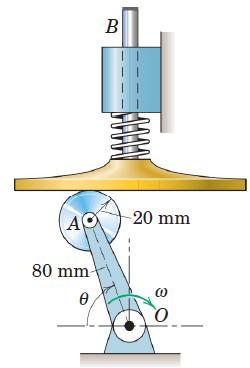
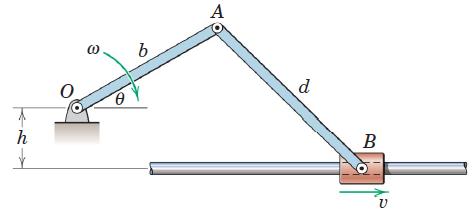
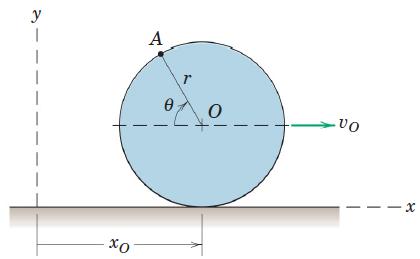
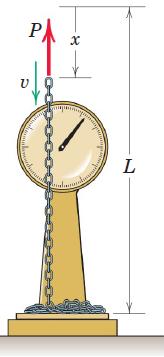
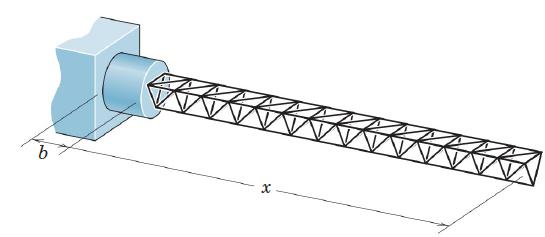
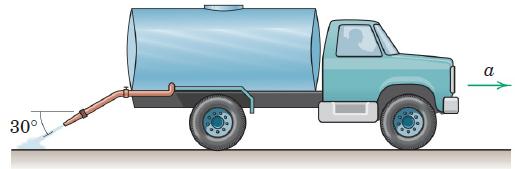
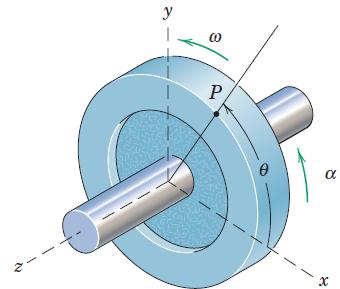
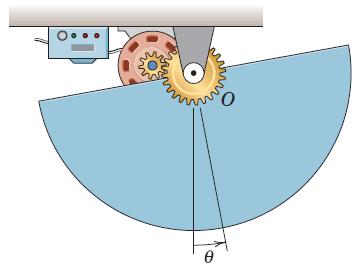
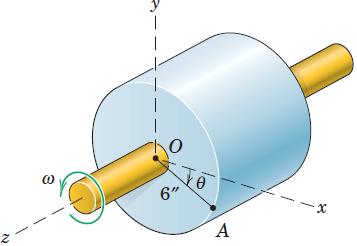
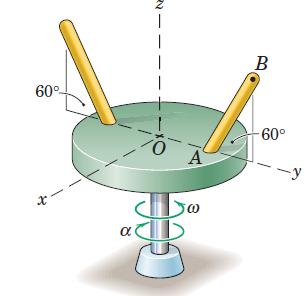
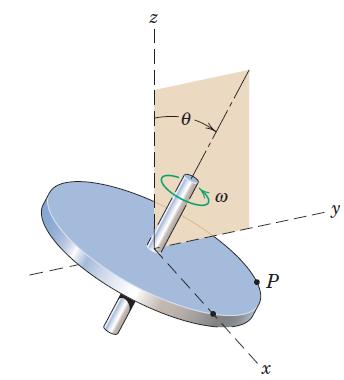
