Question: We consider the following problem in a symmetric n x n matrix variable X where is an empirical covariance matrix,X 1 denotes the sum of
We consider the following problem in a symmetric n x n matrix variable X
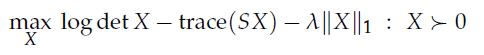
where![]() is an empirical covariance matrix,ΙΙXΙΙ1 denotes the sum of the absolute values of the elements of the positive definite matrix X, and λ > 0 encourages the sparsity in the solution X. The problem arises when fitting a multivariate Gaussian graphical model to data. The ℓ1-norm penalty encourages the random variables in the model to become conditionally independent.
is an empirical covariance matrix,ΙΙXΙΙ1 denotes the sum of the absolute values of the elements of the positive definite matrix X, and λ > 0 encourages the sparsity in the solution X. The problem arises when fitting a multivariate Gaussian graphical model to data. The ℓ1-norm penalty encourages the random variables in the model to become conditionally independent.
1. Show that the dual of the problem takes the form
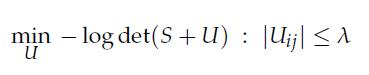
2. We employ a block-coordinate descent method to solve the dual.
Show that if we optimize over one column and row of U at a time, we obtain a subproblem of the form
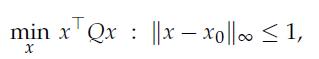
3. Show how you can solve the constrained QP problem above using following methods. Make sure to state precisely the algorithm’s steps.
• Coordinate descent.
• Dual coordinate ascent.
• Projected subgradient.
• Projected subgradient method for the dual.
• Interior-point method (any flavor will do).
Compare the performance (e.g., theoretical complexity, running time/convergence time on synthetic data) of these methods.
4. Solve the problem (using block-coordinate descent with 5 updates of each row/column, each step requiring the solution of the QP above) for a data file of your choice. Experiment with different values of l, report on the graphical model obtained.
max log det X - trace (SX) - A||X||1: X>0 X
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The dual of the problem is given by the following optimization problem max 0 t... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


