![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


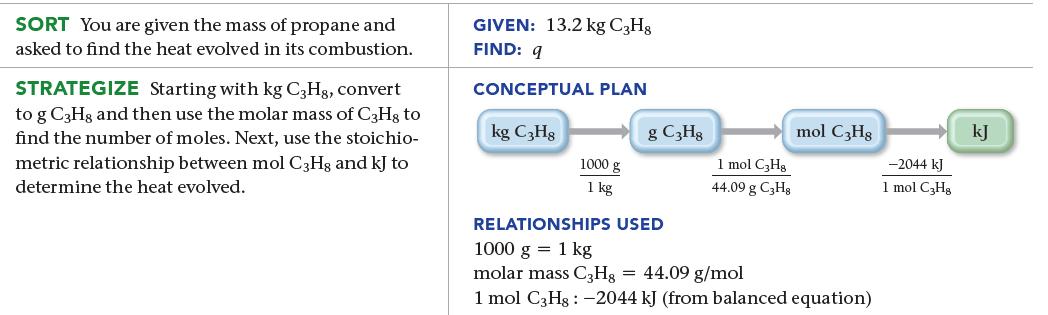
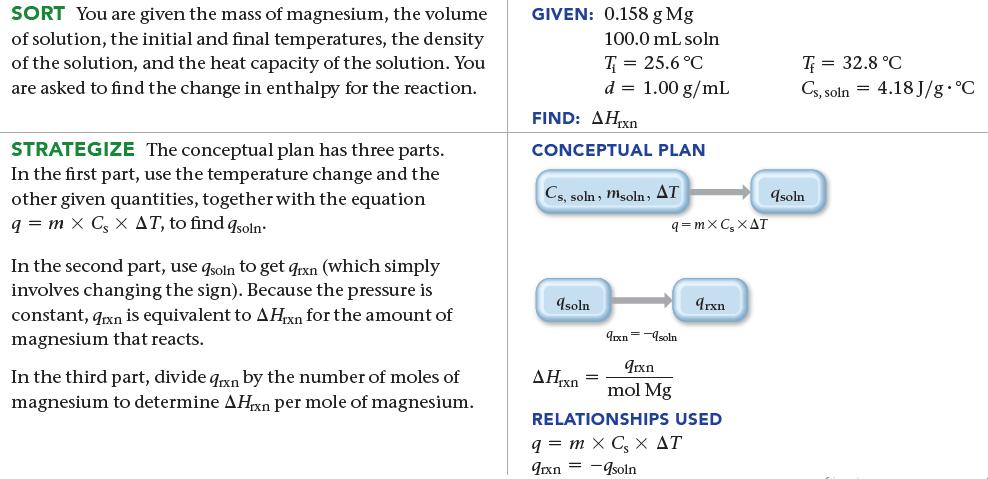
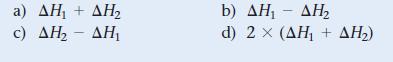
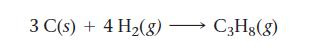
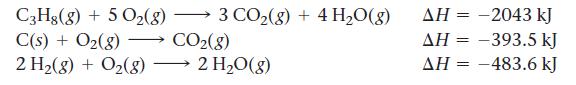