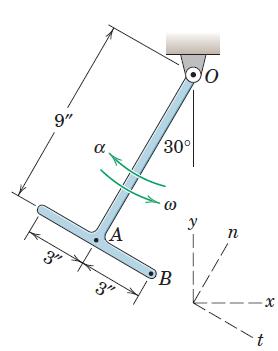
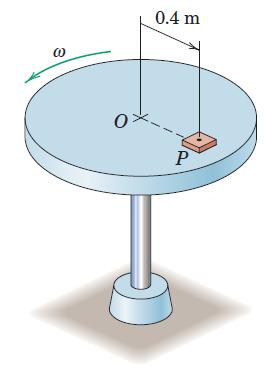
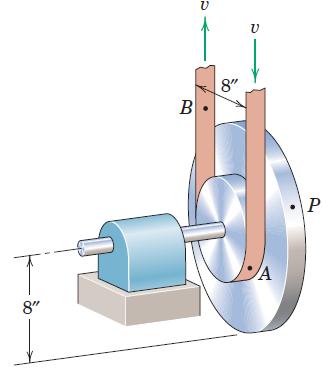
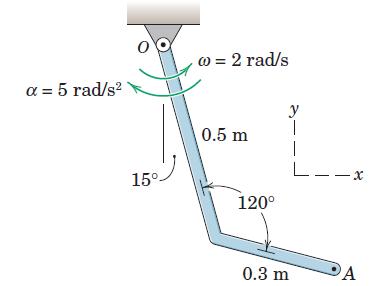
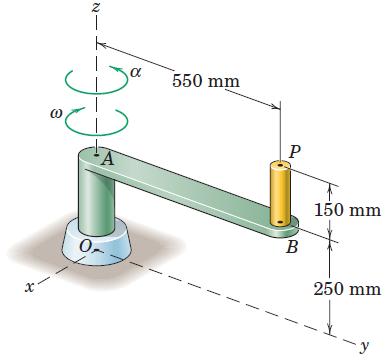
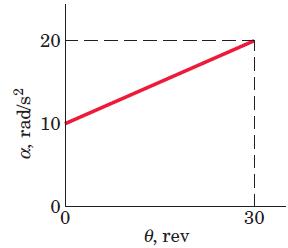
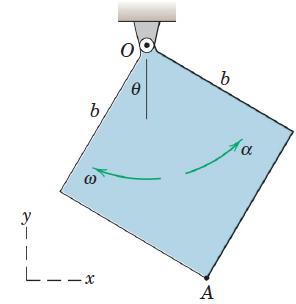
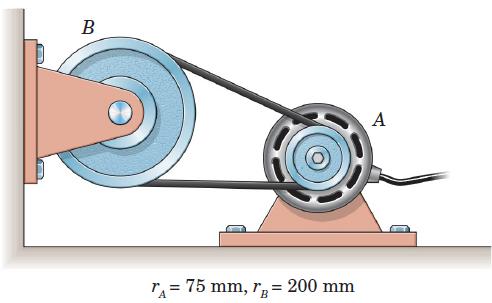
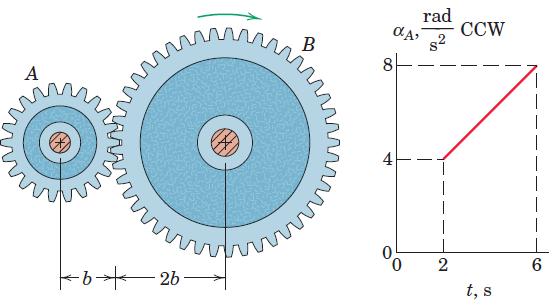
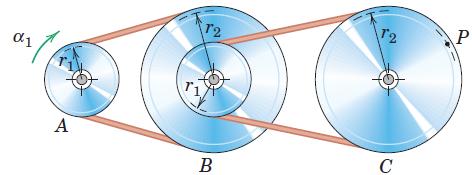
