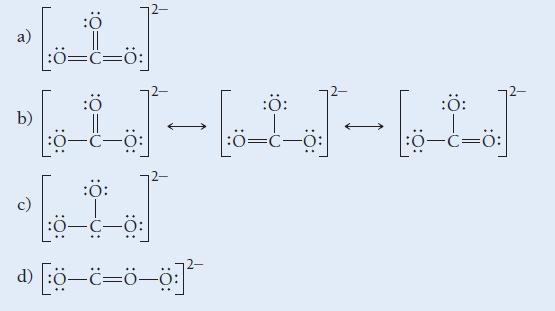
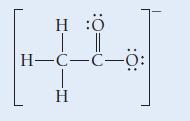
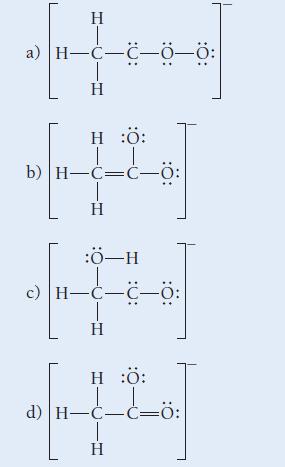
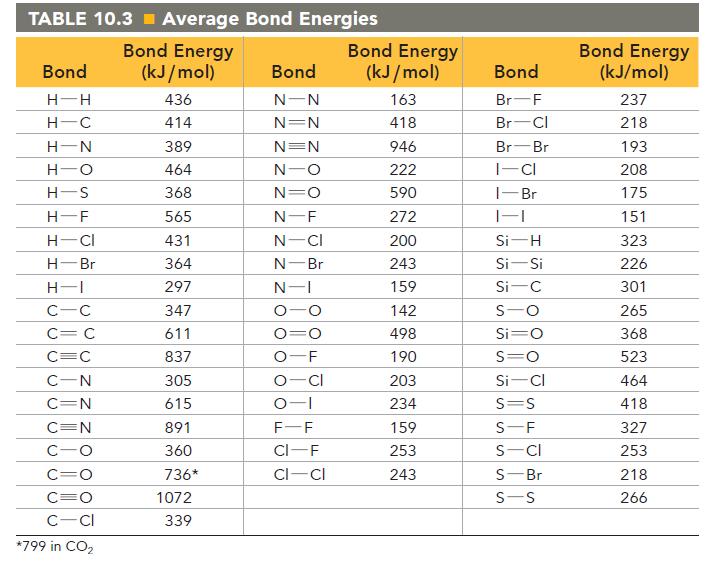
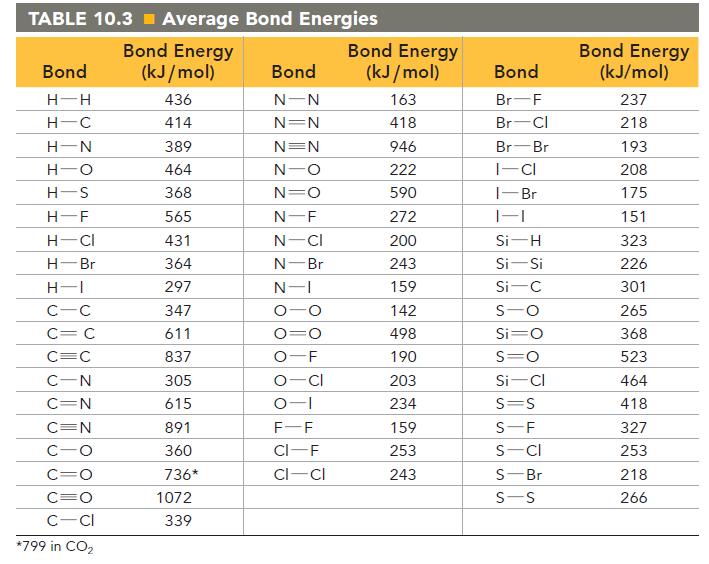
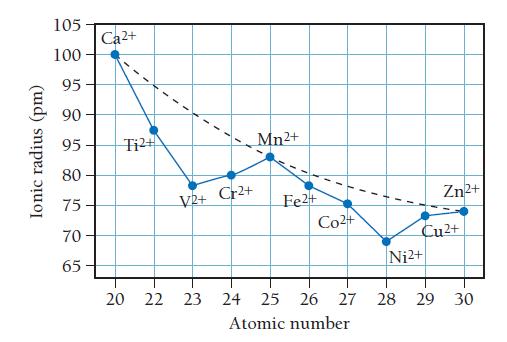
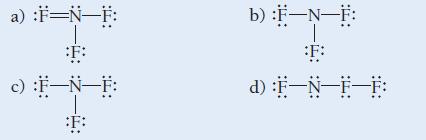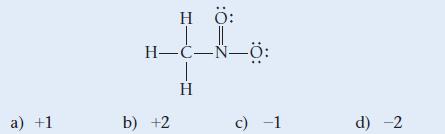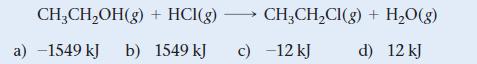![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


![(a) [:S=C=N:] [:$-C=N:] (b) [S-N=C:] ()[:S=C-N:]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/0/3/3/246655472dea25f21700033244876.jpg)