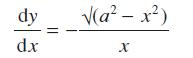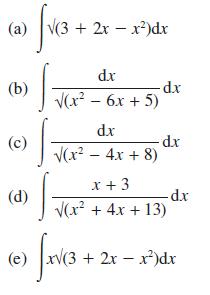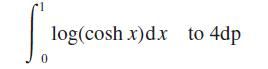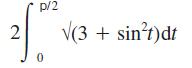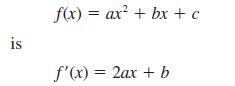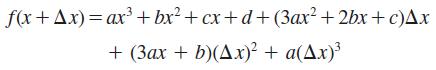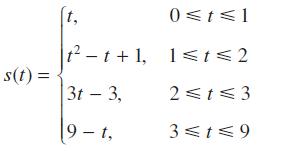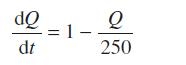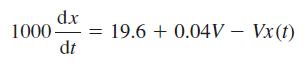![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


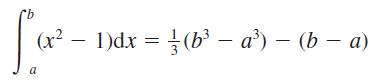
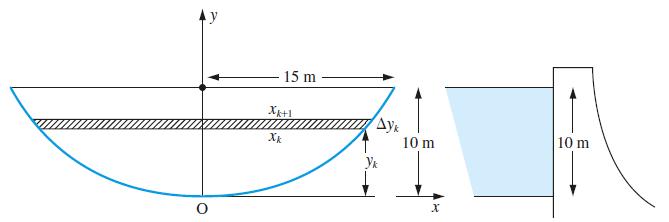
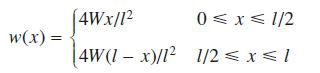
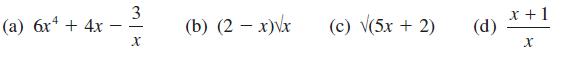
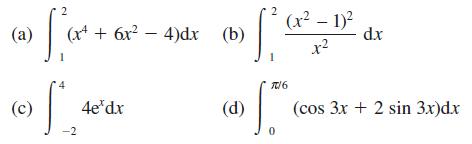
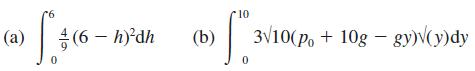
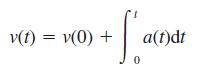
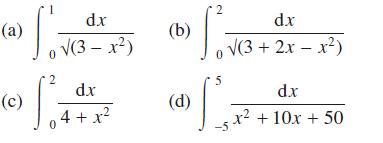
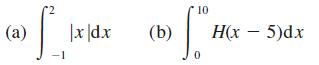

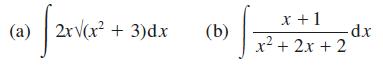
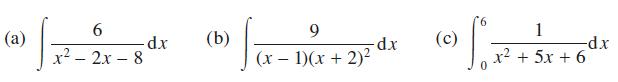
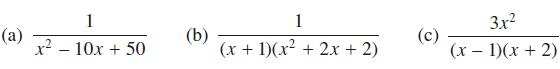
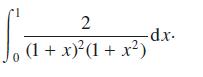
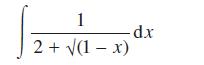
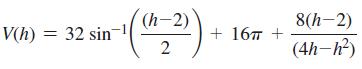
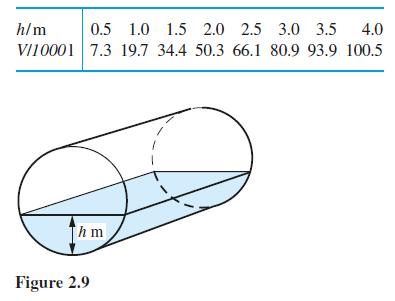
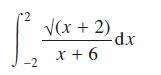
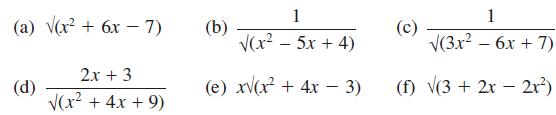
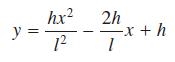
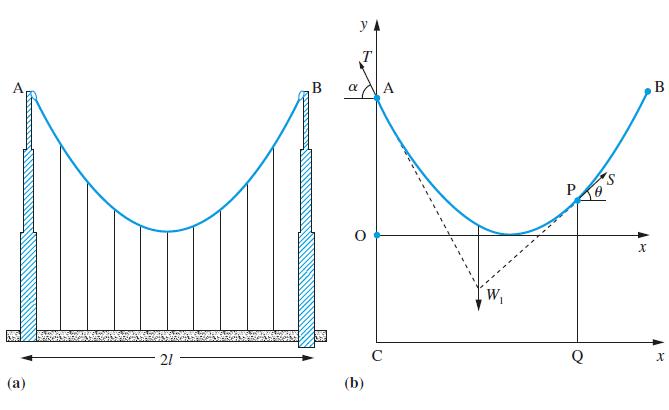
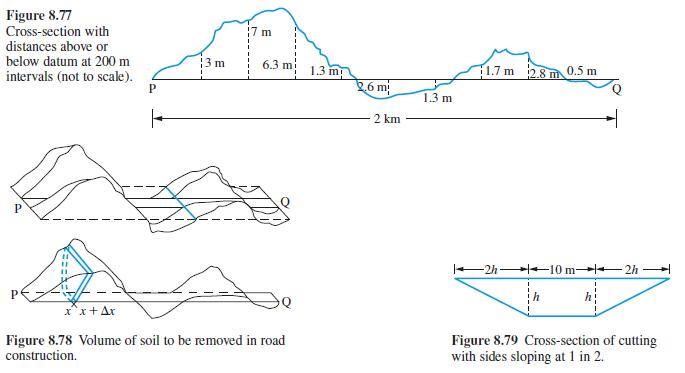
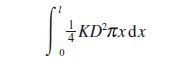
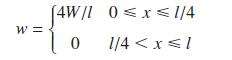
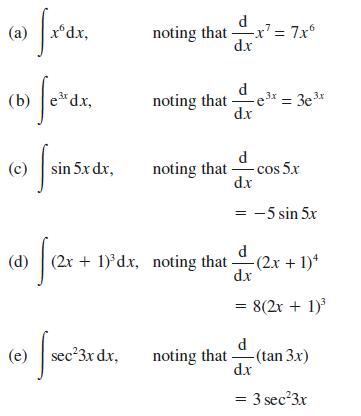
