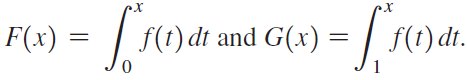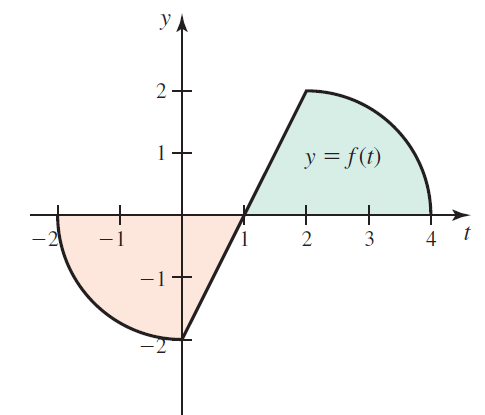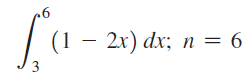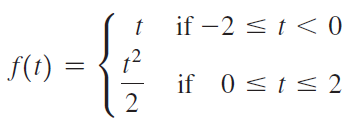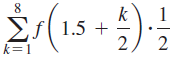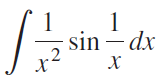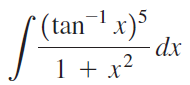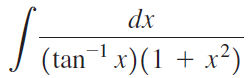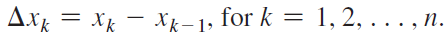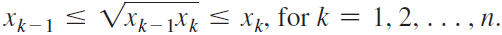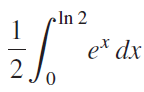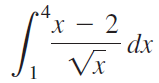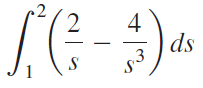![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


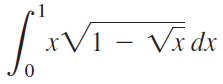
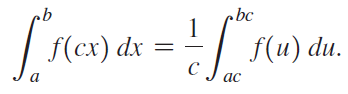
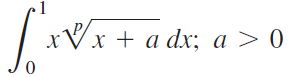
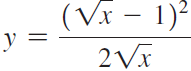
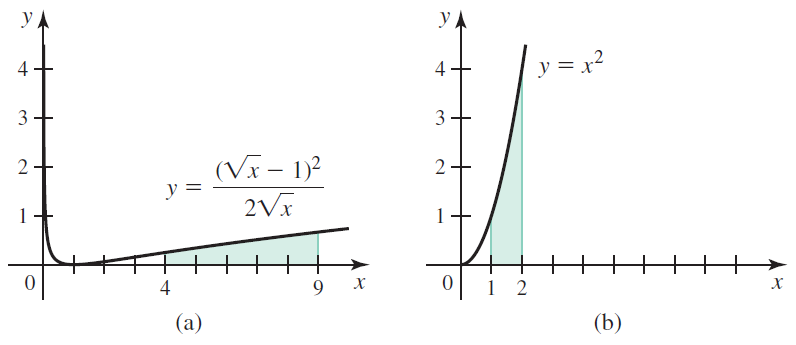
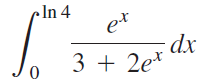
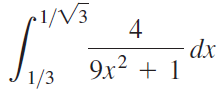
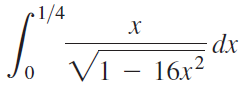
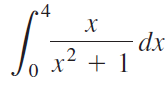
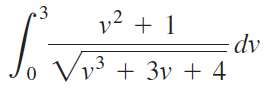
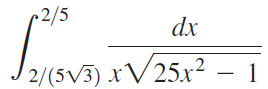
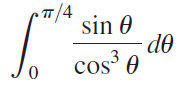
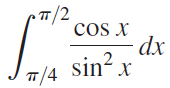
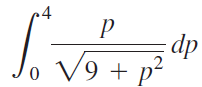
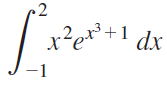
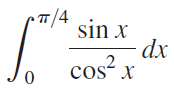
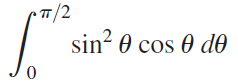
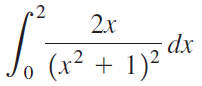
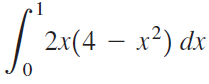
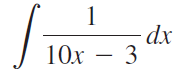
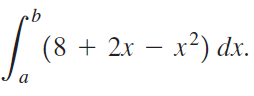
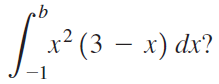
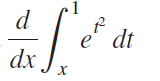
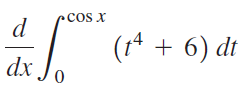
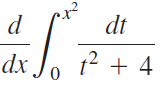
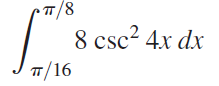
