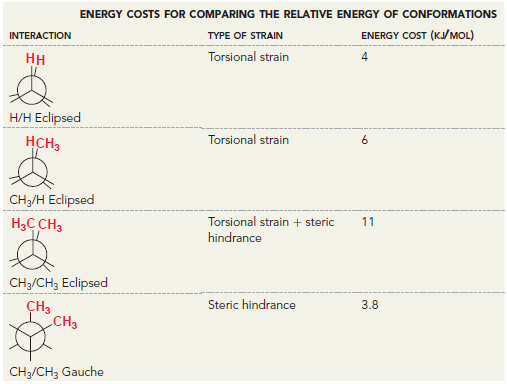
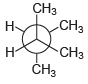
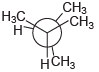
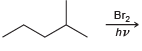
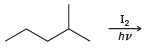
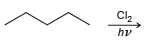
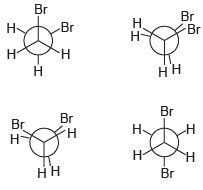
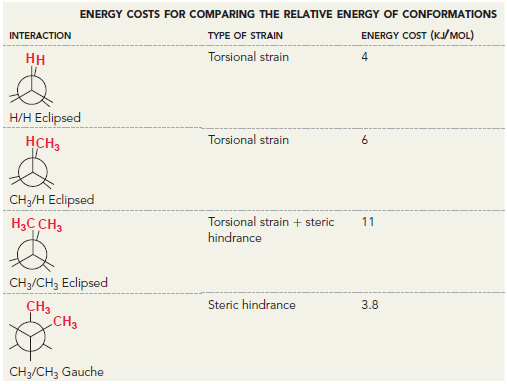
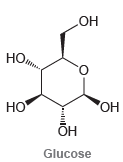
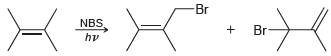
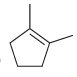
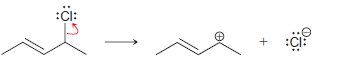
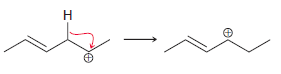
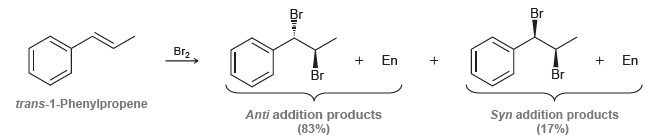
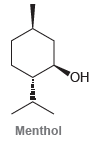
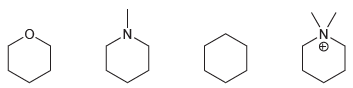
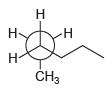
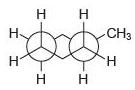
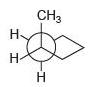
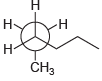
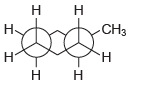
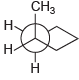
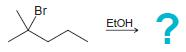
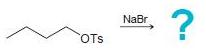
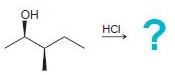
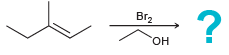
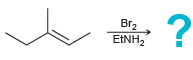
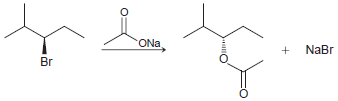
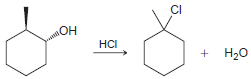
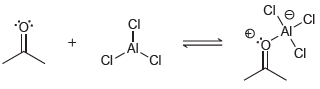
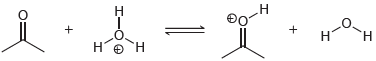
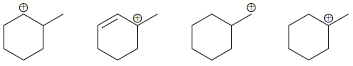
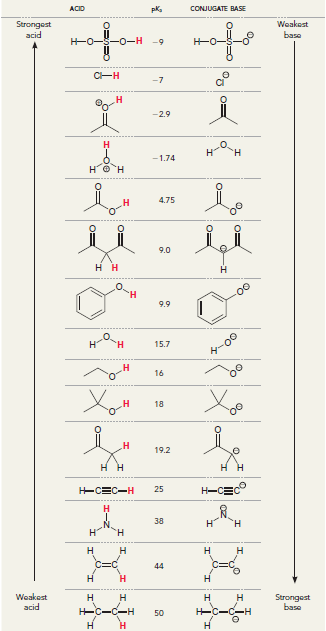
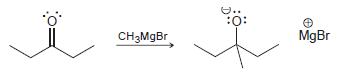
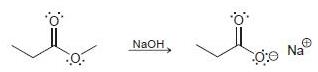
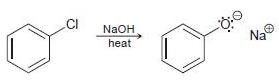
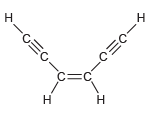
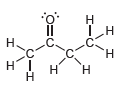
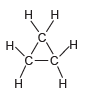
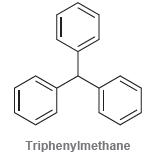
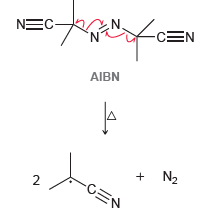
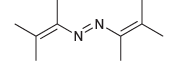
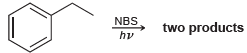
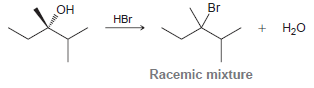
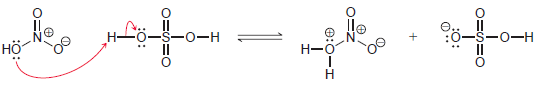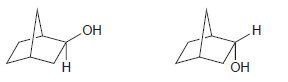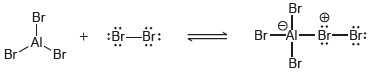![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


