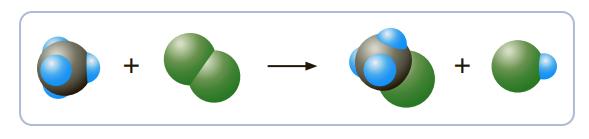
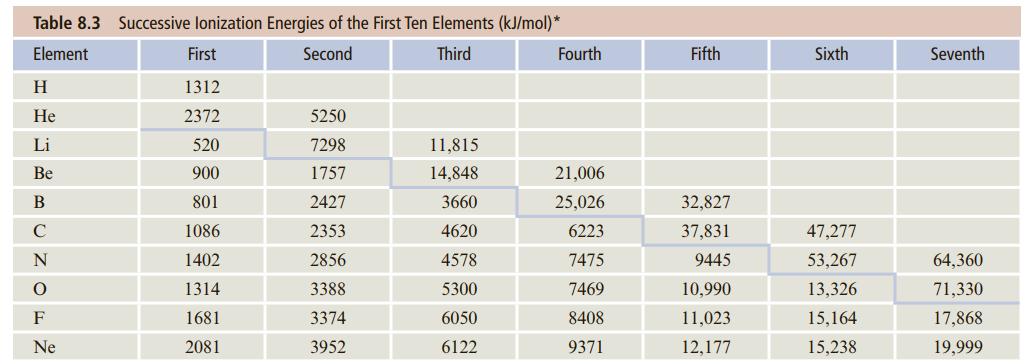
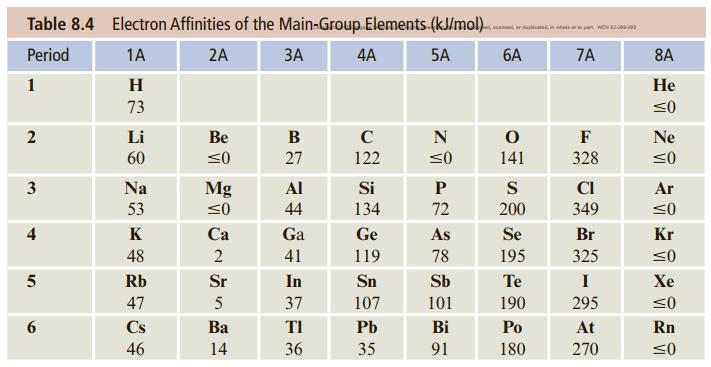
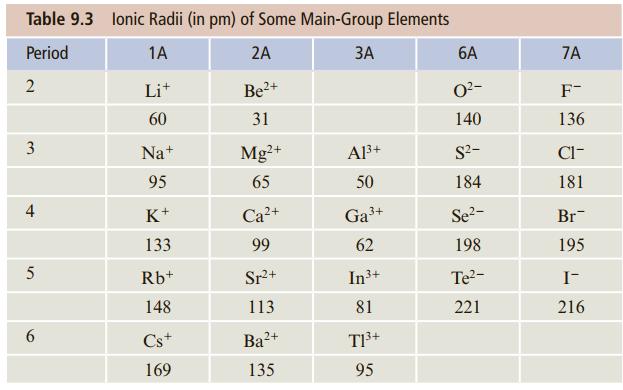
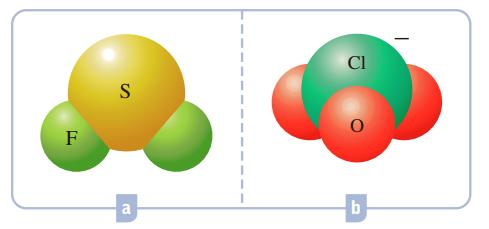
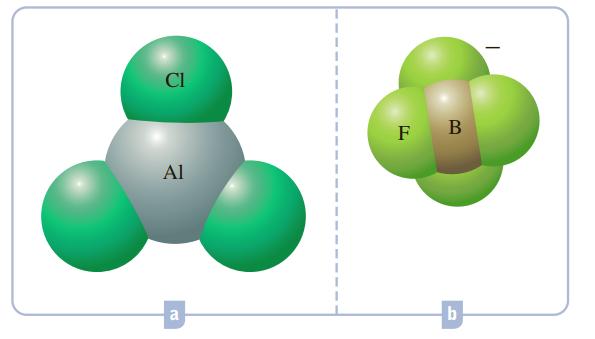
