![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


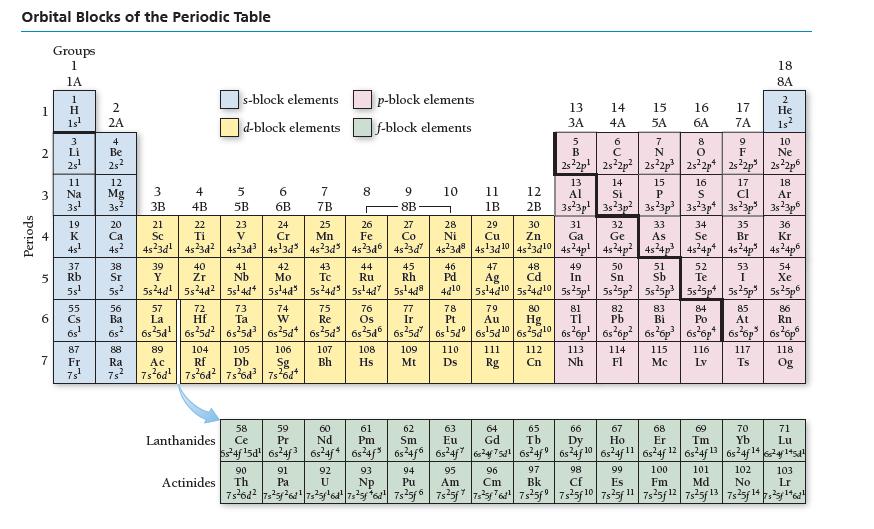
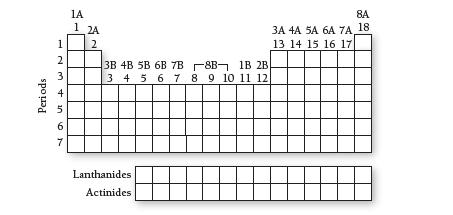
![a) [Ar] b) [Ar] c) [Ar] d) [Ar] 11 45 45 1 45 11 45 11 3d 1 1 1 1 1 3d 1 1 1 1 3d 111 3d](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/0/2/5/1996554536f36b791700025197161.jpg)
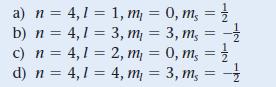
![a) [Ar]4s3d6 c) [Ar]4s03d6 b) [Ar]4s3d4 d) [Ar]4s3d8](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/0/2/5/262655453ae36ff81700025260123.jpg)