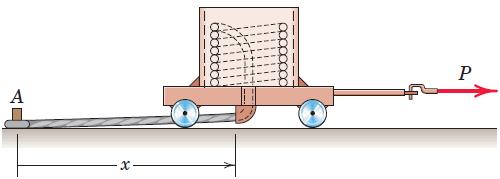
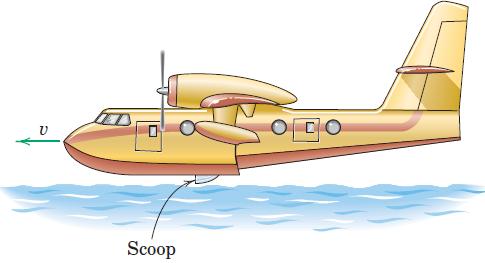
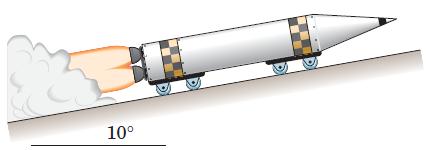
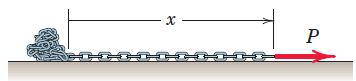
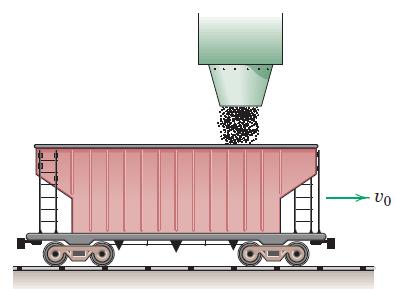
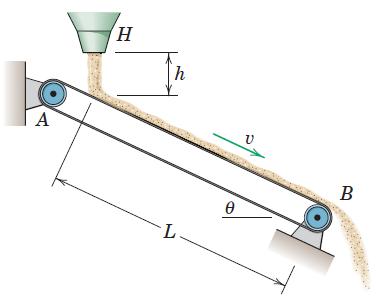
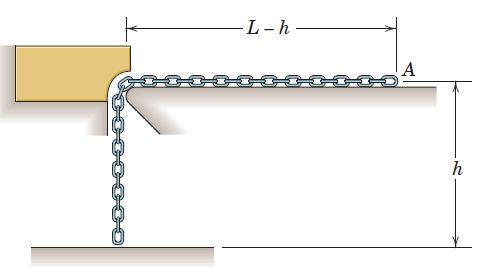
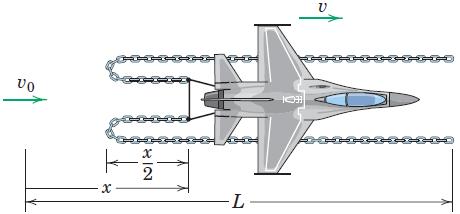
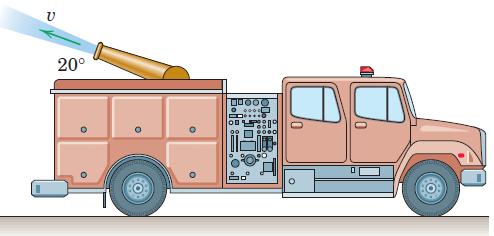
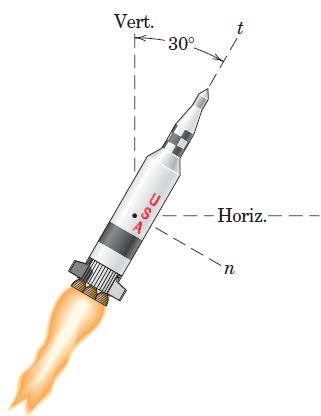
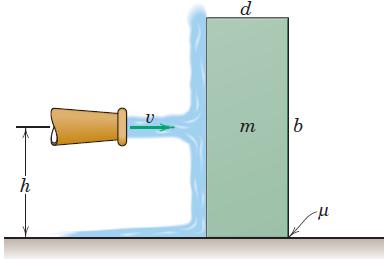