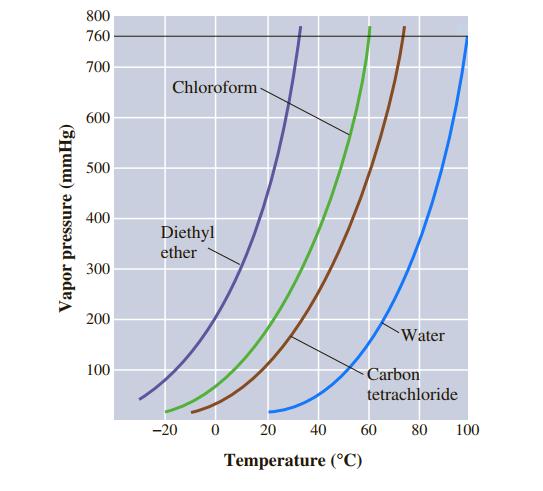
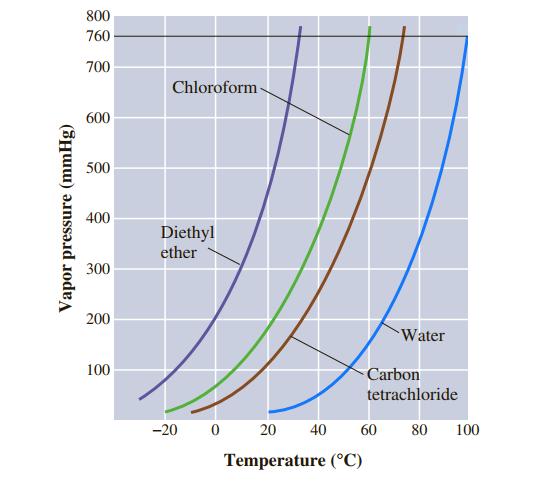
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


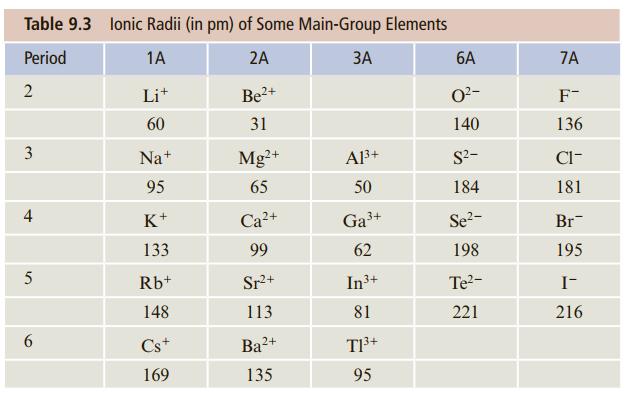
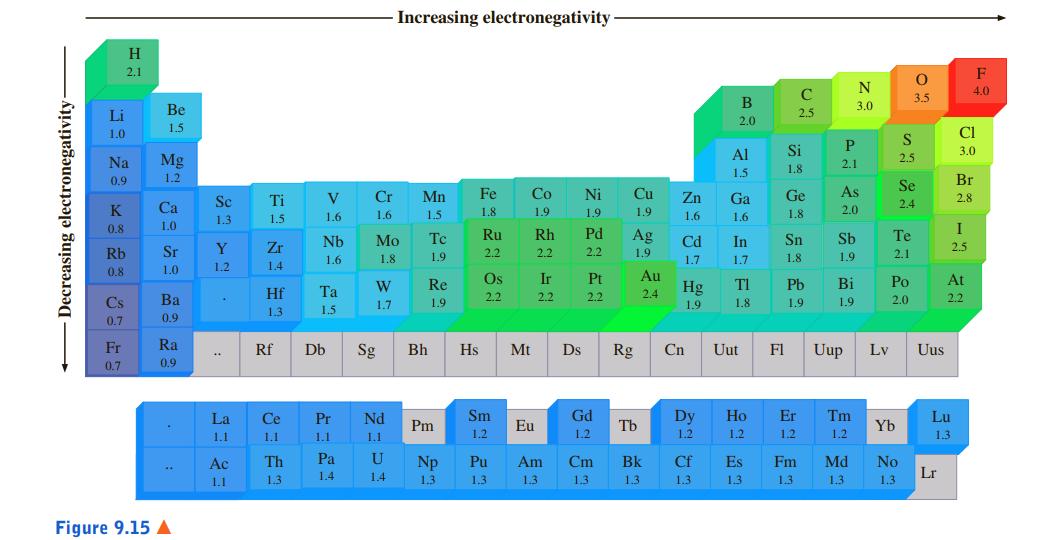
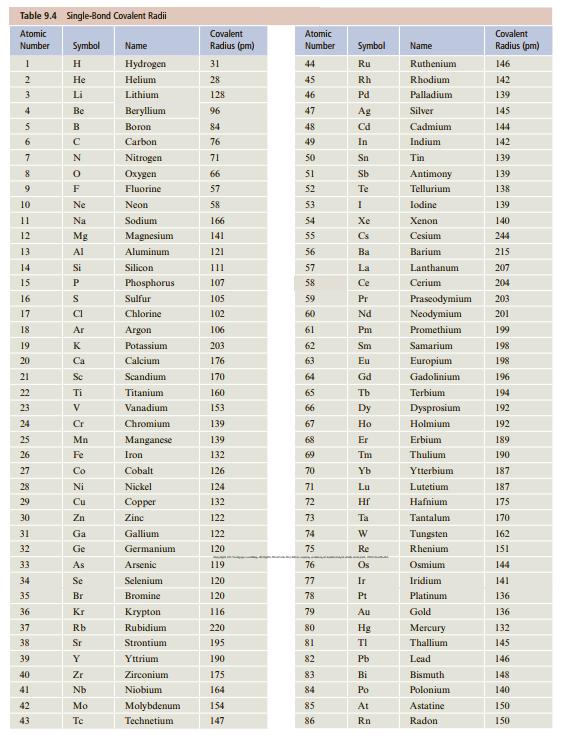
