![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


![(a) K3[Fe(CN)6] (b) [Co(NH3), Br] Br (c) [Cr(NH3)2(en)Cl]C1 (en = ethylenediamine) (d) Ni(CO)4](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/7/7/4/889659ccce9f176b1704774889681.jpg)
![(a) [Ti(HO)6]+ or [Ti(CN)6]- (b) [Cr(NH3)6]+ or [Mo(NH3)6]+](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/7/7/5/090659ccdb258de61704775090136.jpg)
![(a) [FeF]- (b) [Cr(CN),]+ (c) [Mn(HO).]+ (d) [RhC16]-](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/7/7/5/128659ccdd82061a1704775128363.jpg)
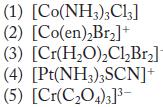
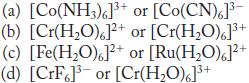
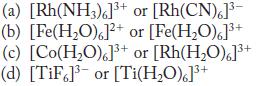

![(a) [CrC16]- (b) [Co(CN), (HO)]- (c) [Mn(HO)]+ (d) [Rh(HO)]+ (e) [V(HO)]+](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/7/8/0/266659ce1ea63b481704780266479.jpg)
![(a) [Cr(HO)]+ (b) [Fe(HO)]2+ (c) [Co(HO),]+ and [Mn(CN)6]- and [Ru(HO)]+ and [Co(CN); (HO)]-](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/7/8/2/157659ce94db8f821704782158392.jpg)