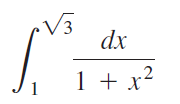
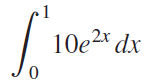
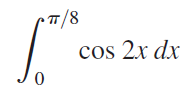
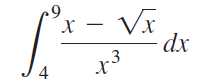
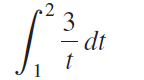
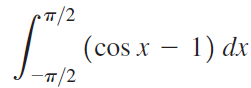
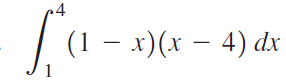
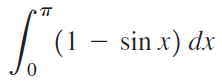
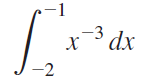
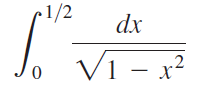
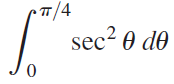
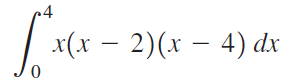
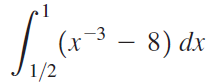
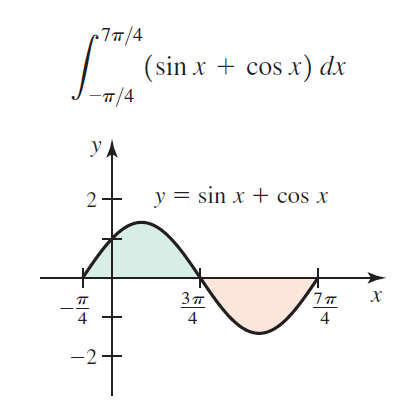
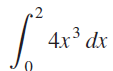
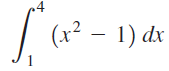
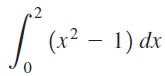
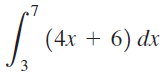
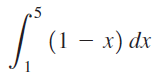
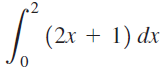
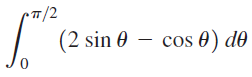
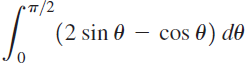
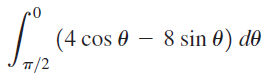
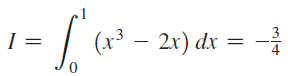
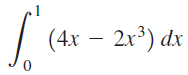
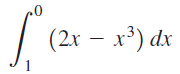
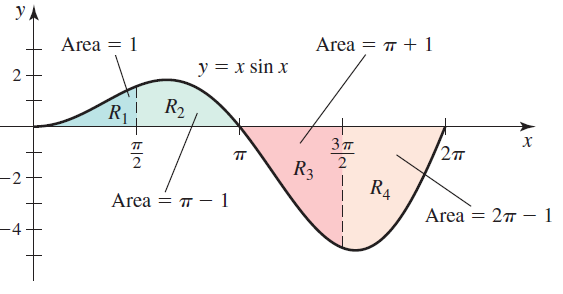
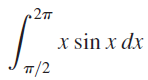
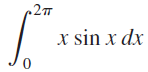
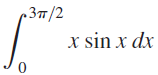
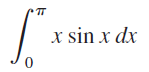
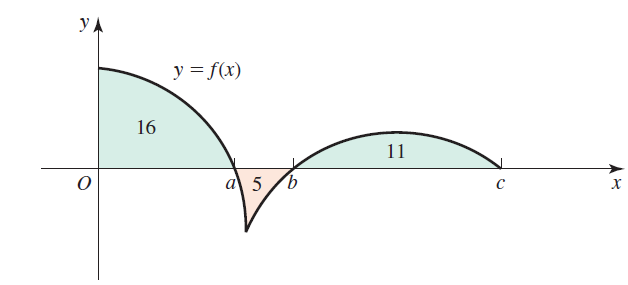
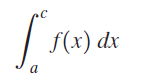
![п lim Ι x-1Δxχ on [-2, 2] Δ-0 Κ1 k=1](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1551/2/7/8/5815c76a1f573c891551261324193.jpg)
![lim Exi In xAxg on [1, 2] A→0 k=1](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1551/2/7/8/5655c76a1e5aed051551261308654.jpg)