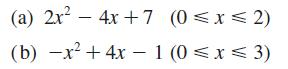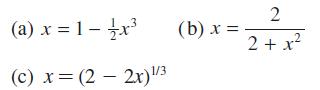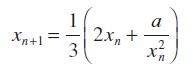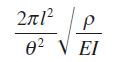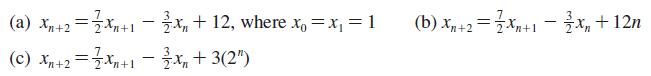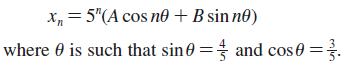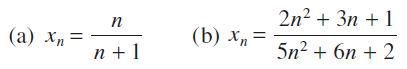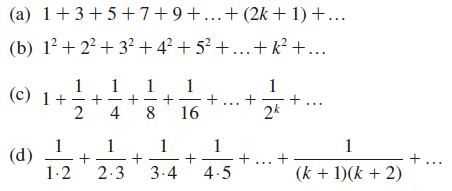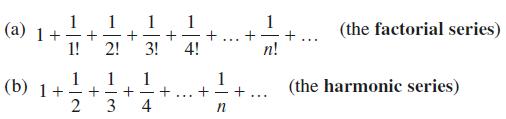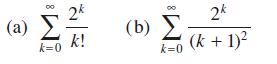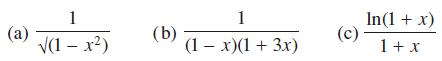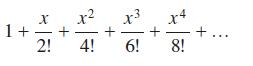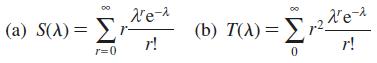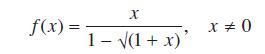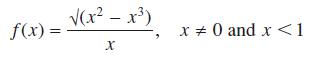![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


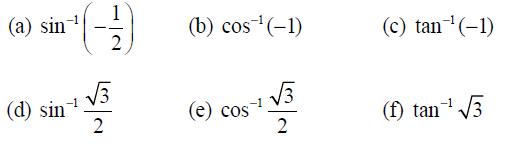
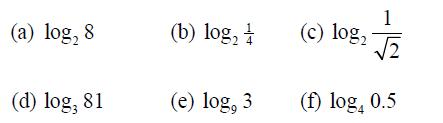
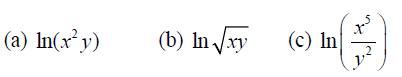
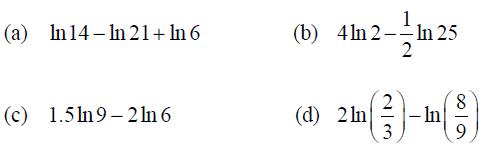
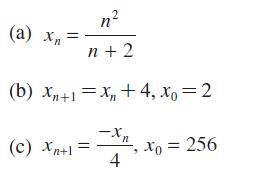
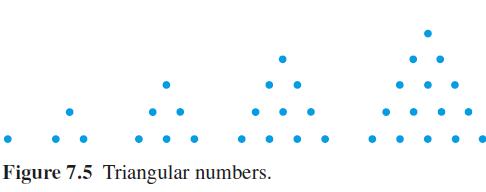
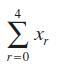
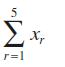

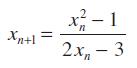
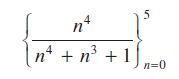
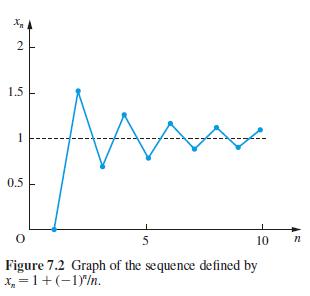
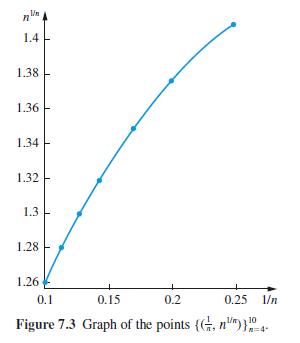
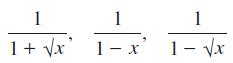
![2 ()--[-] = 1- n 2 n (n style=](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/8/8/5/332659e7c547517e1704885331678.jpg)
![n + 1)4 k41 (k k=]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/8/8/6/084659e7f44398e61704886083938.jpg)
![n k = [ n(n+1)] k=1](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/8/8/6/097659e7f51b34871704886097412.jpg)
