![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


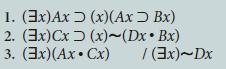
![1. (3x)Ax 2. (3x)Dx 3. An. Bn (x)[(Axv Ex) > Dx] (x) [Dx (Cxv~Bx)] / (3x)Cx](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1696/3/1/7/548651bc06c881051696317547779.jpg)
![1. (x)(Ax Bx) 2. (x)Ax 3. (x)Bx (Cev~Be) [(3x) Cx (Dnv~An)] / (3x)Dx](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1696/3/1/7/530651bc05a4d3051696317529485.jpg)
![1. (x)(Ax. ~Bx) 2. An 3. Am [~(3x) x Bc] (x)(Cx Dx) / (3x)Dx](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1696/3/1/7/512651bc048f15771696317512223.jpg)
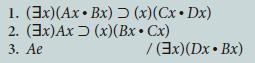
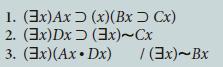
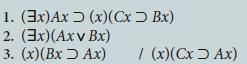
![1. (x)[Ax (Bx=Cx)] 2. An Am 3. Cn. Cm / Bn. ~Bm](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1696/3/1/7/431651bbff7a3c381696317430892.jpg)
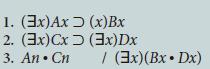
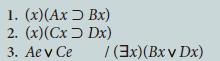
![1. (x)[Jx (KxLx)] 2. (y)~Ky / (32)~Jz](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1696/3/1/6/140651bbaec079bc1696316139276.jpg)