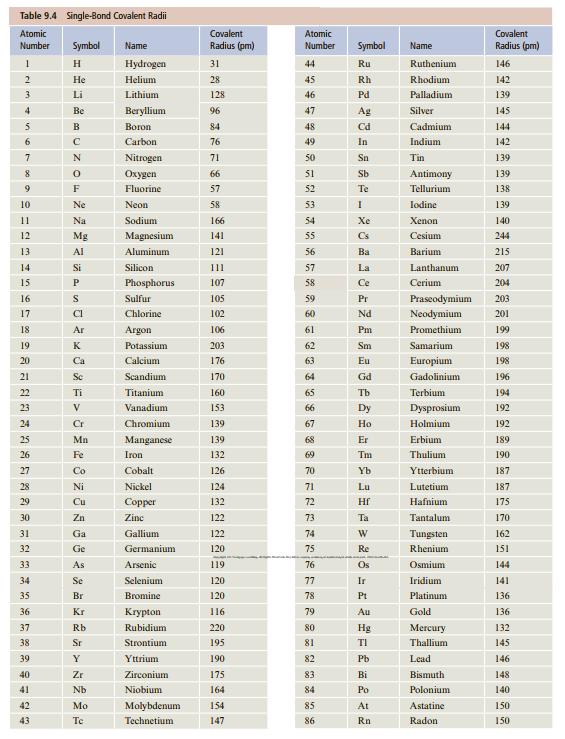
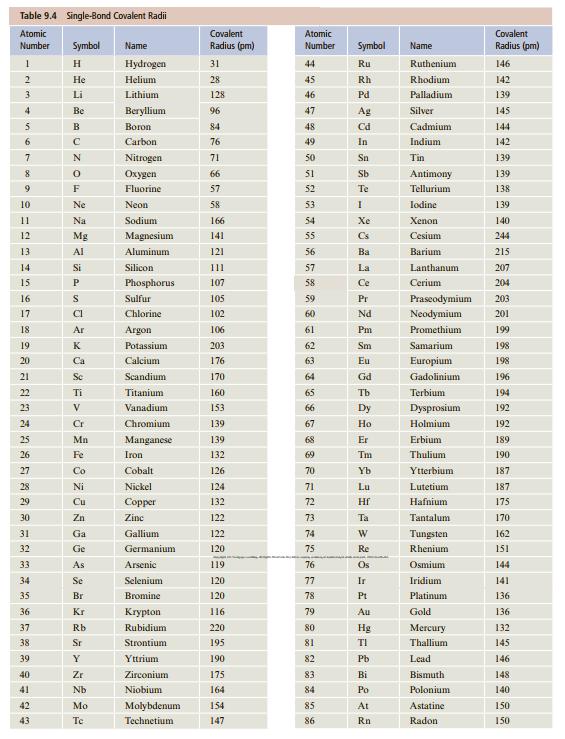
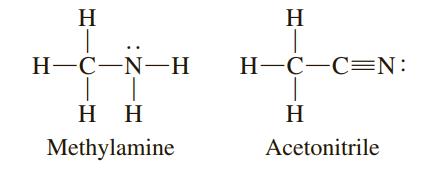
![[ Al·]** [:F:]- a [:0:1²- b C d Mg eSi.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1604/3/7/8/4385fa0df46609011604378436814.jpg)