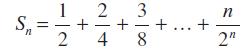
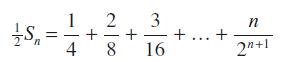
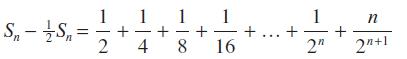
![Sn = a + (a + d)r + (a + 2d)r + ... + [a + (n 1)d]r"-1](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/8/8/6/218659e7fca8d7121704886217996.jpg)
![(1r)S,= a + dr+dr + ... + dr"-1 [a + (n 1)d]r" -](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/8/8/6/232659e7fd8e70bd1704886232228.jpg)
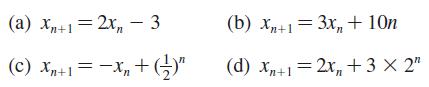
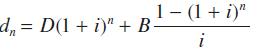
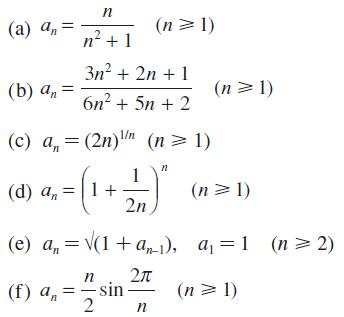
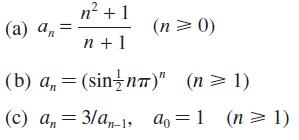
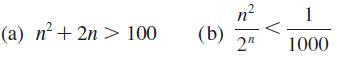
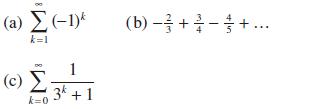
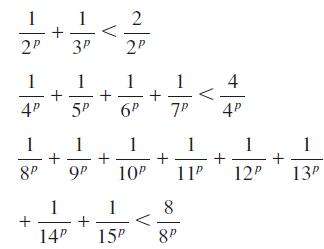
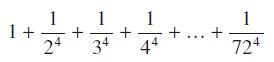
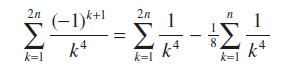
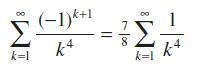
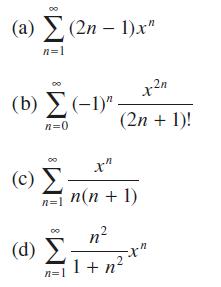
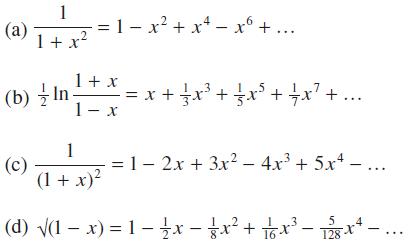
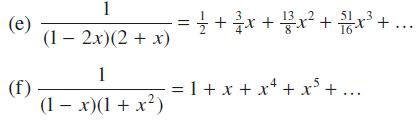
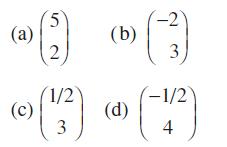
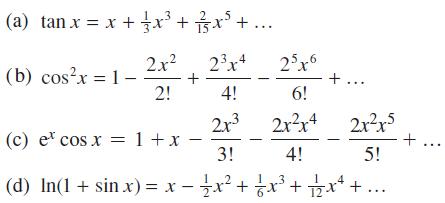
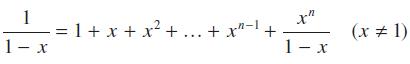
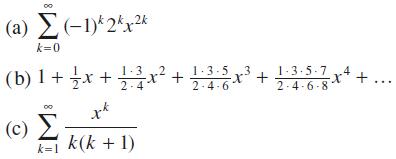
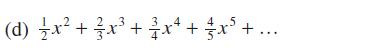
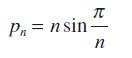
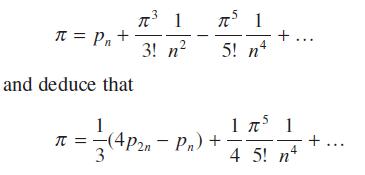
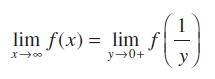
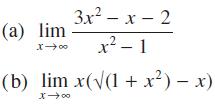
![|x| (a) X (c) tanh 1 X (b) x-1 2 - x (d) [1 - x]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/8/9/2/147659e96f33636f1704892146806.jpg)