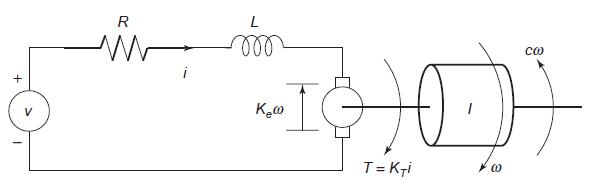
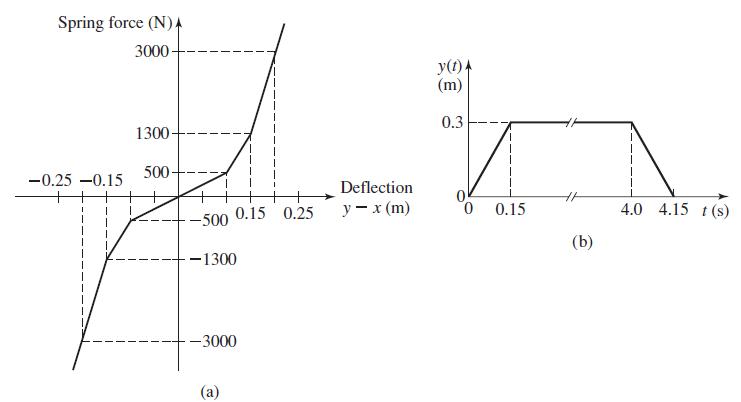
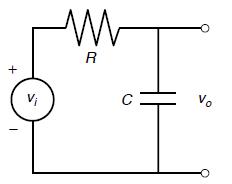
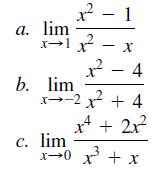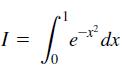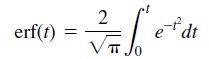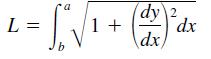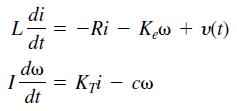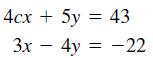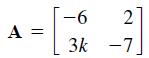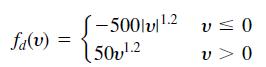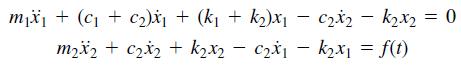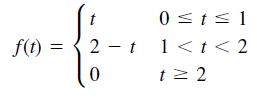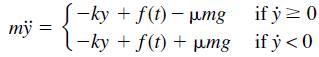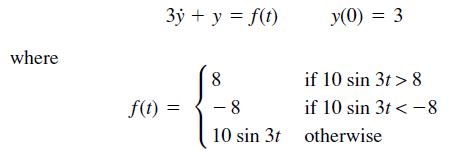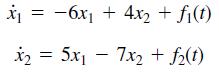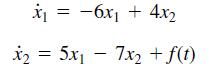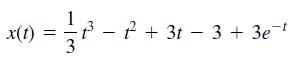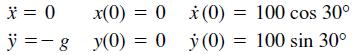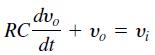![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


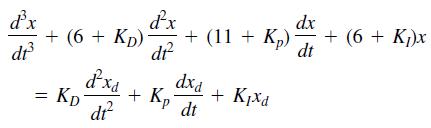
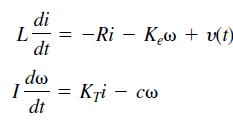
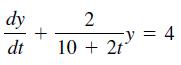
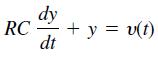
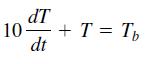
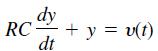
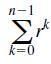
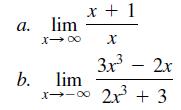
![a. lim x* x0+ b. lim (cos x)/tan x x0+ 1 さ1- c. lim x-0+ sin x d. lim x-0- r 2 - 25 e. lim x-5-x - 10x +25 x - 1 f. lim x→1+ sin[(x - 1)']](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1594/1/0/6/7645f04238ce759c1594106764320.jpg)