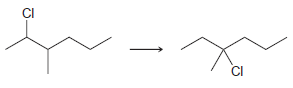
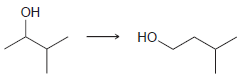
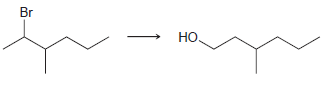
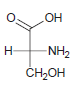
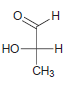
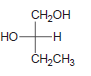

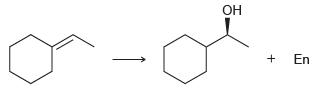
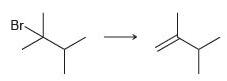
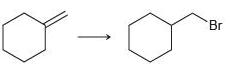
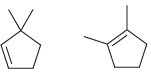
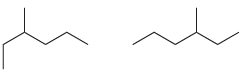
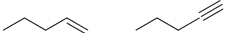
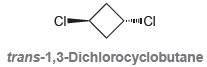
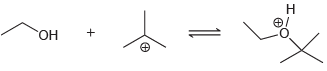
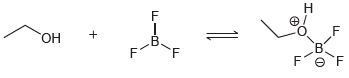
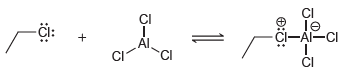
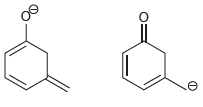
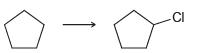
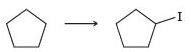

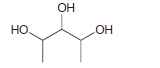
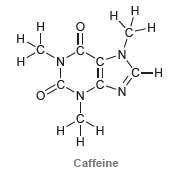
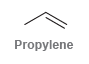
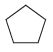
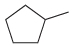
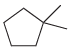
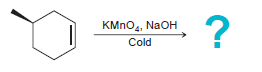
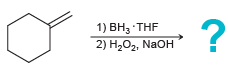
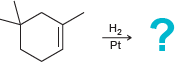
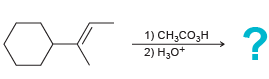
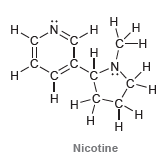
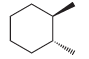
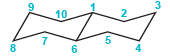
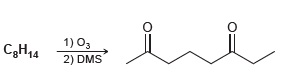
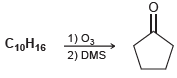
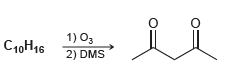
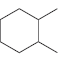
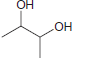
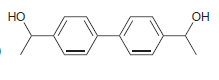
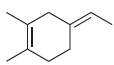
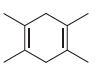
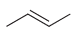
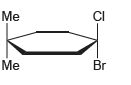
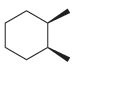
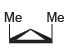
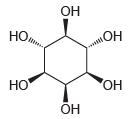
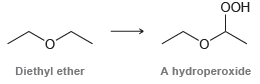
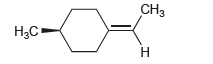
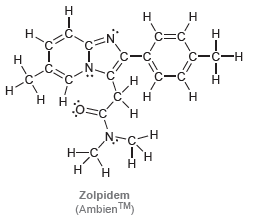
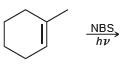
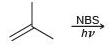
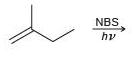

![-OH он [H,SO]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1524/4/5/9/0285add6614d6e451524459006925.jpg)