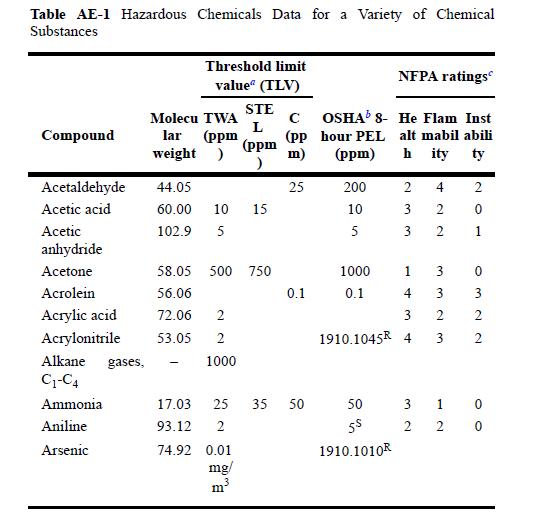
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


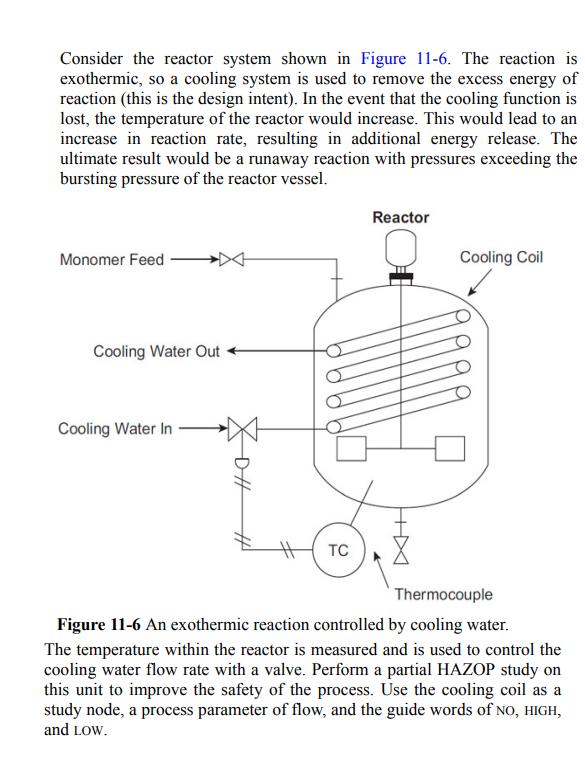
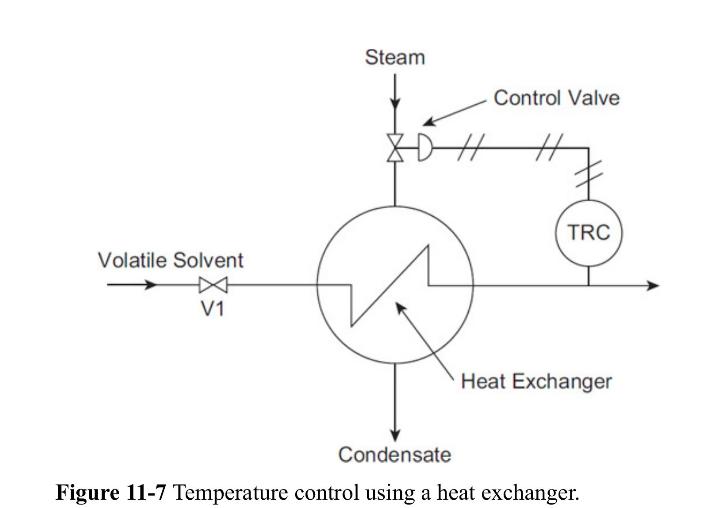
