![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


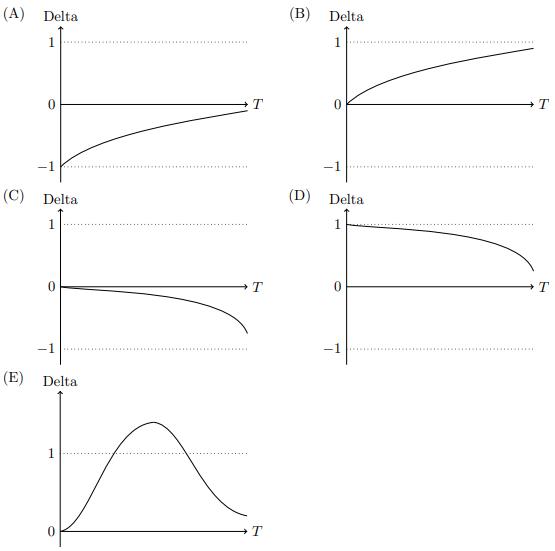
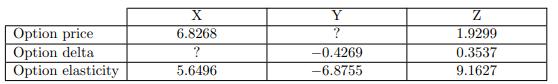
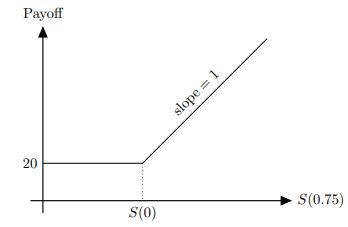
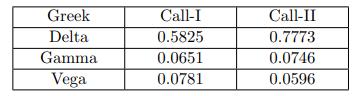
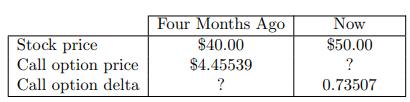
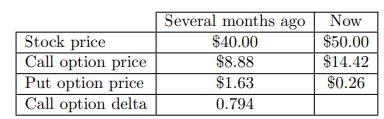
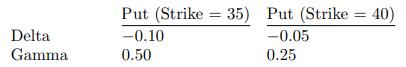
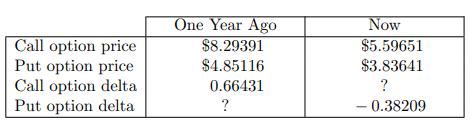

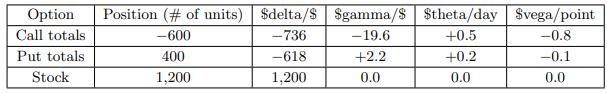
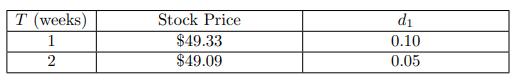

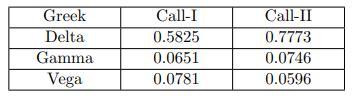
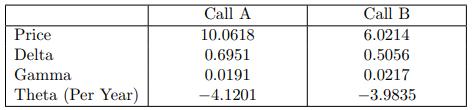
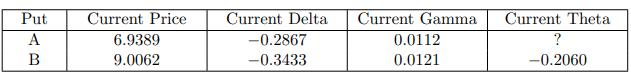
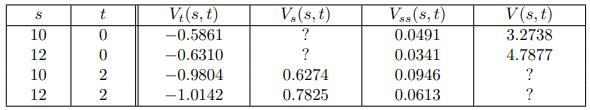
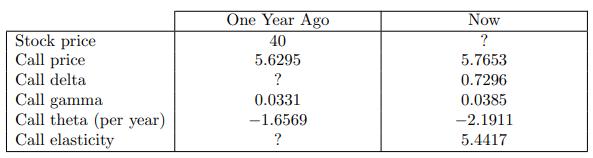
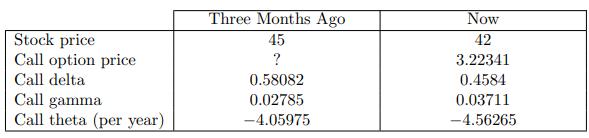
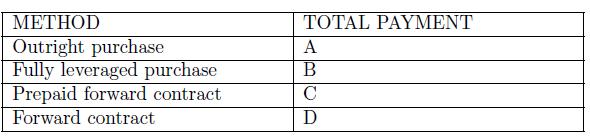
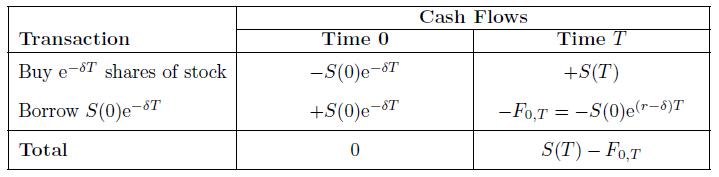
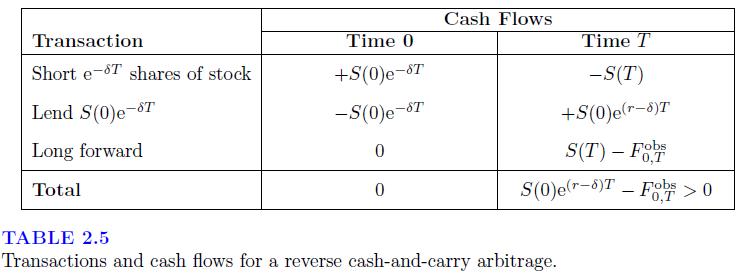
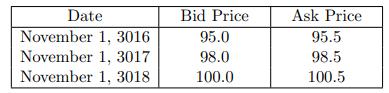
![-FVO,T[C(K) + P(K)] K Payoff Profit S(T)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/5/5/7/945655c747955ce01700557945457.jpg)