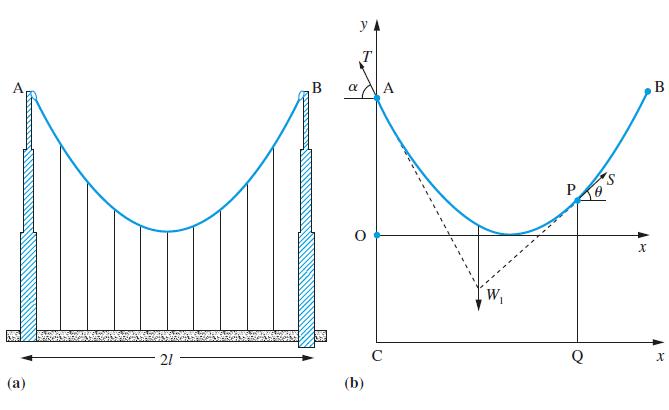
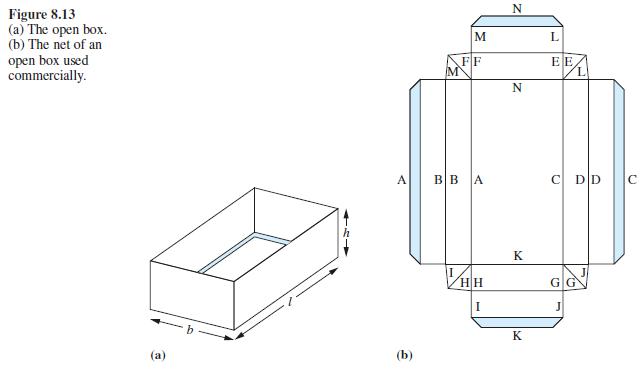
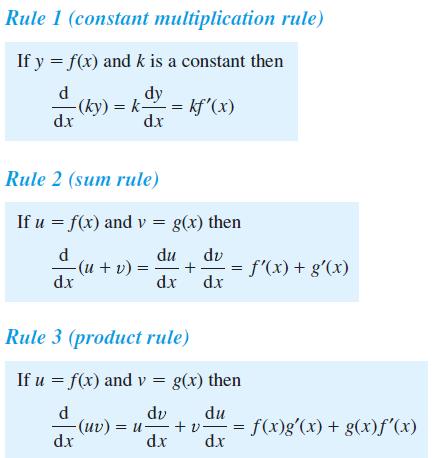
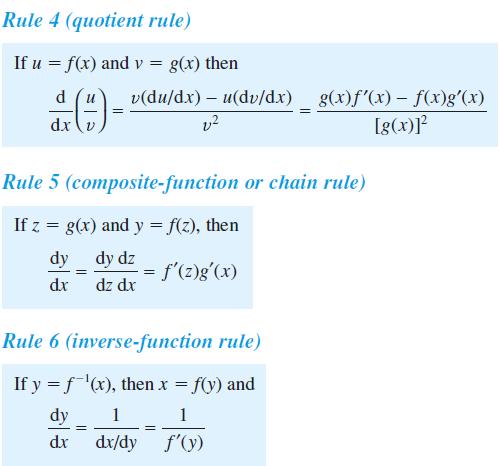
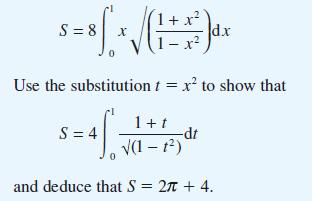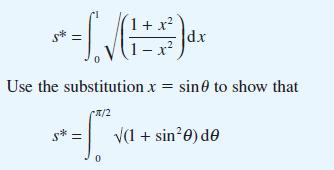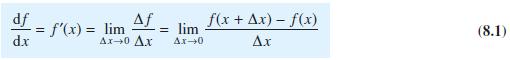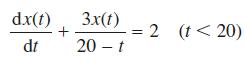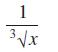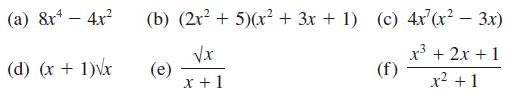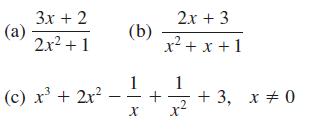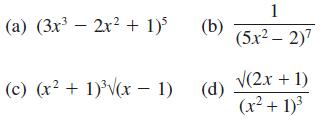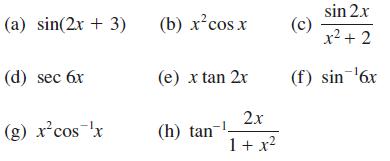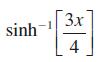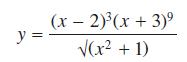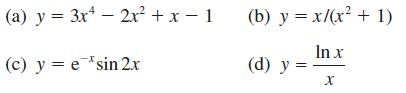![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


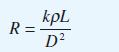
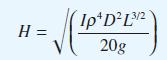
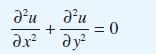
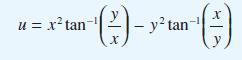
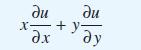
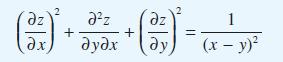
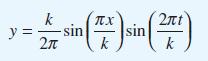
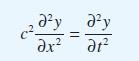
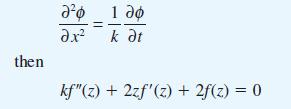
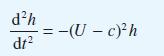

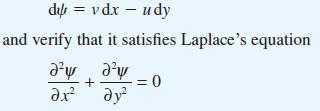
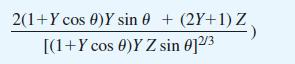
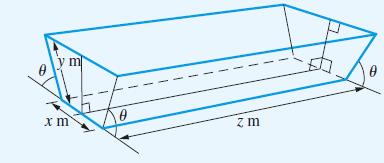