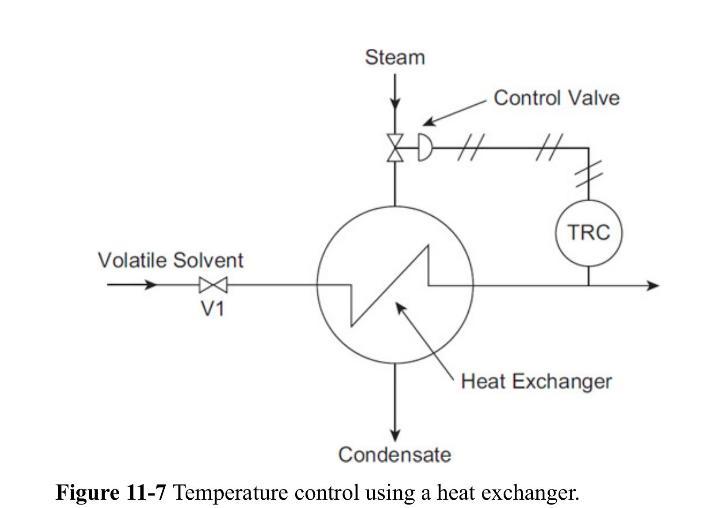
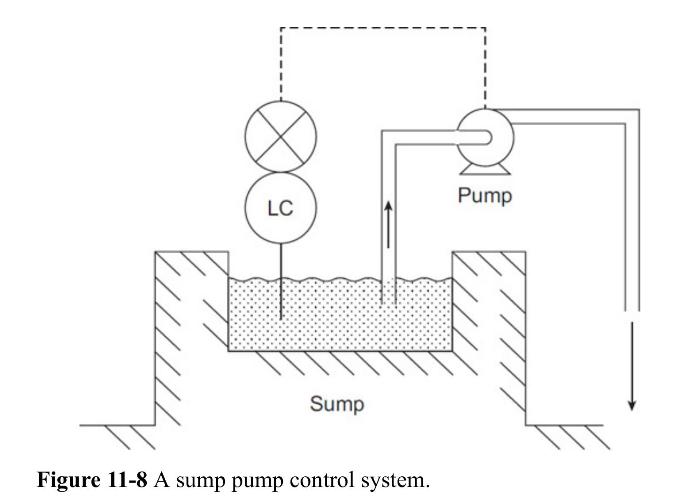
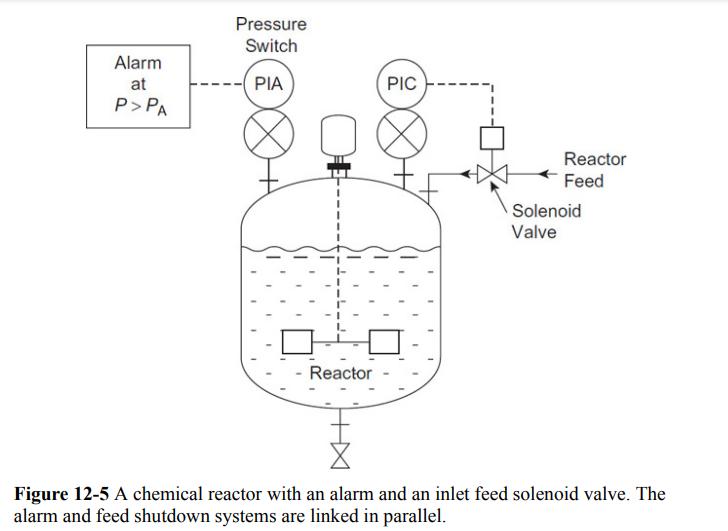
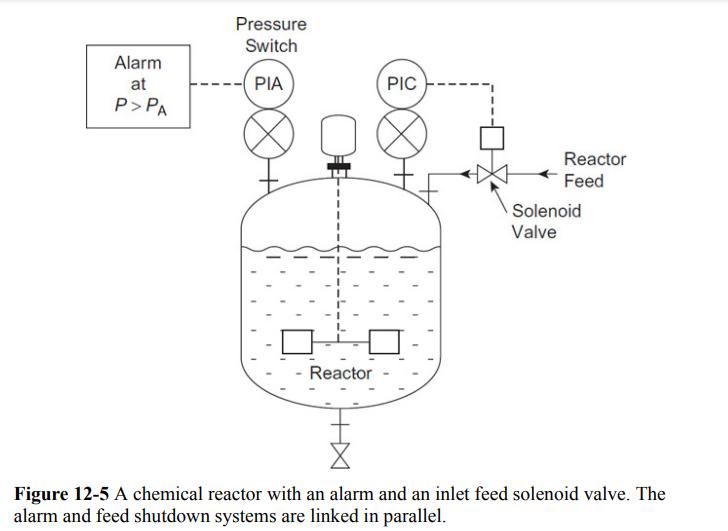
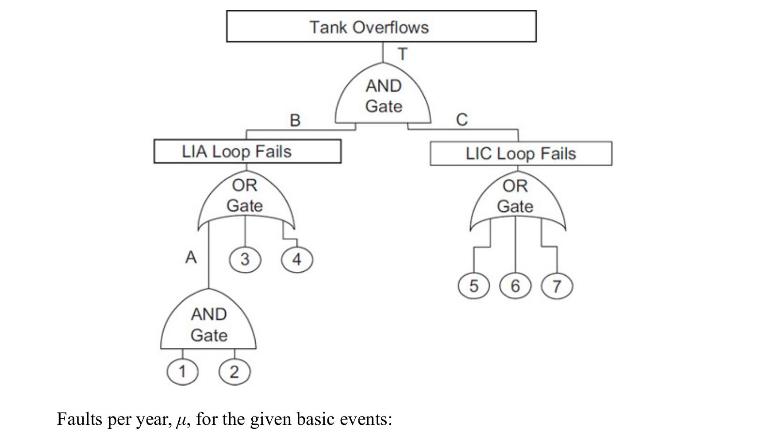

