![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


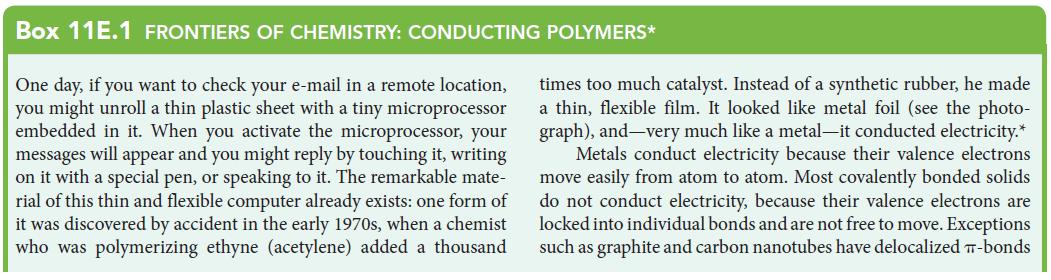
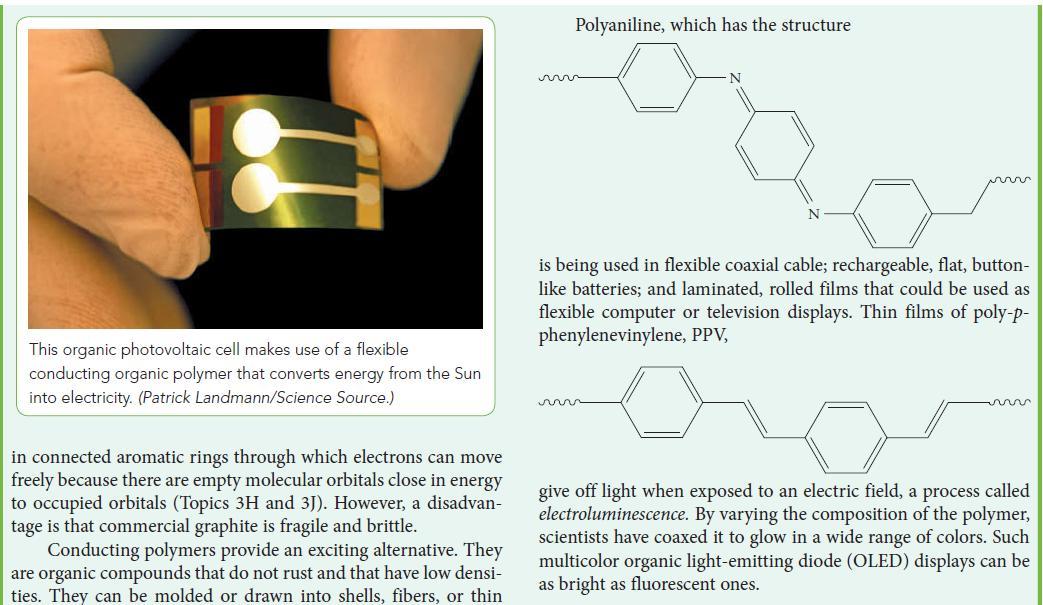
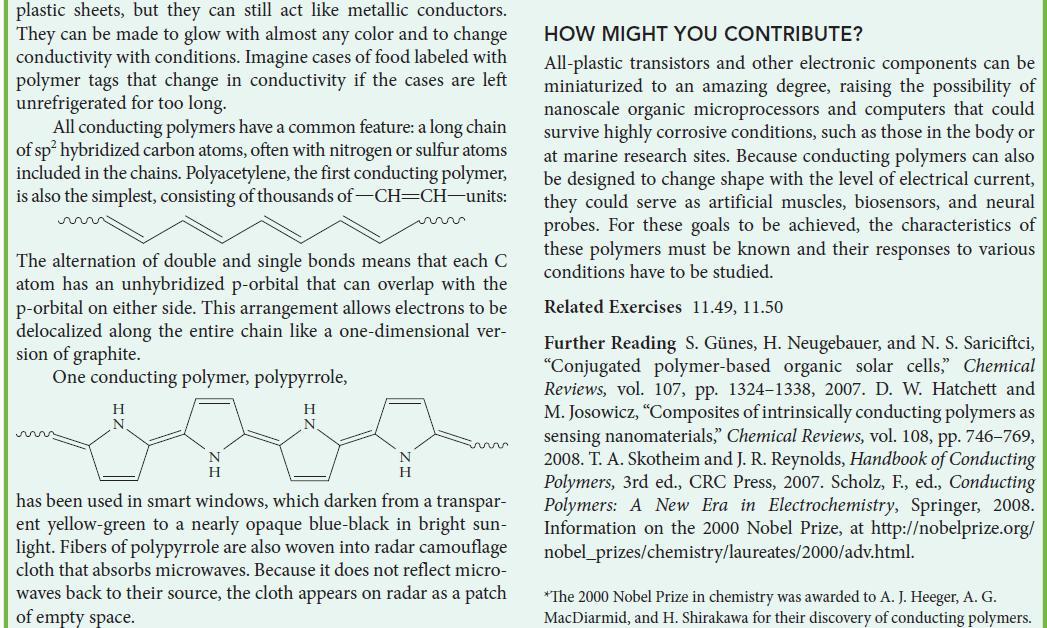
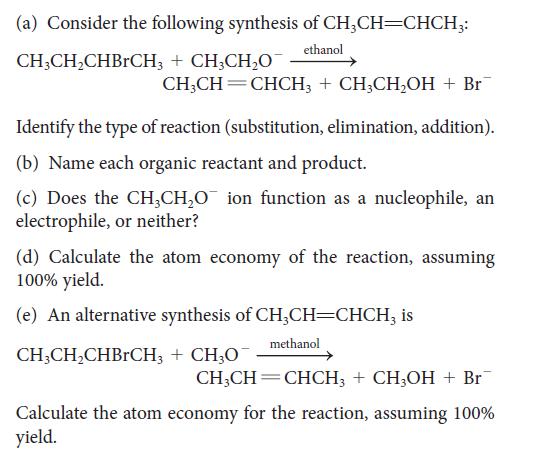
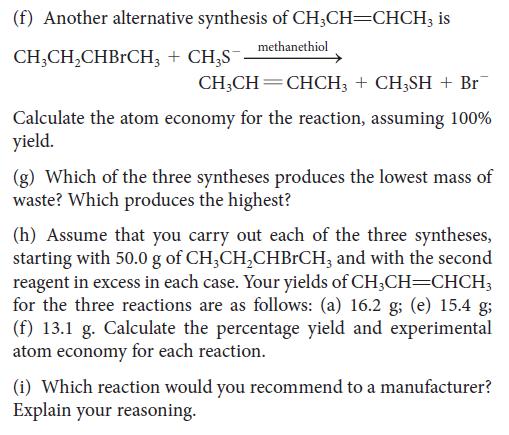
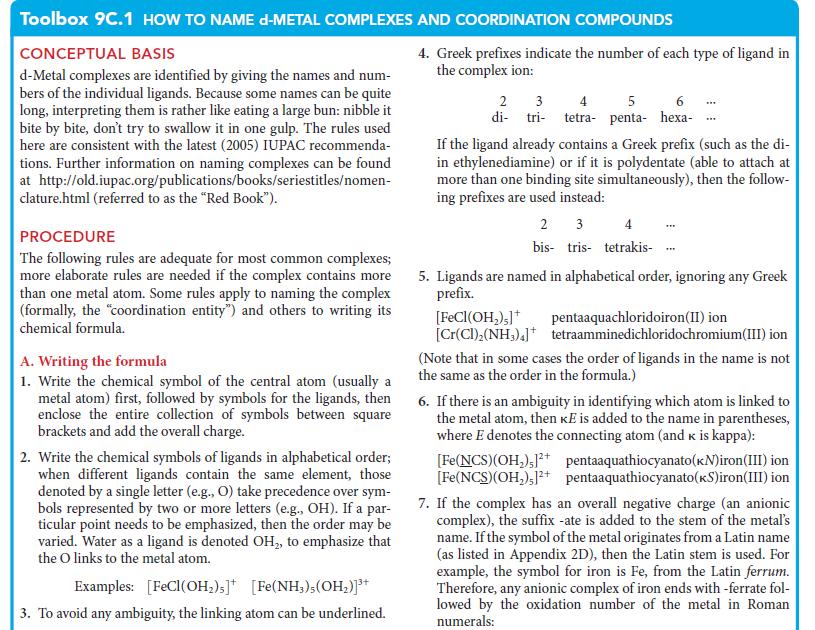
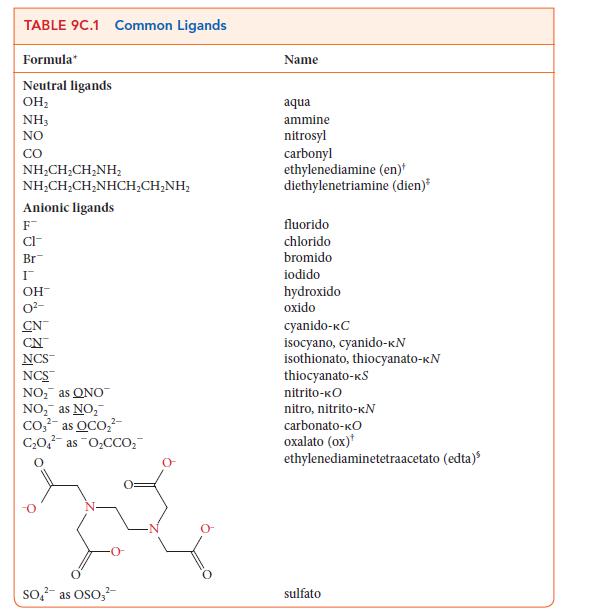
![Examples: [Fe(NCS) (OH), ]2+ [Fe(NCS) (OH), ]+ B. Naming the complex 1. Name the ligands first, and then the](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/1/1/0/5806592a9f48feaf1704110579446.jpg)
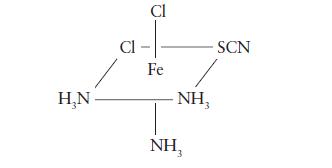
![N N Co N. [Co(en),]+ N 3+ N HC-CH N = / HN NH](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/1/0/2/64565928af5df7201704102644833.jpg)
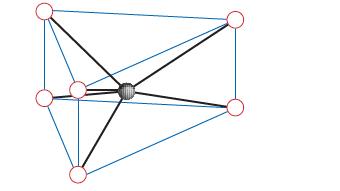
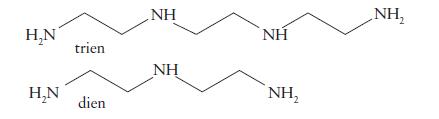
![(a) [Pt(OH)4] [PtCl] and [PtCl(OH)4] [PtCl4] (b) [Cr(en)3] [Co(ox)3] and [Co(en)3][Cr(ox)3] (c) [Fe(CN)(OH),]](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/1/0/2/45865928a3a10dc21704102455681.jpg)
![(a) [Co(NH3),(NO)] Br and [Co(NH3), (ONO)] Br (b) [Pt(NH3)4(SO)](OH) and [Pt(NH3)4(OH)]SO4 (c) [COCI(NCS)](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1704/1/0/2/44665928a2e978651704102445504.jpg)