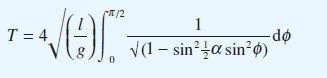
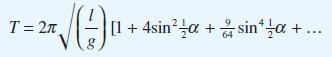
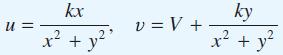
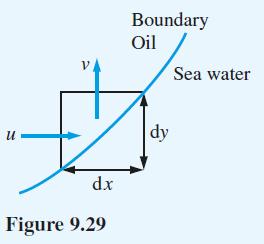
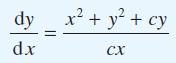
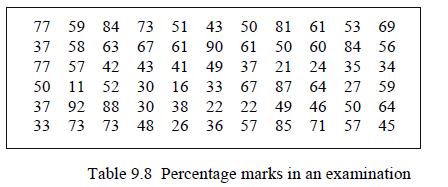
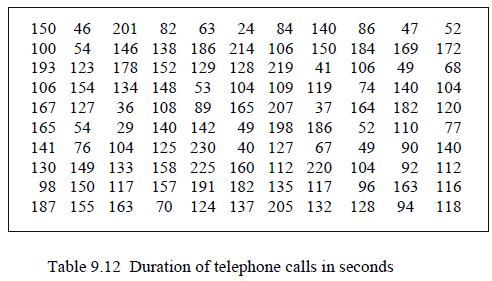
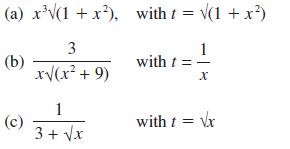
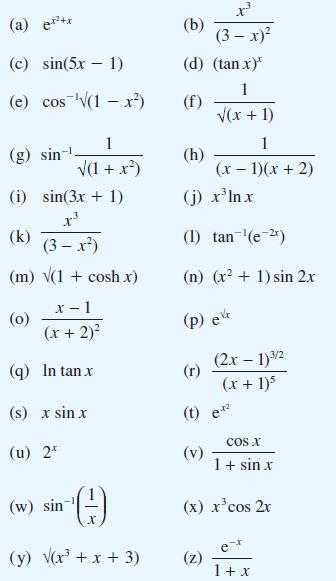
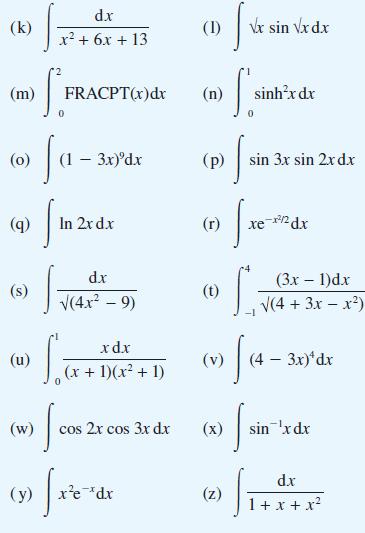
![(a) (c) (e) (i) [xmxdx 1/2 In.x dx -[x]dx xdx (x - 1)(x - 2) (4 - 3x)dx 0 J x dx (x - 1) (b) (d) (h) S (j)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/0/6/2/39565a12ffbcd2641705062396433.jpg)
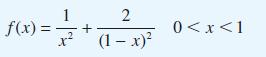
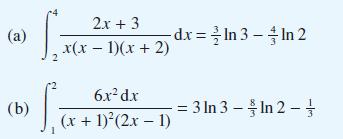
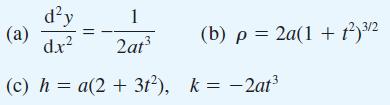
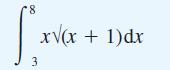
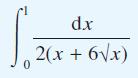
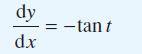
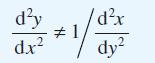
![[f(0)] de](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/3/1/61665a23e60c75dc1705131619351.jpg)
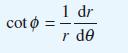
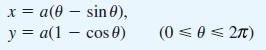
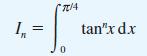
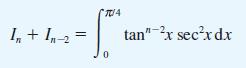
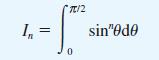