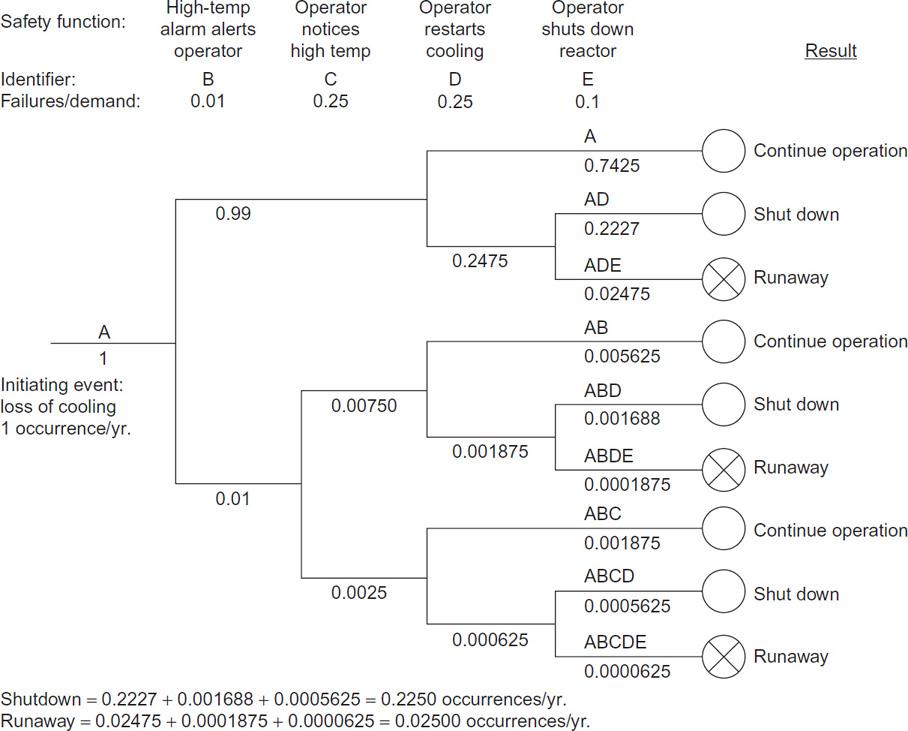
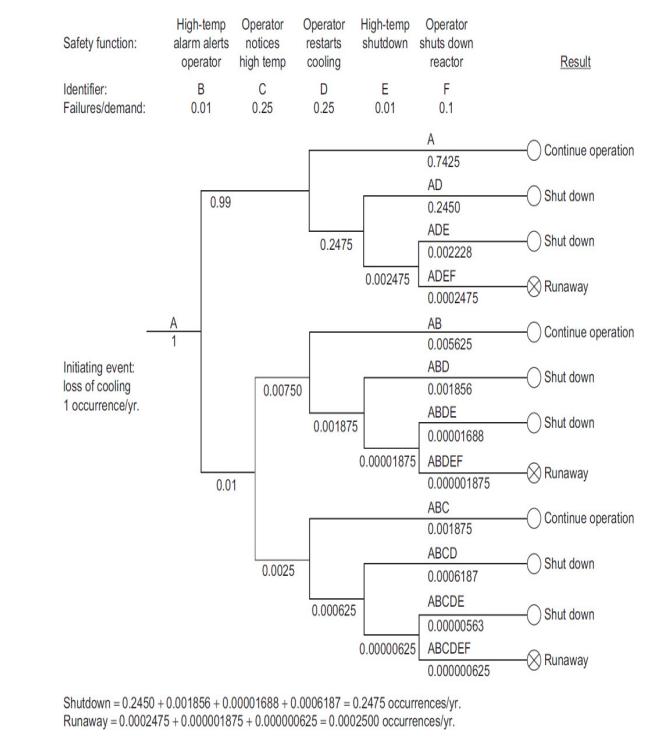
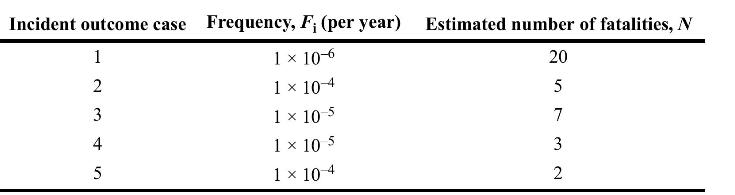

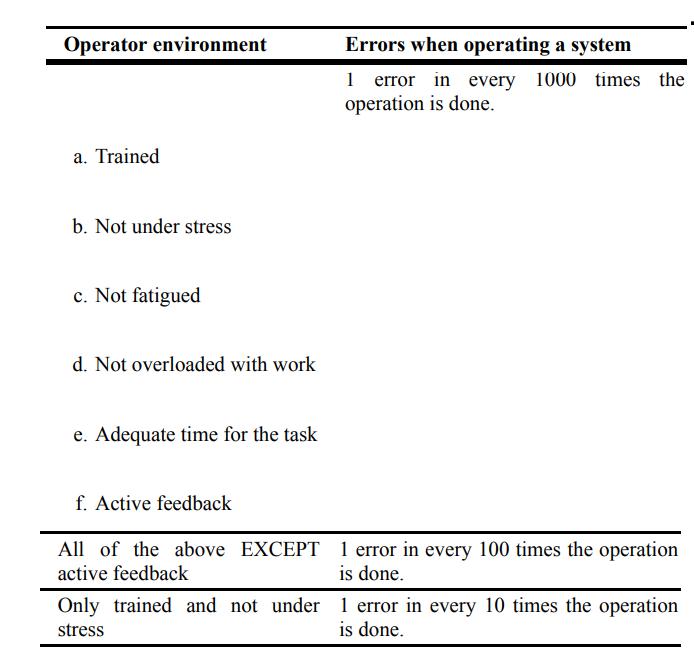