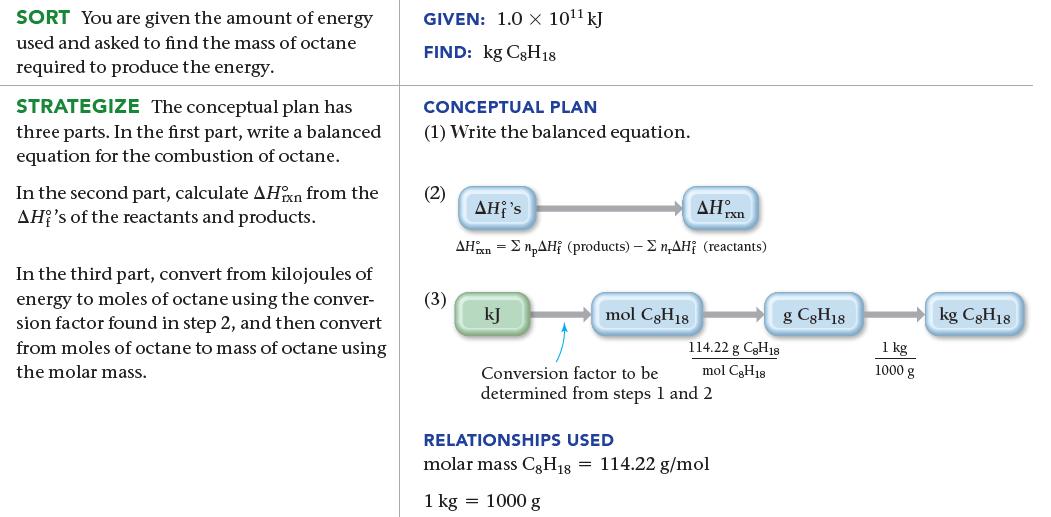
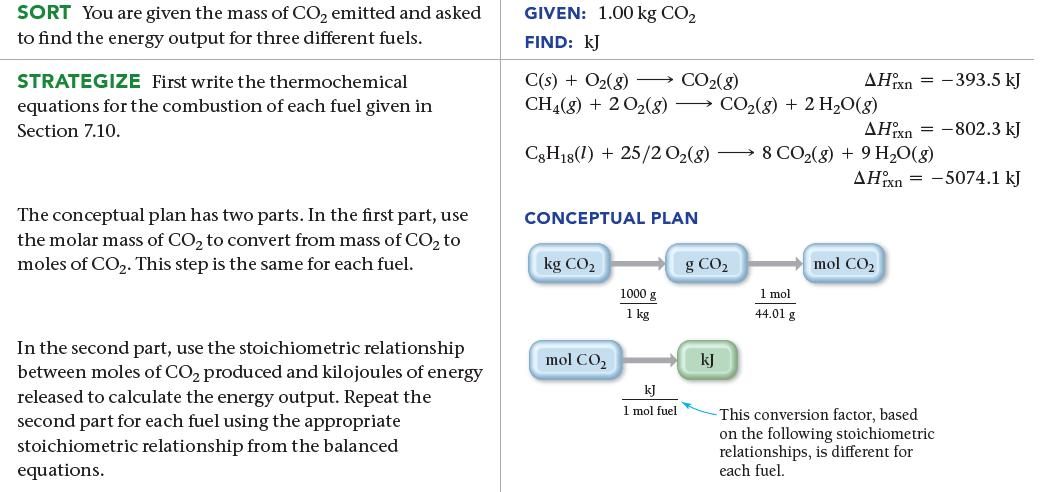

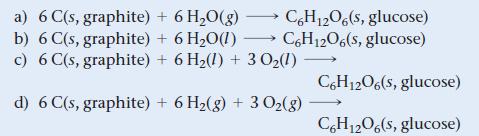
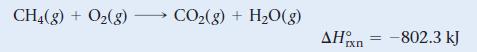
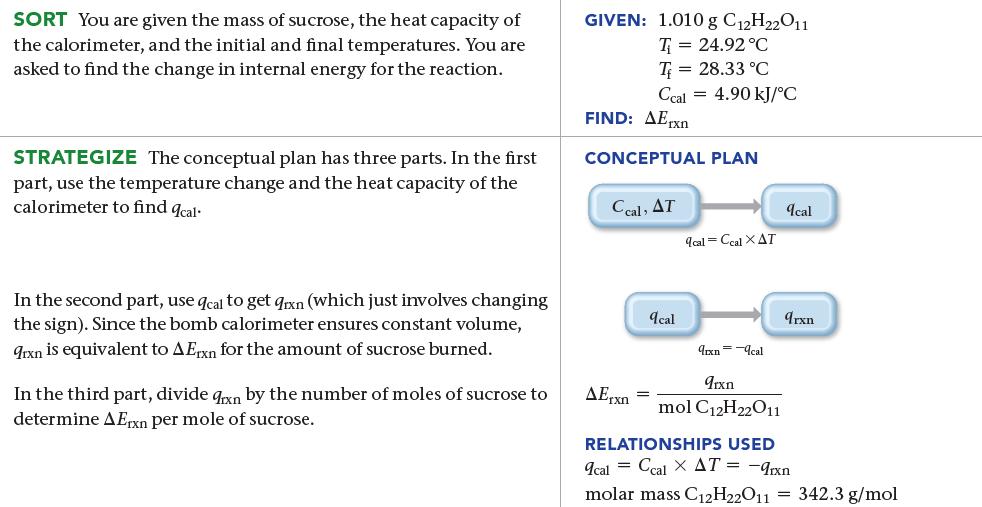


![a) 2 Mg+ [Br] c) Mg+2 [Br] b) Mg: Br: d) :Mg: Br:](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1700/0/3/3/62365547457aa2fb1700033622210.jpg)