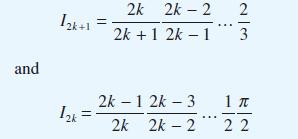
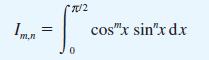
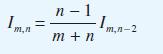
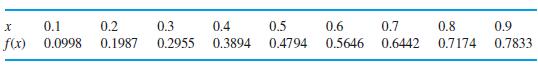
!["I ] = Prove that x"edx I = 1 - nl (n> 0) 0 with I, 1 e . -](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/3/2/87165a243475b4ca1705132873822.jpg)
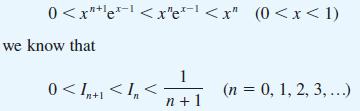
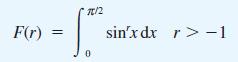

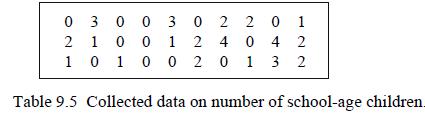
!['h -h f(x)dx= h[af(ah) + bf (Bh)]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/3/3/84265a2471266c811705133842231.jpg)
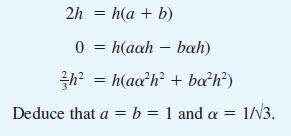
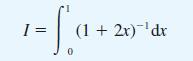
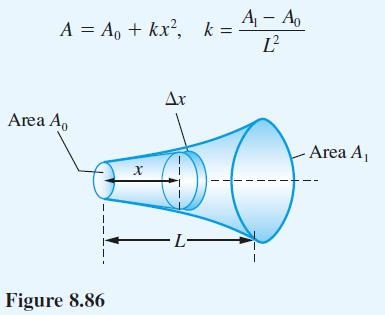
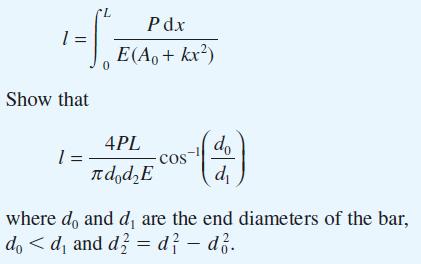
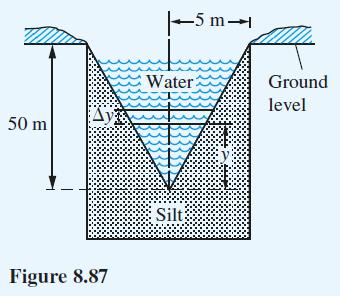
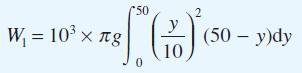
![xp{[ - x] - - - [x)} f(x): 0 ) = 0](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/3/5/20765a24c67bbec31705135207525.jpg)
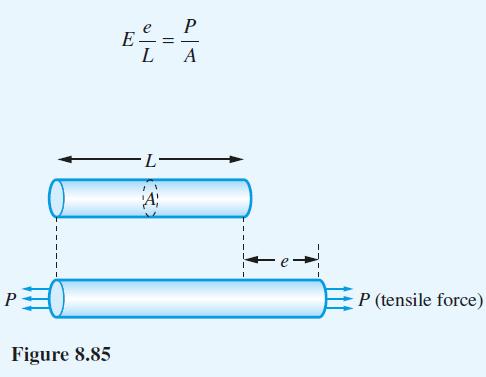
![E(a) = Show that T 0 [h(x) - f(x)]dx E(a) = 71 [a + 8a](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/3/5/72365a24e6bd9fe51705135723598.jpg)
![F G B D E [T]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/1/3/5/93965a24f43d64211705135939195.jpg)