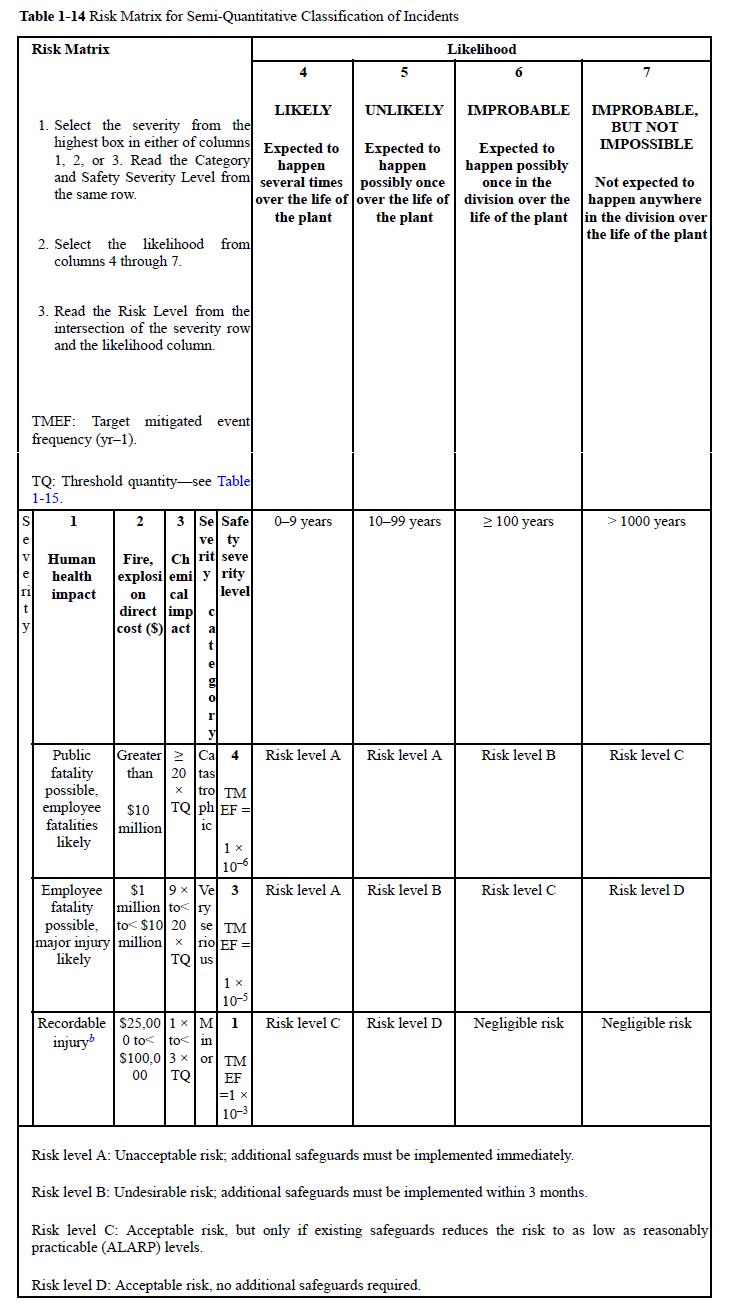

![P-50 [1 + 5*()] Y-5 Y - = 1+ Y-5/ erf 2 (2-6)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/9/3/2/40865ae7678c2e931705932406869.jpg)