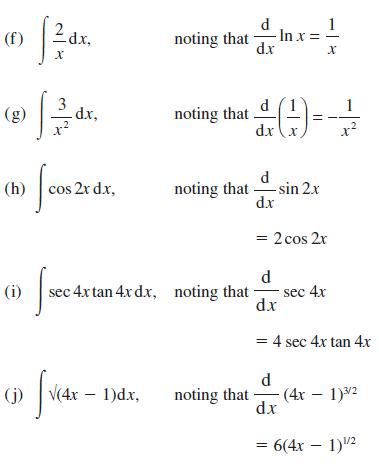
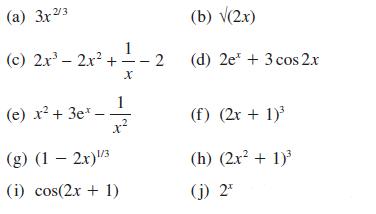
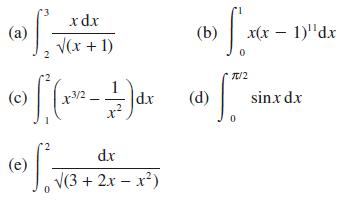
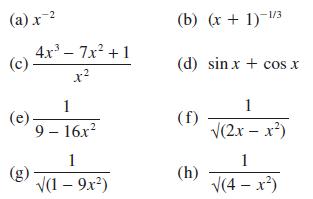
![(i) (k) 1 (1- x - x) 1 (5 + 4x x) - (1) 1 [x(1-x)] 1 x + 6x + 13](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/0/3/9/87665a0d8045367a1705039877073.jpg)
![(a) (c) (e) 3 [lx 3 S. 3 |x2|dx [x]dx x[x]dx 0 (b) fax. 0 (d) (x - 2)H(x - 2)d.x 3 S. 0 FRACPT(x)d.x](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/0/3/9/90165a0d81d6b1c11705039902198.jpg)
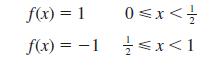
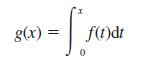
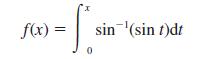
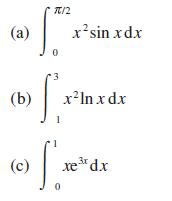
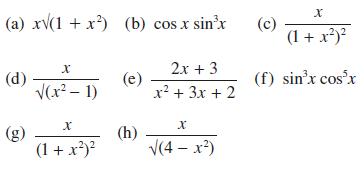
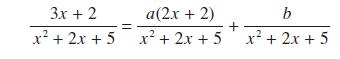
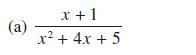
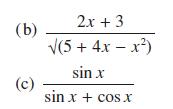
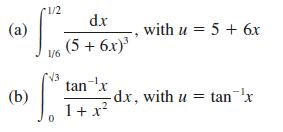
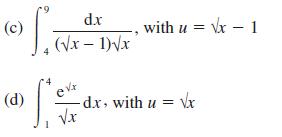
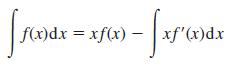
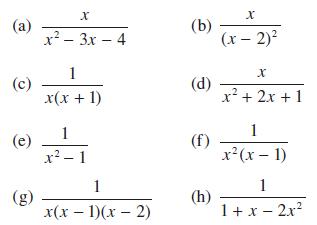
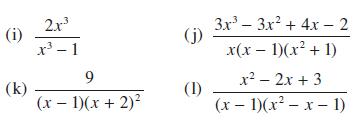
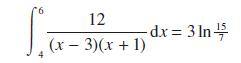
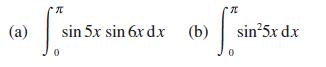
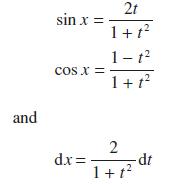
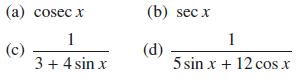
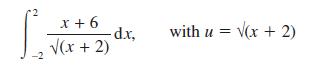
![a + (a-x) y = In [ - ( - x)] - (a - x) x](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/0/4/1/73365a0df45196831705041733908.jpg)