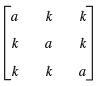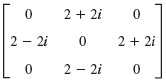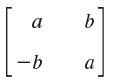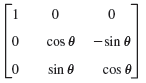![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


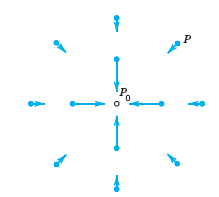
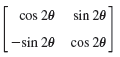
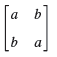

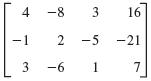

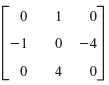
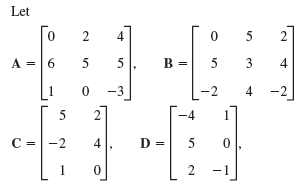
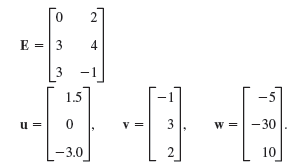
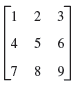



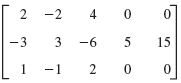
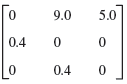
![Let 4 -2 3 -3 A =-2 1 B = -3 6. 1 2 2 -2 1. a = [1 -2 0], 0), b = 3 2 -2](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1542/3/8/9/7455beefff102c0c1542259338654.jpg)
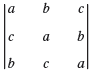

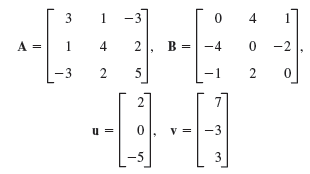

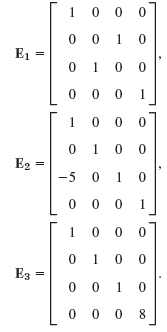
![[2.0 0.4] 2.0] [0.4](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1542/8/8/1/5825bf6812e2d7981542326550731.jpg)