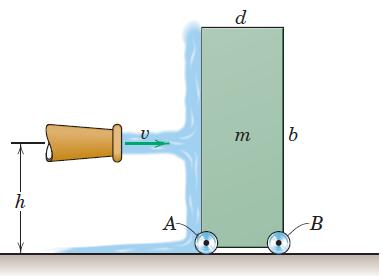
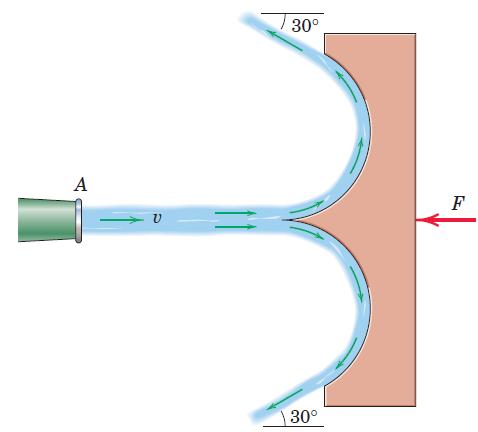
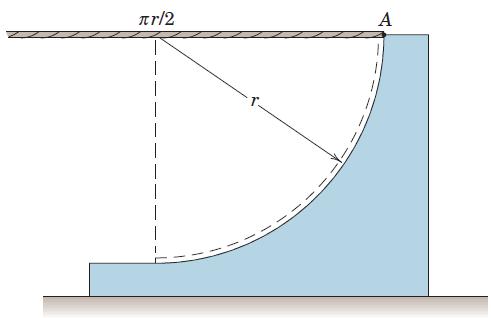
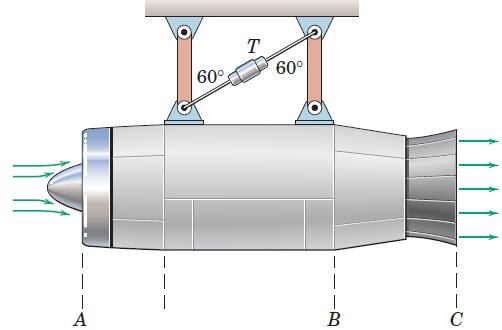
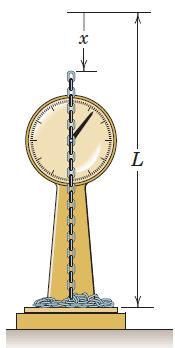
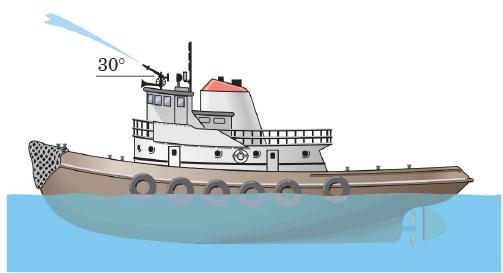
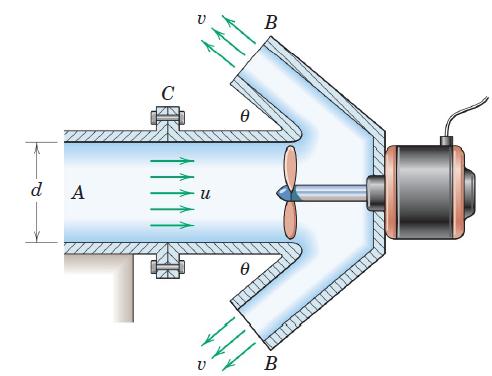
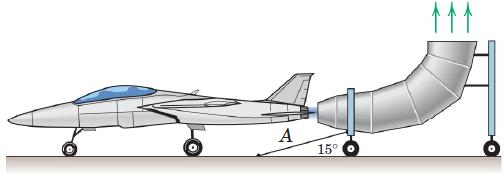
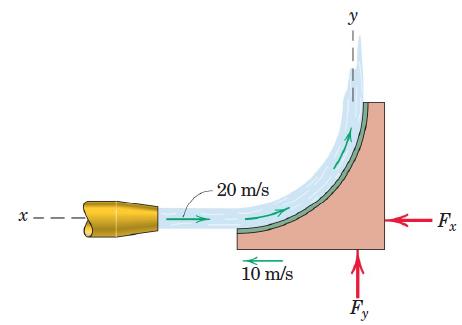
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()