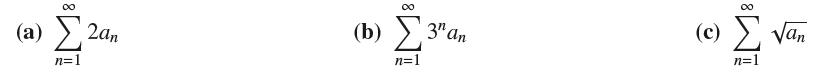
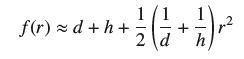
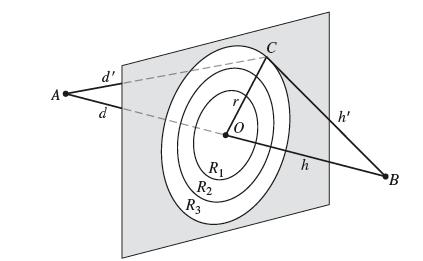
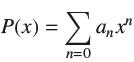
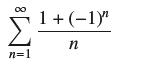
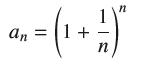
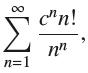
![(a) Prove that the series converges absolutely if [c] e. en! 27. Verify this numerically. nonn+1/2 (c) Use](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/7/0/9/547657d492b6a31f1702709549321.jpg)
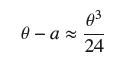
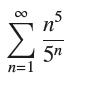
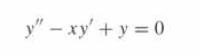
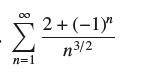
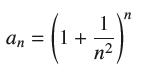
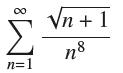
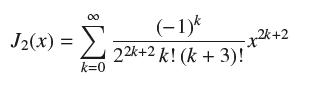
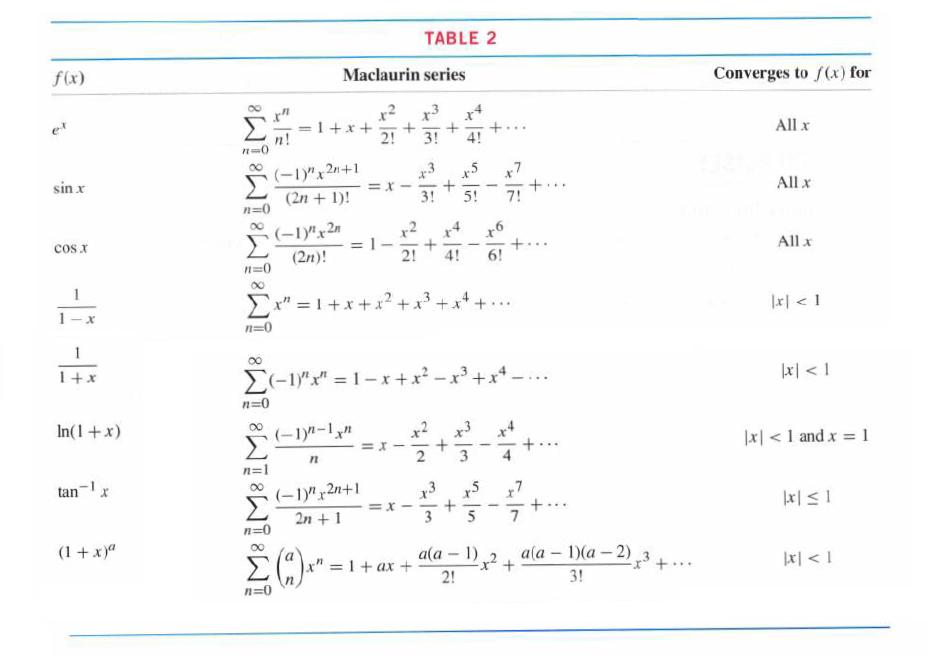
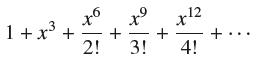
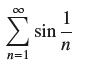
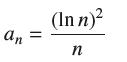
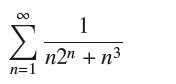
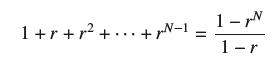
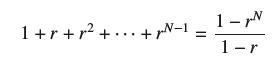
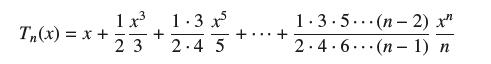
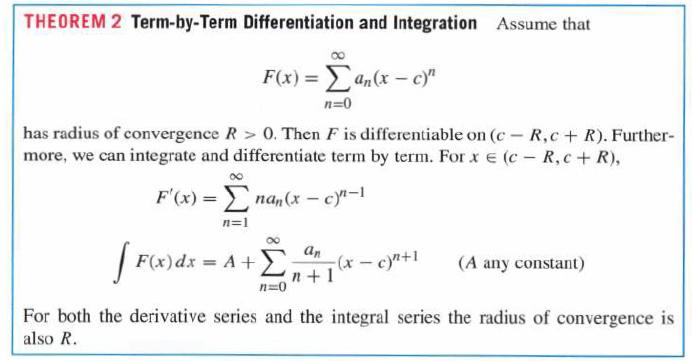
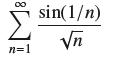
![bn = n] n In 1+ n](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/4/5/4/56665796526537b91702454566050.jpg)
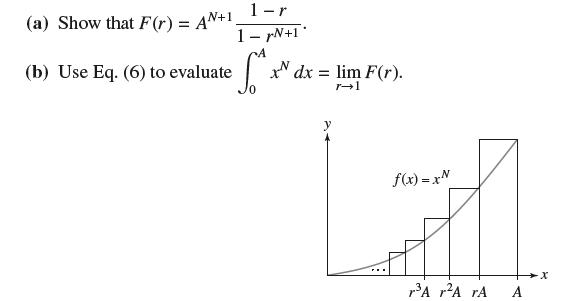
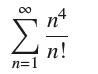
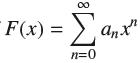
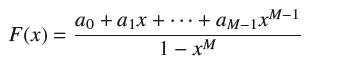
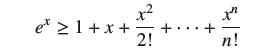
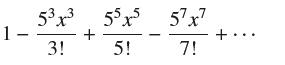
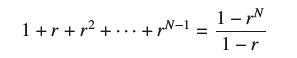
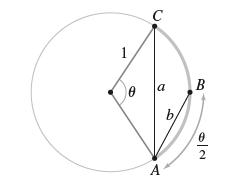
![1 1 + x (b) Show, by integrating over [0, 1], that 4 = 1 = = 1= x + x. 1 Pr + 3 5 1 7 + ..+(-1)-12N-2 + +](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1702/5/5/5/753657af069519041702555754072.jpg)